UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th July 2025
Agriculture Can Employ Youth, Boost Global GDP by 1.4% Amid Labour Shortage Risk

Why in News?
The FAO’s 2025 report highlights the potential of agrifood systems to address global youth unemployment.
Introduction
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations released its report titled “The Status of Youth in Agrifood Systems” on July 3, 2025.
- The report underscores the urgent need to address global youth unemployment by tapping into the transformative potential of agrifood systems.
- It highlights how agriculture and allied sectors can be instrumental in generating employment, enhancing food security, and promoting inclusive economic growth.
Key Findings of the Report
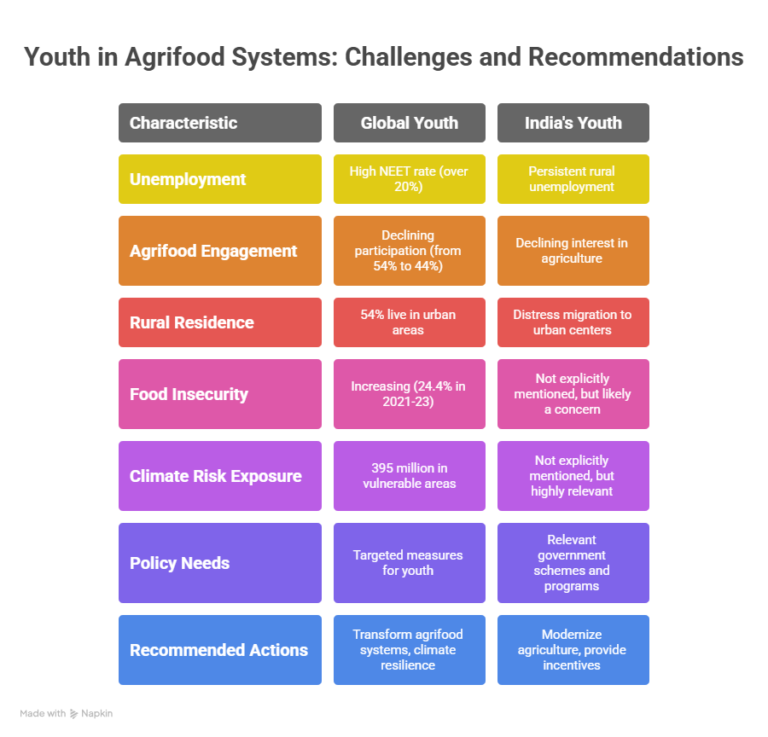
Rising Youth Unemployment
- According to the report, over 20 percent of the world’s 1.3 billion youth (aged 15–24) are classified as NEET – Not in Employment, Education, or Training.
- This issue is particularly acute among youth aged 20 to 24 years, who are transitioning from education into the workforce.
Untapped Potential of Agrifood Systems
- The FAO estimates that increasing youth engagement in agrifood systems could lead to a 1.4 percent increase in global GDP.
- Notably, about 45 percent of this GDP boost would come directly from increased employment and productivity in agriculture and related food systems.
- Agrifood systems are defined broadly to include:
- Crop and livestock production
- Fisheries and aquaculture
- Food storage, processing, distribution, and marketing
- Supporting services such as agri-tech, logistics, and finance
Declining Youth Participation in Agriculture
- Despite its potential, the share of working youth engaged in agrifood systems has declined from 54 percent in 2005 to 44 percent in 2025.
- Nevertheless, a higher proportion of youth (44 percent) than adults (38 percent) still rely on agrifood systems for their livelihoods.
Major Concerns Raised
Looming Labour Shortage in Rural Agrifood Systems
The report warns of a significant labour shortage in rural agricultural areas. As of 2025:
- 54 percent of youth live in urban areas, especially in regions such as East Asia.
- In countries with industrialised agrifood systems, rural youth represent only 5 percent of the population.
- This demographic shift raises concerns about the future sustainability of agricultural production, especially in developing countries.
High Levels of Youth Food Insecurity
Food insecurity among young people is rising at an alarming rate:
- It increased from 16.7 percent during 2014–16 to 24.4 percent during 2021–23.
- Youth living in low- and lower-middle-income countries are the most affected, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Exposure to Climate Risks
The report estimates that 395 million rural youth are living in areas expected to suffer from climate change-induced declines in agricultural productivity. These include:
- Regions vulnerable to droughts, floods, and heatwaves
- Economies dependent on traditional and subsistence agriculture
- Areas in sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia
FAO's Recommendations
1. Transform Agrifood Systems
The report calls for a transformation of agrifood systems from traditional, labour-intensive models to modern, climate-smart, technology-driven systems. This transformation should include:
- Access to education and vocational training in agriculture
- Improved land rights and access to productive resources
- Affordable finance, digital tools, and market linkages
2. Targeted Policy Measures for Youth
Governments are urged to introduce policy incentives that:
- Make agriculture an attractive career option for youth
- Support youth entrepreneurship and agri-startups
- Ensure youth participation in policy-making and decision-making related to food systems
3. Climate Resilience and Green Jobs
To adapt to the worsening climate crisis, youth must be equipped with:
- Skills in sustainable agriculture and resource management
- Knowledge of climate-resilient crop varieties and water-efficient techniques
- Opportunities in green jobs and circular economy models
Implications for India
Youth Demographics and Agrarian Economy
India has one of the largest youth populations in the world, with nearly 50 percent of its population under the age of 25. However, the country also faces:
- Persistent rural unemployment
- Declining interest in agriculture among the youth
- Distress migration from villages to urban centres
Relevant Government Schemes and Programs
Several Indian policies and schemes align with FAO’s recommendations:
- PM-KUSUM: Promotes solar energy use in agriculture
- Agri-Clinics and Agri-Business Centres (ACABC): Encourages agri-entrepreneurship
- Skill India Mission and PMKVY: Provides vocational training
- Start-up India and Stand-up India: Supports innovation and youth-led agritech ventures
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Focuses on youth self-employment in rural areas
Suggested Way Forward
India needs to:
- Modernize agriculture through digital technologies, AI, drone use, and precision farming
- Provide targeted subsidies, training, and incentives for young farmers and entrepreneurs
- Strengthen rural infrastructure and supply chains
- Promote climate-adaptive and low-carbon agricultural practices

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

