UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 25th June 2025
Iran-Israel Conflict and the Rising Nuclear Threat

Why in News?
- Iran and Israel declared a ceasefire after a 12-day conflict involving missile strikes on Iran’s nuclear sites, raising global concerns over nuclear non-proliferation and international law violations.
Introduction
- Israel and Iran announced a ceasefire after 12 days of intense hostilities involving missile strikes and aerial assaults.
- This conflict, triggered by Israel’s alleged “pre-emptive” strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities, rapidly escalated into a regional war involving U.S. military intervention.
- The episode raises critical concerns regarding the violation of international norms, the erosion of nuclear non-proliferation frameworks, and the growing threat of nuclear brinkmanship in the 21st century.
Genesis of the Conflict
- Trigger Event: Israel initiated airstrikes under the pretext of pre-empting Iran’s nuclear development.
- Escalation: The strikes expanded into a full-fledged regional war, with the U.S. joining in by targeting Iranian nuclear installations.
- Outcome: The ceasefire announcement came after significant damage to Iranian nuclear infrastructure, especially uranium enrichment facilities.
Legal and Ethical Dimensions
Iran’s Status:
- Iran is a signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
- It had agreed to international inspections and adhered to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) signed with the P5+1 to ensure peaceful nuclear use.
Israel’s Position:
- Not a signatory to the NPT.
- Possesses a known but undeclared nuclear arsenal, without any international oversight.
- The unilateral strikes by Israel (and the U.S.) on a sovereign state complying with international law raises serious questions about the credibility of global nuclear governance.
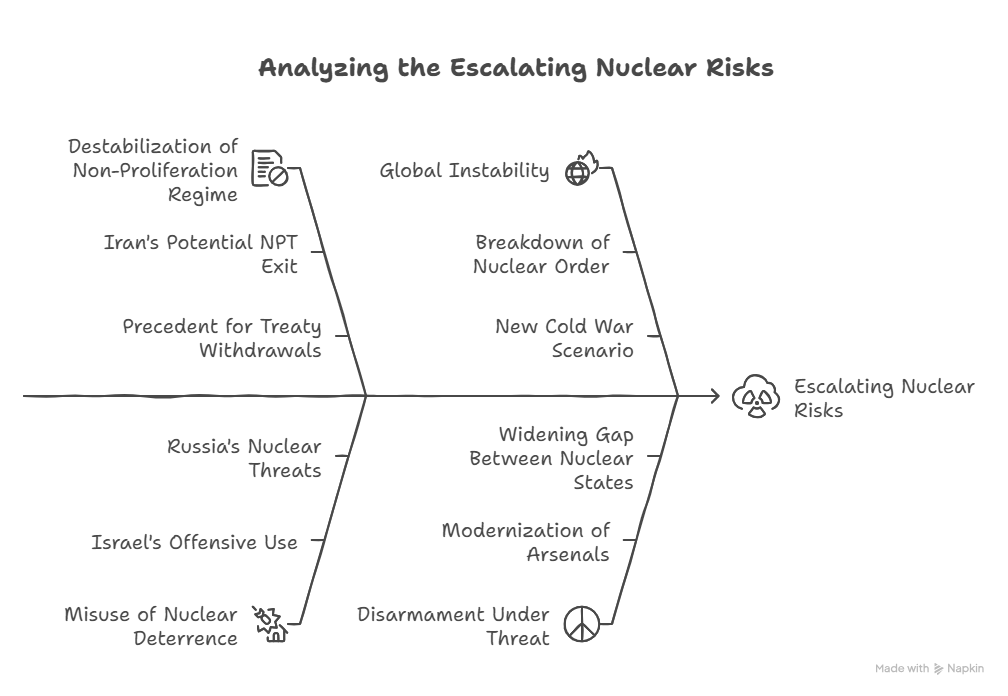
Strategic and Security Implications
- Destabilisation of the Non-Proliferation Regime
- Iran, feeling betrayed and insecure, is now considering exiting the NPT—its parliament is debating a bill to this effect.
- This could set a dangerous precedent for other nations to withdraw from international treaties and pursue nuclear deterrence unilaterally.
- Nuclear Deterrence Misused
- The traditional idea of nuclear deterrence is being misappropriated:
- Israel’s aggressive use of conventional and nuclear-linked military power suggests it may view nuclear capability as an offensive tool, not just a defensive one.
- The U.S. protection emboldens Israel to act with impunity in Gaza and broader West Asia.
- Russia’s nuclear threats in the Ukraine conflict further underline a pattern of great powers normalising nuclear rhetoric and threats to achieve political goals.
- Global Instability
- These developments reflect a breakdown in global nuclear order, once anchored on mutual deterrence, treaties like the NPT, and norms of restraint.
- The world risks a new Cold War-like scenario, or worse, a multi-front nuclear standoff involving:
- Iran and Israel in West Asia,
- Russia and NATO in Europe,
- China-U.S. tensions in the Indo-Pacific,
- Indo-Pakistan nuclear risks in South Asia.
Disarmament Under Threat
The ideal of global nuclear disarmament, espoused through treaties like the NPT and initiatives like the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), is rapidly eroding:
- Nuclear-armed states are modernising and expanding their arsenals.
- The gap between nuclear haves and have-nots is widening.
- Emerging regional powers may now view nuclear acquisition as necessary for regime survival and deterrence.
The Path Ahead: A Renewed Diplomatic Imperative
To arrest this dangerous slide, the global community must act urgently and decisively:
- Reinforce Multilateral Frameworks
- Revive the JCPOA and ensure that Iran’s peaceful nuclear program is safeguarded through mutual guarantees.
- Strengthen the NPT, ensuring all members adhere to both disarmament and non-proliferation commitments.
- Hold Violators Accountable
- Pressure non-signatories like Israel to join the NPT and allow international inspections.
- Discourage unilateral military action, especially against compliant states.3. Foster Disarmament and Transparency
- Initiate confidence-building measures and regional nuclear-free zone proposals, especially in volatile regions like West Asia.
- Promote dialogue between nuclear and non-nuclear states under the auspices of the UN or IAEA.
- Global Leadership for Stability
- The UN Security Council and G20 must lead a global conversation on nuclear risks.
- Promote diplomatic, not military, solutions to regional conflicts.
Conclusion
- The Iran-Israel conflict is a wake-up call for the international community. It reflects how easily the world can spiral into nuclear brinkmanship when treaties are weakened, diplomacy is sidelined, and great powers act with impunity.
- If unchecked, this could usher in a more volatile and fragmented global order than even the Cold War.
- The urgent need of the hour is to rebuild trust, restore international norms, and revive the global disarmament agenda, or risk a future where nuclear war is no longer an unthinkable scenario.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

