UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 14th July 2025
Nominated Members in Rajya Sabha: Article 80 and Recent Appointments
Why in News?
In July 2025, the President of India nominated four eminent individuals to the Rajya Sabha under Article 80(3) of the Constitution, recognizing their contributions to law, diplomacy, history, and social service.

Introduction
- The Rajya Sabha, also known as the Council of States, is the Upper House of the Indian Parliament.
- It represents the interests of the States and Union Territories and serves as a deliberative body that reviews and refines legislation.
- The composition of Rajya Sabha is outlined in Article 80 of the Constitution of India.
Article 80
Clause (1): Composition of Rajya Sabha
“The Council of States shall consist of:
(a) Twelve members to be nominated by the President in accordance with the provisions of clause (3); and
(b) Not more than two hundred and thirty-eight representatives of the States and of the Union territories.”
Explanation:
- The total membership of the Rajya Sabha is 250.
- Out of these, 238 members are elected by the Legislative Assemblies of the States and Union Territories.
- 12 members are nominated by the President under Clause (3) of Article 80.
Clause (3): Qualifications for Nominated Members
“The members to be nominated by the President under sub-clause (a) of clause (1) shall consist of persons having special knowledge or practical experience in respect of such matters as the following, namely—
- Literature
- Science
- Art
- Social service”
Explanation:
- Nominated members must be distinguished in any one or more of these fields.
- The intention of the Constitution is to bring eminent voices from non-political fields into the law-making process.
- These members can participate in debates, discussions, and committee work, thus enriching the quality of parliamentary deliberation.
Significance of Nominated Members
i. Non-Electoral Representation
- These individuals do not go through the electoral process.
- They represent professional, academic, or public service excellence that might not otherwise be represented in Parliament.
ii. Expertise in Law-Making
- Their domain-specific knowledge supports the Rajya Sabha in scrutinising complex legislation (e.g., health, environment, education).
iii. National Recognition
- Nomination acts as a national acknowledgment of their service to society in their respective fields.
Rights and Limitations of Nominated Members
Aspect | Explanation |
Voting Rights | Can vote on all matters in Rajya Sabha except the election of the President of India. |
Privileges | Enjoy all parliamentary privileges like elected members. |
Tenure | Same as elected members — 6 years. One-third retire every 2 years. |
Eligibility | Must be Indian citizens and at least 30 years of age (as per Article 84). |
Current Context: July 2025 Nominations
- The Union Government recommended, and the President of India nominated four eminent individuals to the Rajya Sabha to fill the seats vacated by retiring nominated members.
List of Nominated Members and Their Qualifications Under Article 80(3)
Name | Field of Recognition | Basis of Nomination |
Ujjwal Nikam | Law, Criminal Justice, Social Service | Special Public Prosecutor known for securing conviction in high-profile terror cases (26/11). His work strengthens the criminal justice system and upholds constitutional values. |
C. Sadanandan Master | Education, Social Service | Senior BJP leader from Kerala, known for surviving political violence and dedicating his life to youth empowerment and teaching. |
Harsh Vardhan Shringla | Foreign Affairs, Diplomacy | Former Foreign Secretary and Ambassador to the U.S. Played a key role in India’s G20 presidency and diplomatic strategy. |
Dr. Meenakshi Jain | Literature, History, Education | Historian and scholar noted for contributions to Indian historiography and political thought. |
These individuals were chosen based on their contributions to nation-building, fitting within the four categories outlined in Article 80(3).
Constitutional Philosophy Behind Nominations
- The framers of the Constitution envisioned the Rajya Sabha not merely as a second legislative chamber but also as a forum that includes wisdom, intellect, and experience from different domains.
- Thus, Article 80(3) ensures that Parliament is not just politically representative but also professionally and intellectually diverse.
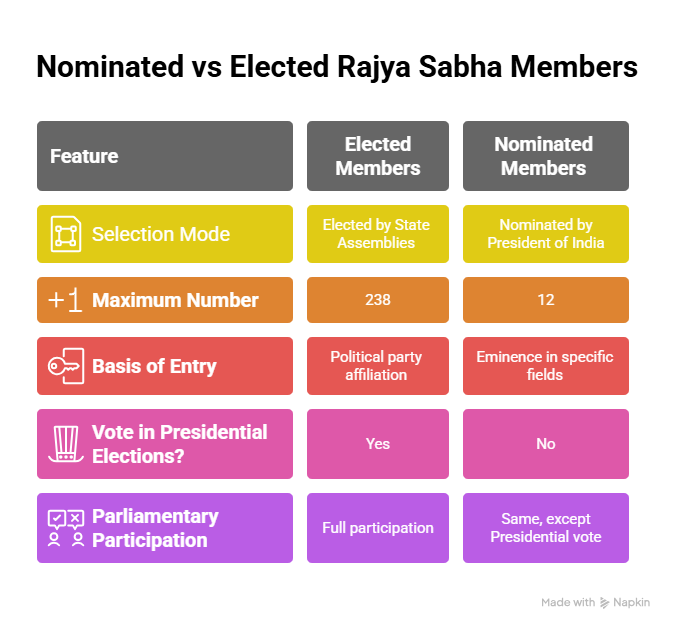
Comparison: Nominated vs Elected Members of Rajya Sabha
Feature | Elected Members | Nominated Members |
Selection Mode | Elected by State Legislative Assemblies using proportional representation | Nominated by President of India |
Maximum Number | 238 | 12 |
Basis of Entry | Political party affiliation and vote | Eminence in Literature, Science, Art, or Social Service |
Can Vote in Presidential Elections? | Yes | No |
Parliamentary Participation | Full participation in debates, committees, and voting | Same, except Presidential vote |
Conclusion
- The nomination of members to the Rajya Sabha under Article 80 is a unique constitutional innovation. It allows non-political experts, scholars, and public servants to become part of the legislative process.
- This strengthens democracy by incorporating diverse and informed voices into national policymaking.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

