UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 6th June 2025
Security Forces Launch Anti-Insurgency Operation Along India-Myanmar Border
Why in News?
- Security forces launched an anti-insurgency operation in Pongchau Circle, Longding district of Arunachal Pradesh, near the India-Myanmar border.
Background:
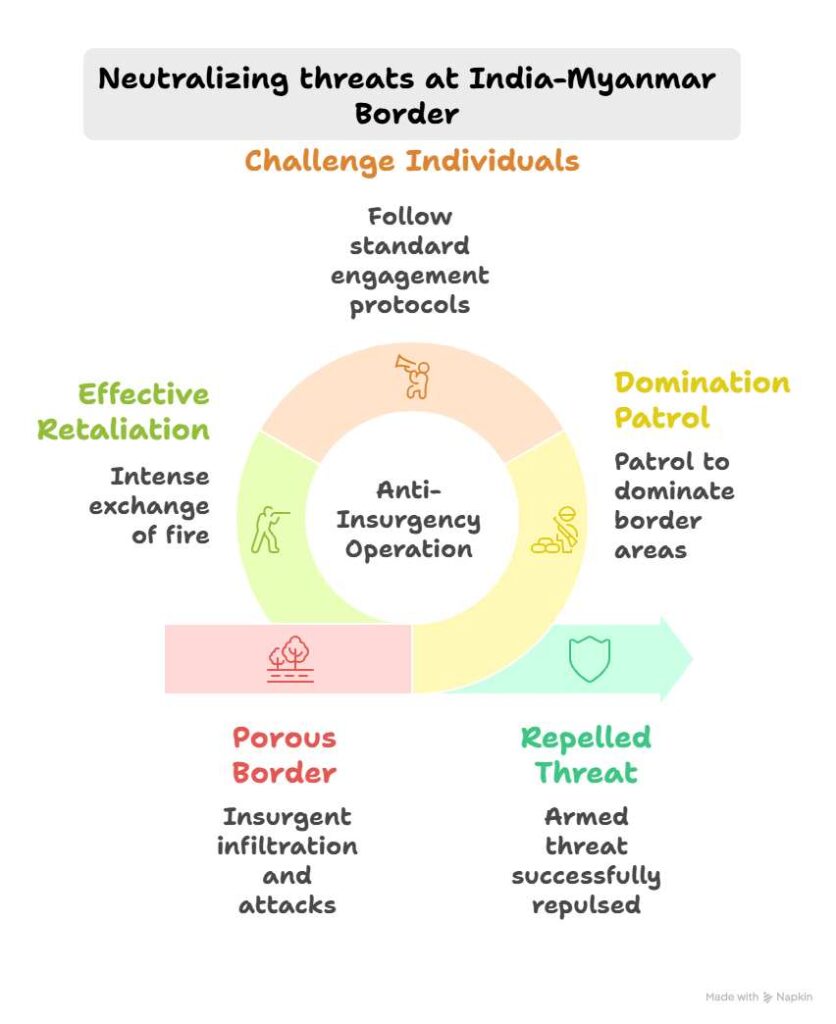
Indian security forces launched a domination patrol in the Pongchau Circle of Longding district, Arunachal Pradesh, following specific intelligence about the movement of armed elements near the India-Myanmar border.
Objective of the Operation:
- The patrol aimed to dominate the border areas and neutralize threats based on reports of unknown armed individuals in the thick forested region of Pongchau Circle.
- These operations are often carried out to maintain border security, prevent insurgent infiltration, and assert territorial control in sensitive areas.
Nature of Encounter:
- Upon spotting movement, security forces challenged the individuals as per the standard engagement protocols.
- The patrol party then came under heavy and indiscriminate fire, indicating well-armed insurgents equipped with heavy-calibre weapons.
- Security forces retaliated effectively, leading to a brief but intense exchange of fire.
Outcome:
- The hostile elements, identified only as “unknown cadres,” retreated across the international border into Myanmar, taking advantage of the dense forest cover.
- Post-operation search revealed no casualties on the Indian side, but the militants managed to escape.
- The Defence Ministry confirmed the successful repulsion of the armed threat, reaffirming its readiness and vigilance along the sensitive border region.
Strategic Significance:
India-Myanmar Border Challenges:
- The India-Myanmar border is porous, spanning 1,643 km, and traverses through Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram.
- It is frequently exploited by insurgent groups (such as NSCN factions, ULFA, etc.) who operate on both sides of the border and use Myanmar as a safe haven.
Cross-Border Insurgency:
- Such operations highlight the persistent threat from insurgent groups who exploit the difficult terrain and lack of border fencing.
- Insurgents often launch attacks in India and retreat into Myanmar, making it difficult to pursue them without bilateral cooperation.
Implications for Internal Security:
Security Forces’ Readiness:
- The operation underscores the alertness and preparedness of Indian troops in responding to cross-border threats.
- Highlights the need for frequent domination patrols, especially in highly forested and hilly terrains of the Northeast.
Border Management:
- Reinforces the importance of modernizing surveillance, enhancing inter-agency coordination, and using technology (like drones) for real-time intelligence.
- It also suggests the need for infrastructure development (roads, border outposts) to facilitate rapid troop movement.
Policy Measures and Forward Outlook:
India-Myanmar Cooperation:
- India has engaged Myanmar under the Act East Policy and conducted joint operations like Operation Sunrise (2019) to eliminate insurgent camps.
- Such incidents demand greater coordination and mutual action protocols with Myanmar to curb safe havens for militants.
Internal Security Doctrine:
- This operation is a reminder of the multidimensional nature of India’s internal security threats—ranging from terrorism, insurgency to illegal border crossings.
- The government’s focus should remain on border area development, insurgency resolution through dialogue, and robust intelligence mechanisms.
Conclusion:
- The border operation in Pongchau, Arunachal Pradesh, exemplifies the ongoing security challenges India faces in its Northeastern frontier.
- While security forces were successful in preventing armed infiltration, the incident highlights vulnerabilities that necessitate enhanced vigilance, cross-border cooperation, and comprehensive counter-insurgency strategies.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

