UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 3rd June 2025
Strengthening the U.S.-India subsea cable agenda
Why in News?
- India and the United States are intensifying cooperation on subsea cable infrastructure under the TRUST framework to enhance digital resilience and counter China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific.
Introduction
- In an era marked by digital interdependence, the strategic and commercial relationship between India and the United States is deepening, particularly in critical technologies and digital infrastructure.
- While much attention has focused on an imminent bilateral trade agreement and the Technology for Resilient, Open and Unified Security and Trust (TRUST) framework — the successor to iCET (Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology) — an equally important yet less discussed area is subsea cables.
- These cables form the physical foundation of global digital connectivity and are increasingly becoming a frontline issue in geostrategic rivalry, especially in the Indo-Pacific.
Significance of Subsea Cables
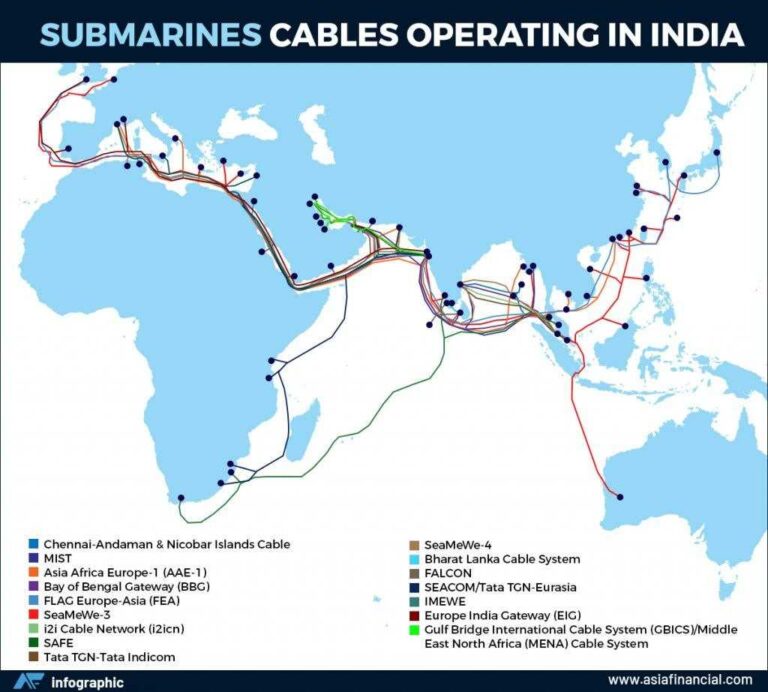
- Backbone of Global Internet: Over 95% of international data traffic is transmitted through subsea fiber-optic cables. From financial transactions to military communications, these cables underpin almost all global digital interactions.
- Cloud and Critical Infrastructure: Once landed, these cables connect to cloud data centers and national digital infrastructure, making their security a matter of national interest.
- Strategic Asset: In the context of growing Chinese investments in subsea infrastructure under its Digital Silk Road Initiative, trusted and secure alternatives have become essential for maintaining open and resilient communication networks.
India’s Current Position and Challenges
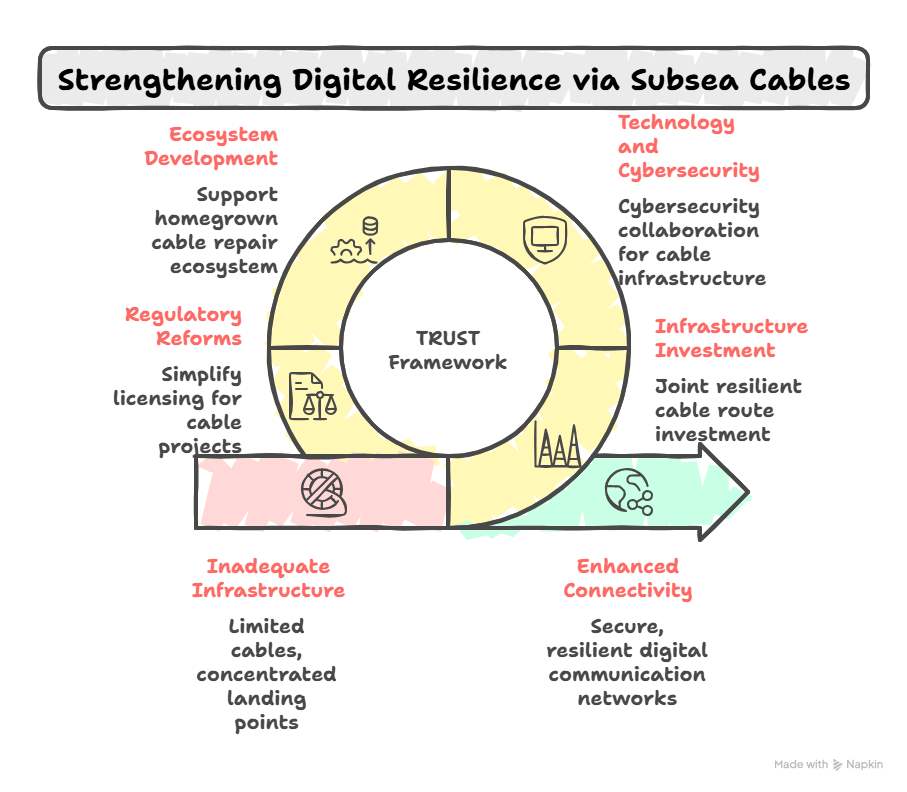
1. Inadequate Infrastructure
- India currently has only 17 international subsea cables, significantly fewer than Singapore’s 26, despite India’s much larger geographic size and coastline.
- Cable landing stations are concentrated in five coastal cities — Mumbai, Chennai, Kochi, Tuticorin, and Thiruvananthapuram — leading to a vulnerability in case of regional disruptions.
2. Bottlenecks in Licensing and Maintenance
- Setting up subsea cables in India involves navigating over 50 clearances from multiple ministries, creating high entry barriers for global investors.
- India depends on foreign-flagged cable repair ships based in Singapore and Dubai, resulting in 3–5-month delays in repairing outages due to customs and naval clearance issues.
Strategic Opportunity for India
1. Geographic Advantage
- India’s location near strategic maritime choke points — Strait of Hormuz, Bab-el-Mandeb, and Strait of Malacca — positions it as a natural transit hub for global cable networks.
- India lies at the crossroads of Europe-Africa-Asia cable routes, providing an opportunity to become a digital connectivity hub for the Global South.
2. Rising Digital Demand
- India’s bandwidth demand is projected to grow at 38% CAGR between 2021 and 2028, driven by data consumption, digital services, and growing cloud infrastructure.
- India’s digital economy — one of the fastest-growing in the world — demands resilient and high-capacity subsea connectivity to sustain its momentum.
India-U.S. Collaboration: A Strategic Imperative
The TRUST framework, evolving out of the U.S.-India iCET, recognizes India’s role as a net security provider in the Indo-Pacific. Subsea cables now fall under the strategic purview of this framework, with implications in both security and commerce.
Areas of Cooperation
- Infrastructure Investment
- Joint investment in resilient and trusted subsea cable routes using secure vendors.
- Encouragement of U.S. tech companies to take anchor positions in Indian cable projects (e.g., Meta’s 50,000-km Indian Ocean cable).
- Technology and Cybersecurity
- Collaboration on cybersecurity for subsea cables, cable landing stations, and associated infrastructure.
- Establishing a redundant and distributed network of landing points across India’s extensive coastline.
- Domestic Ecosystem Development
- Support for India to develop a homegrown cable repair ecosystem, including Indian-flagged vessels, crew training, and depot infrastructure.
- Regulatory Reforms
- Advocacy for India to simplify the licensing regime for subsea cable projects, thereby attracting greater private sector investment.
Strategic Significance in the Indo-Pacific
- Enhanced India-U.S. cooperation in subsea cables is a geostrategic counter to China’s Digital Silk Road, particularly in Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Indian Ocean Region.
- It aligns with U.S. objectives to promote open, secure, and resilient infrastructure in the Indo-Pacific, while reinforcing India’s aspirations to become a regional digital power.
Way Forward
- Simplify India’s cable licensing framework.
- Invest in domestic cable repair and maintenance capabilities.
- Ensure diversification of cable landing stations across India.
- Implement the TRUST framework with clear deliverables.
- Institutionalize bilateral subsea cable cooperation within broader trade and tech agreements.
Such steps will not only enhance regional digital resilience but also establish India as a key digital transit hub in the Indo-Pacific, while fortifying U.S. strategic presence in the region.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.