UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 20th June 2025
Centre launches portal on gender budgeting

Why in News?
The Government of India has increased Gender Budget allocations by 4.5 times in the past 11 years.
Introduction
- Gender equality is not only a fundamental human right but a necessary foundation for a peaceful, prosperous, and sustainable world.
- In India, Gender Budgeting has evolved as a vital governance mechanism to promote women’s empowerment and gender equality through targeted public expenditure.
- The recent announcement by the Union Government on June 19, 2025, marks a significant milestone: Gender Budget allocations have increased from ₹0.98 lakh crore in 2014–15 to ₹4.49 lakh crore in 2025–26 — a 4.5-fold increase over 11 years.
What is Gender Budgeting?
- Gender Budgeting refers to the application of gender mainstreaming in the budgetary process.
- It entails examining how financial allocations impact women and men differently and ensuring that public policies and expenditures contribute to gender equity.
- It is not a separate budget, but an assessment of the gender-specific impact of government budgets.
- It seeks to address gender-based inequalities through better targeted interventions.
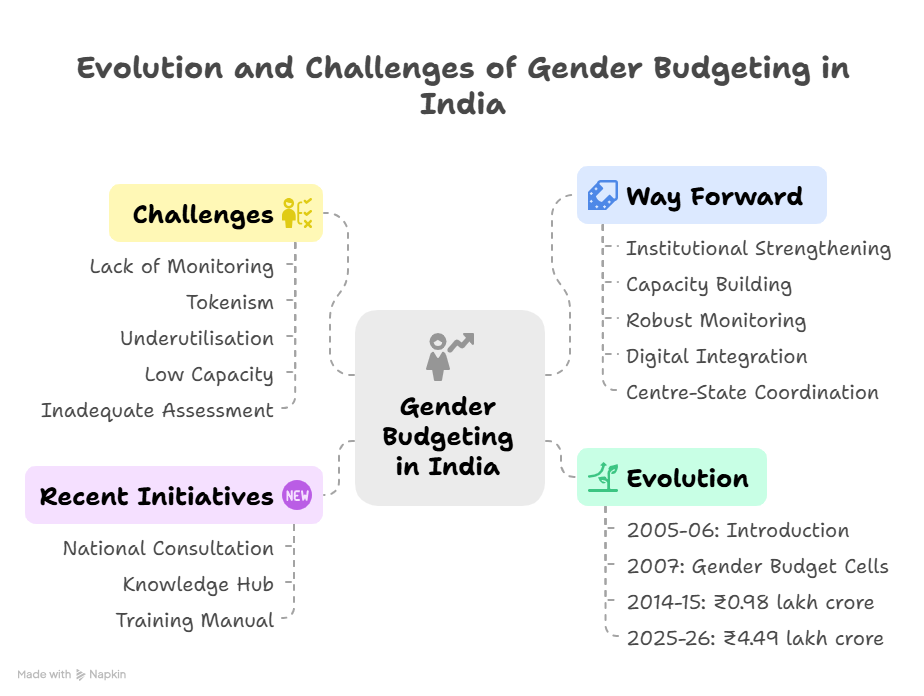
Evolution of Gender Budgeting in India
Year | Development |
2005–06 | Introduced in the Union Budget as a fiscal reporting mechanism. |
2007 onwards | Establishment of Gender Budget Cells in various ministries. |
2014–15 | Gender Budget: ₹0.98 lakh crore. |
2025–26 | Gender Budget: ₹4.49 lakh crore (37% increase over previous year). |
The approach has gradually shifted from being a technical budgeting tool to a strategic instrument for inclusive governance.
Recent Initiatives and Announcements (2025)
1. National Consultation on Gender Budgeting
- First-of-its-kind event hosted by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD).
- Participants: Senior officers from 40 Central Ministries/Departments and 19 States, representatives from UN Women, Asian Development Bank, and national-level institutions.
- Objectives:
- Strengthen gender budgeting across sectors.
- Share best practices and innovative models from States and Ministries.
2. Launch of the ‘Gender Budgeting Knowledge Hub’
- A digital platform developed by MoWCD.
- Aims to serve as a central repository of:
- Policy briefs
- Scheme-level data
- Best practices
- Gender-disaggregated statistics
- Beneficiaries: Policymakers, researchers, state governments, and implementing agencies.
3. Draft Training Manual on Gender Budgeting
- A capacity-building tool to support officials in understanding:
- Gender impact assessments
- Budget planning with gender lens
- Monitoring and evaluation of outcomes
Significance of the ₹4.49 Lakh Crore Gender Budget (2025–26)
- Reflects a 37% increase over 2024–25 allocation.
- Covers sectors like:
- Women’s safety
- Skilling and entrepreneurship
- Health and maternal care
- Education and nutrition
- Rural livelihoods
- Aligns with India’s commitments under SDG 5: Achieve Gender Equality and Empower All Women and Girls.
Challenges in Gender Budgeting Implementation
Despite significant budgetary allocations, the outcomes remain sub-optimal due to:
- Lack of Outcome Monitoring: Few schemes have gender-disaggregated performance indicators.
- Tokenism in Budgeting: Many ministries allocate funds without integrating gender concerns into scheme design.
- Underutilisation of Funds: Poor planning and lack of coordination often lead to funds lying unspent.
- Low Capacity at State Level: Absence of trained personnel and weak Gender Budget Cells in several states.
- Inadequate Gender Impact Assessment: Schemes lack pre- and post-implementation gender audits.
Way Forward
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Activate and empower Gender Budget Cells in all ministries and departments.
- Make Gender Budgeting a core part of outcome budgeting and performance management.
- Capacity Building:
- Roll out the Training Manual across states.
- Regular training programs for officials at all levels.
- Robust Monitoring & Evaluation:
- Develop gender-sensitive indicators and conduct third-party audits.
- Integrate real-time dashboards with gender-disaggregated data.
- Digital Integration:
- Promote wider use of the Gender Budgeting Knowledge Hub.
- Encourage use of digital tools for planning, tracking, and reporting.
- Centre–State Coordination:
- Foster peer learning through sharing of best practices.
- Link gender budgeting performance with incentives and grants under centrally sponsored schemes.
Conclusion
- Gender Budgeting has transitioned from a symbolic initiative to a substantive fiscal and governance reform tool in India.
- The significant rise in budgetary allocation reaffirms the government’s intent to promote gender equity.
- However, effective implementation, institutional commitment, and impact assessment are crucial to convert these financial inputs into meaningful outcomes for women and marginalized genders.
- As India moves forward, gender budgeting must be integrated into the mainstream policy framework, making equity not just a goal but a reality.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

