UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 19th July 2025
EU sanctions Gujarat refinery as it targets Russia’s energy sector

Why in News?
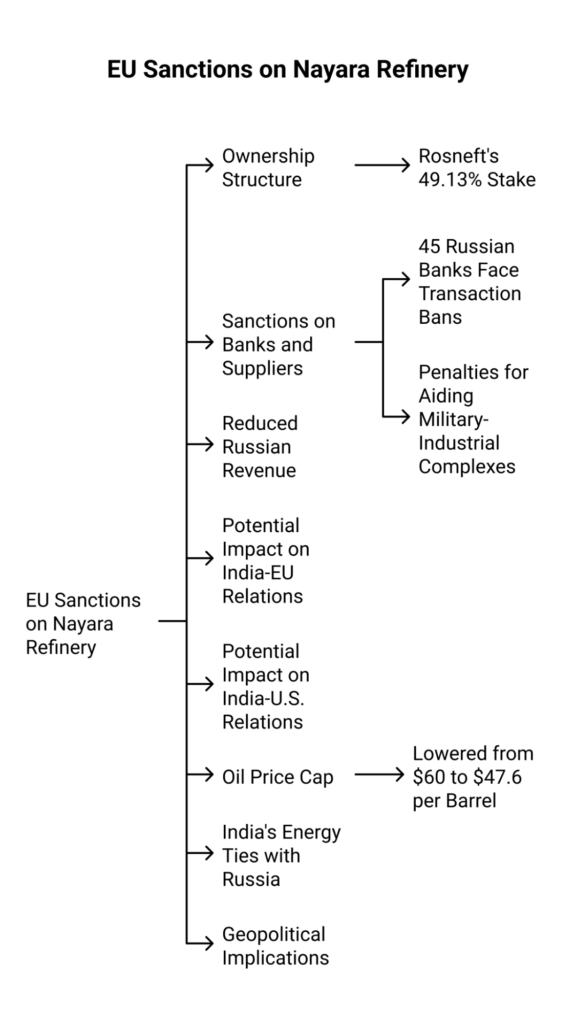
The European Union imposed sanctions on Gujarat’s Nayara refinery for links to Russia’s Rosneft, as part of its 18th sanctions package targeting Russia’s energy and military networks amid the Ukraine war.

Background
On July 18, 2025, the European Union (EU) announced its 18th sanctions package against Russia, targeting the energy sector, financial institutions, and military-industrial suppliers, with India’s Nayara Energy refinery in Gujarat included for the first time. The move coincides with the U.S. Congress debating tighter sanctions on Russian crude buyers like India, China, and Brazil.
Reason for sanction:
1. Rosneft’s stake makes it a proxy entity aiding Russian energy exports.
2. Oil Price Cap Revised
- The oil price cap for Russian crude, applicable if G7-based services like shipping or insurance are used, has been lowered from $60 to $47.6 per barrel.
- Aims to reduce Russia’s revenue from oil exports.
3. Ban on Refined Products and Pipelines
- EU-wide import ban on refined petroleum products made from Russian oil.
- Full transaction ban on Nord Stream 1 and 2 pipelines between Russia and Germany.
India’s Response and Global Implications
- The sanctions come amid India’s increasing energy ties with Russia.
- India warned against “double standards” regarding oil imports, emphasizing its right to ensure energy security.
- Nayara Energy is reportedly in talks with Reliance Industries regarding a possible stake sale, which could be accelerated due to sanctions pressure.
Significance and Strategic Implications
- First EU sanction on an Indian-based refinery, reflecting broader scrutiny of countries perceived as bypassing or indirectly supporting Russian energy exports.
- Highlights increasing geopolitical complexities in energy trade, especially for countries like India balancing strategic autonomy with global alliances.
- May affect India-EU and India-U.S. energy and trade relations, especially if secondary sanctions are enforced.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

