UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 16th July 2025
South Asia Achieves Historic Immunization Milestone; India Reduces Zero-Dose Children by 43%

Why in News?
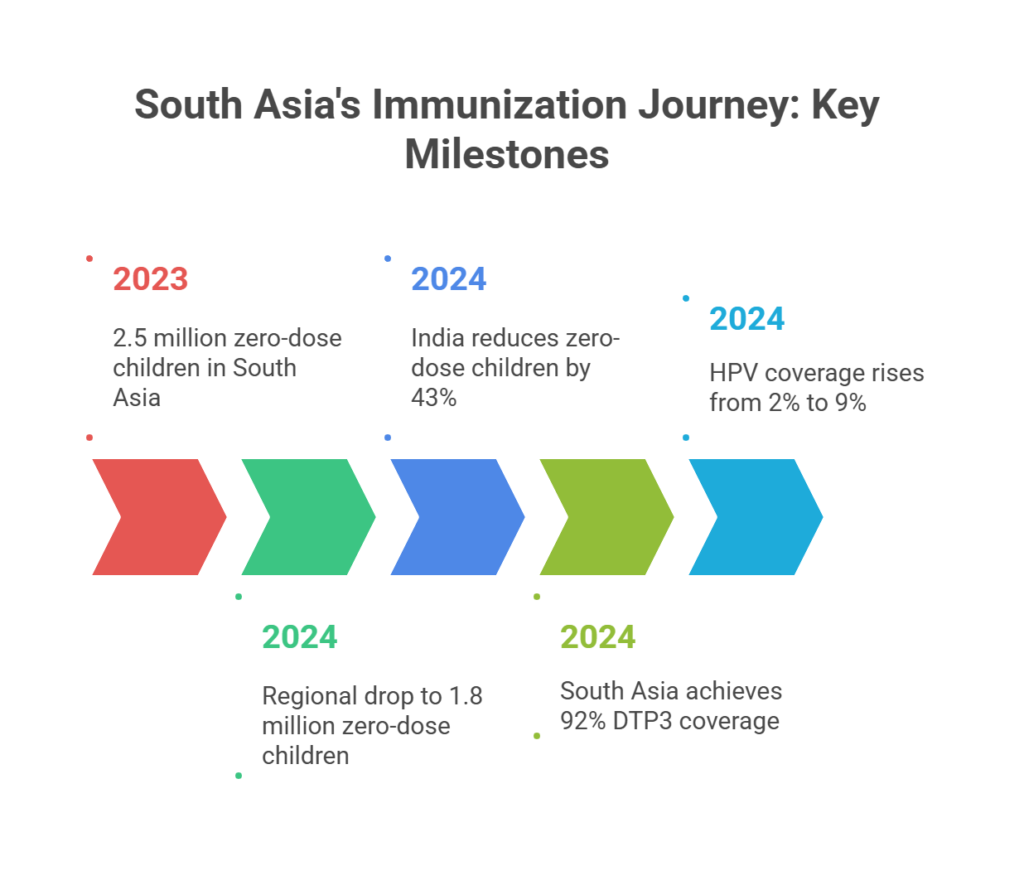
- As per the WHO–UNICEF 2024 data released on July 15, 2025, South Asia recorded its highest-ever childhood immunization rates.
Background and Context
- Immunization as a Public Health Priority: Immunization remains one of the most cost-effective public health interventions, preventing millions of deaths annually worldwide.
- South Asia, with its large and diverse population, has historically faced challenges like rural outreach, vaccine hesitancy, and infrastructural gaps.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Record High Coverage:
- DTP3 Coverage: South Asia achieved its highest-ever DTP3 (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) coverage at 92% in 2024.
- First-dose DTP: Improved to 95%, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.
- Reduction in Zero-dose Children:
- Regional drop by 27% (from 2.5 million in 2023 to 1.8 million in 2024).
- India alone reduced its zero-dose children by 43% (from 1.6 million to 0.9 million).
- Progress in Measles Control:
- 93% of infants received the first dose; 88% received the second dose.
- Measles cases fell by 39% regionally, but coverage was still below the 95% herd immunity threshold.
- HPV Vaccination Gains:
- Regional HPV coverage rose from 2% to 9%.
- Bangladesh vaccinated over 7.1 million girls; Nepal launched its national HPV campaign vaccinating 1.4 million girls.
- Bhutan, Maldives, Sri Lanka also saw notable increases.
- Country-wise Trends:
- India and Nepal are leading the gains.
- Pakistan achieved its highest-ever DTP3 coverage (87%).
- Afghanistan remains a concern with lowest coverage and slight decline.

Enablers of Progress
- Strong Political Will: Sustained commitment by governments.
- Frontline Workers: Tireless work of community health workers, especially women.
- Digital Tools: Better data systems and targeted outreach campaigns.
- Donor and Partner Support: Consistent financial and technical backing from global agencies.
Challenges Ahead
- Coverage Gaps: Despite gains, 2.9 million children in the region remain un- or under-vaccinated.
- HPV Vaccination: Still low; India and Pakistan yet to fully roll out national HPV programmes.
- Equity Issues: Hard-to-reach rural, conflict-affected, and marginalized communities continue to lag behind.
- Surveillance Needs: Strengthening systems to detect and control vaccine-preventable disease outbreaks remains vital.
Way Forward -Policy Implications
- Sustain Political Commitment: Immunization must remain a top priority in health budgets.
- Invest in Frontline Workers: Training, incentives, and safety for community health workers need continued attention.
- Expand HPV Programmes: Timely rollout in India and Pakistan is critical for cervical cancer prevention.
- Bridge Equity Gaps: Focus on rural, tribal, and conflict-prone areas to reach ‘zero-dose’
children. - Strengthen Surveillance: Robust data systems to monitor coverage and disease trends.
- Public Awareness: Combat vaccine hesitancy through community trust-building and clear communication.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

