UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 18th July 2025
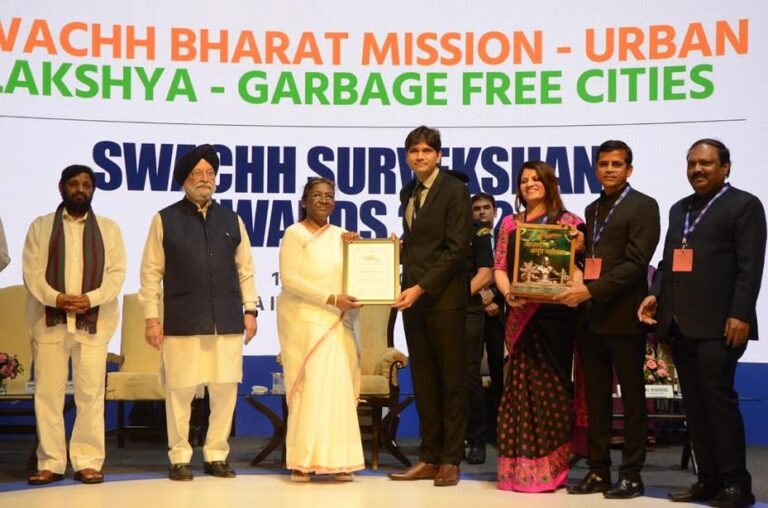
Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 awards

Why in News?
Recently the government released rankings for Swachh Survekshan 2024-25.

Introduction
- Ahmedabad has been ranked the cleanest city in the country among those with a population of over 10 lakh in the Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 awards.
- The city was followed by Bhopal and Lucknow. This year’s survey introduced a new ‘Super Swachh League’ category to recognise cities that have consistently ranked in the top three positions over the past three years.
- These cities were kept out of the national ranking to allow for newer contenders to be recognised.
About Swachh Survekshan
- Swachh Survekshan is the world’s largest urban sanitation and cleanliness survey, conducted by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) under the Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban.
- It aims to foster a spirit of healthy competition among cities, encouraging them to improve urban sanitation and solid waste management.
- First introduced: 2016
- Initial coverage: 73 cities
- Current edition: 2024-25
- Cities surveyed this year: 4,589 urban local bodies (ULBs)
- The survey assesses cities based on various parameters, including waste collection, processing, scientific disposal, citizen feedback, and innovations in sanitation.
National Rankings (Cities with population over 10 lakh)
- Ahmedabad
- Bhopal
- Lucknow
These rankings mark a shift in recognition as past winners like Indore and Surat were excluded from the competition this year and included in a new category.
Introduction of ‘Super Swachh League’ Category
To ensure greater inclusivity and allow newer cities a chance at top ranks, a separate category called the ‘Super Swachh League’ has been created. This category includes cities that have maintained top three positions for the past three years.
- Cities with population above 10 lakhs: Indore, Surat, Navi Mumbai, Vijayawada
- Cities with population between 3 lakhs to 10 lakhs: Noida, Chandigarh, Mysuru, Ujjain, Gandhinagar
This move seeks to maintain high standards among consistent performers while broadening the competitive landscape for others.
Other Rankings (Cities with population between 3 lakh and 10 lakh)
- Mira Bhayandar
- Bilaspur
- Jamshedpur
These cities demonstrated notable improvements in solid waste management, cleanliness, and citizen participation.
Special Recognitions
- Uttar Pradesh Government and Prayagraj Municipal Corporation received special recognition for effective waste management during the Mahakumbh, showcasing successful sanitation handling during large-scale religious gatherings.
Status of Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0)
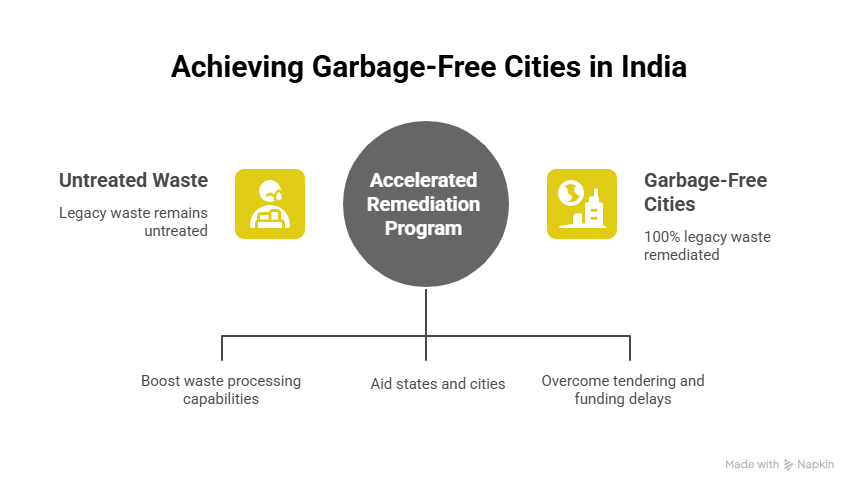
The second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 2.0), launched in 2021, aims to move from an ‘Open Defecation Free’ (ODF) model to ‘Garbage-Free Cities’. One of its key objectives is to remediate 100 percent of legacy waste (dumpsites) in urban areas by 2026.
However, according to the SBM-U dashboard:
- Only 58 percent of legacy waste has been remediated
- 42 percent of waste across cities remains untreated
This reveals a significant implementation gap with just one year remaining to meet the mission’s target.
New Campaign: Accelerated Dumpsite Remediation Programme
In response to delays in dumpsite remediation, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs announced a new initiative to be launched on 15 August 2025. The Accelerated Dumpsite Remediation Programme aims to fast-track the process through:
- Increased waste processing capacity
- Financial and technical assistance to states and cities
- Resolution of issues related to financing and tendering delays
The Union Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs, Manohar Lal Khattar, emphasized that the central government will work closely with state governments to identify and overcome the causes of delay.
Significance of the Swachh Survekshan Framework
Swachh Survekshan serves multiple governance objectives:
- Promotes competitive federalism by encouraging cities to outperform each other in cleanliness.
- Enhances citizen engagement through feedback and participation.
- Builds accountability by publishing transparent rankings.
- Encourages innovation in urban waste management techniques.
- Reinforces environmental sustainability and public health outcomes in rapidly urbanizing regions.
Challenges Ahead
Despite visible progress, several challenges remain:
- Dumpsite remediation remains behind schedule in many cities.
- Behavioural change at the citizen level is still evolving, especially in waste segregation.
- Funding constraints, especially among smaller municipalities, hinder sustained progress.
- Monitoring and compliance mechanisms need to be strengthened for long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
- Swachh Survekshan 2024-25 marks a strategic shift in India’s urban sanitation journey.
- The introduction of the Super Swachh League ensures recognition of past champions while motivating emerging cities to achieve higher standards.
- However, the pending task of legacy waste remediation demands urgent and coordinated action.
- As India advances toward its vision of ‘Garbage-Free Cities’ under SBM-U 2.0, the coming year will be critical to meeting ambitious targets and realising the mission’s full potential.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

