UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 30th March 2025
Kerala is constituting India’s first commission for the elderly
Why in News?
- In March 2025, Kerala became the first Indian state to pass a bill establishing a State Commission for Senior Citizens.
- The move is driven by the fast-paced ageing of Kerala’s population and rising instances of neglect, poverty, and abuse among the elderly.
Demographic Context
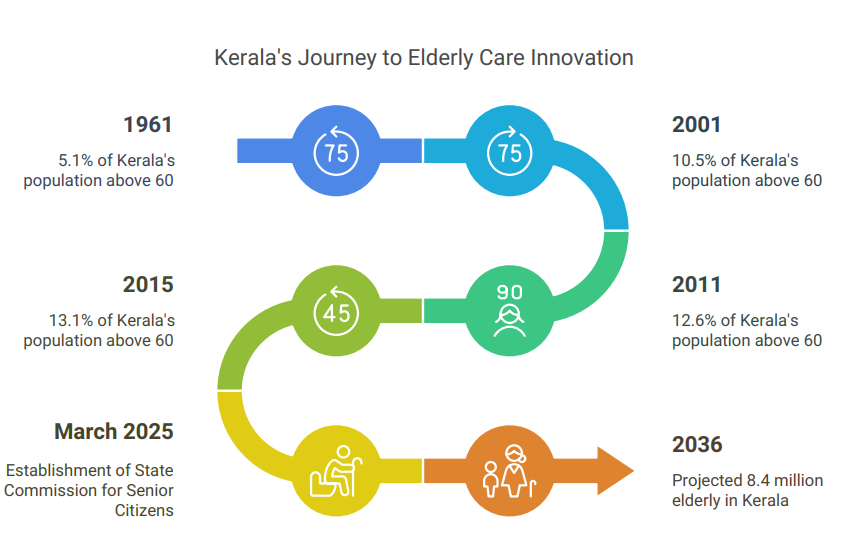
- Kerala is ageing faster than the national average:
- 1961: 5.1% of population above 60 years (India: 5.6%)
- 2001: 10.5% (India: 7.5%)
- 2011: 12.6% (India: 8.6%)
- 2015: 13.1% (India: 8.3%)
- As of 2025:
- 4.8 million elderly (60+) in Kerala
- 15% of them are 80+, the fastest-growing elderly group
- Women outnumber men; most are widows
- Projected to reach 8.4 million elderly by 2036
Why the Commission Was Needed
- Increasing elder abuse, especially financial and emotional neglect by younger generations
- Lack of awareness about legal rights and welfare schemes, especially the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007
- Kerala’s need to institutionalise elderly protection, as envisioned in the National Policy on Senior Citizens (2011)
- Desire to build a model for elderly care for other states
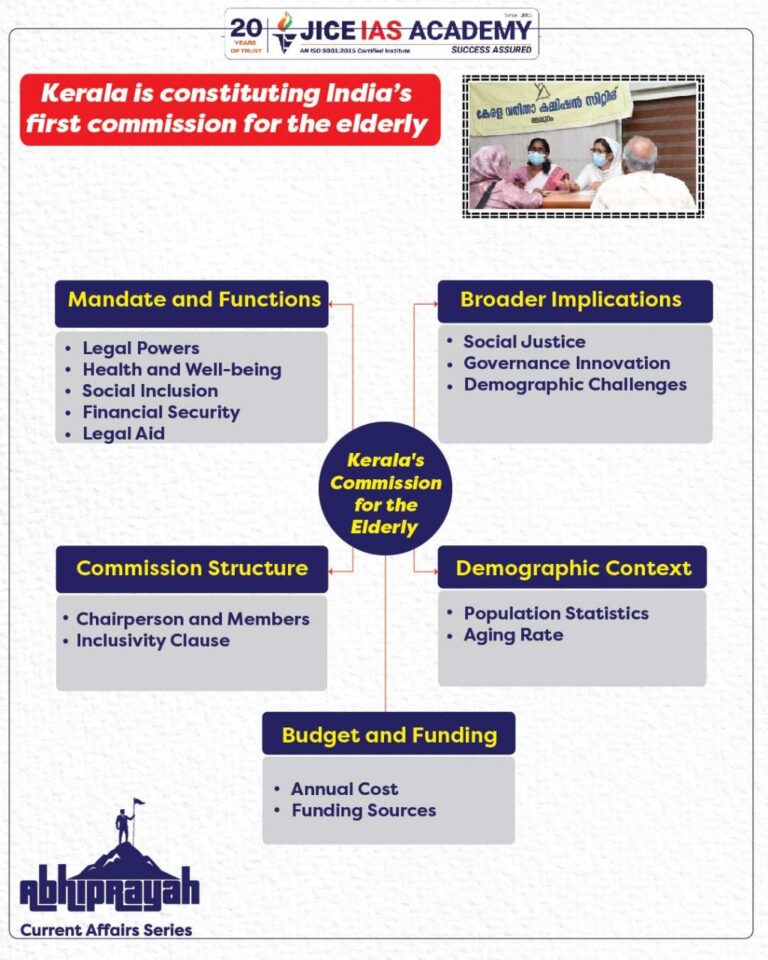
Structure and Composition
- Chairperson + 3 Members, all of whom will be senior citizens
- Inclusivity clause:
- At least one member from SC/ST
- At least one woman member
- Chairperson’s status: Equivalent to a state government secretary
- Tenure: 3 years
- Subject experts can be invited but won’t have voting rights
Mandate and Functions
Legal and Protective Powers
- Powers equivalent to a civil court
- Can investigate grievances, issue protective measures
- Submit reports to the government for conflict resolution
- Can also address elderly-related complaints in prisons, lock-ups and custodial facilities
Health and Mental Well-being
- Conduct regular medical check-ups
- Ensure access to affordable and geriatric care
- Provide mental health support to address loneliness and depression
Social Inclusion & Purpose
- Encourage intergenerational bonding through community programs
- Promote active ageing by harnessing elderly skills for community benefit
Financial Security
- Facilitate access to:
- Pensions
- Social security schemes
- Financial literacy support
Rehabilitation and Legal Aid
- Support destitute elderly
- Provide legal aid where required
- Recommend policy changes for elder care infrastructure
Budget and Funding
- Annual cost: ₹1 crore for operations and salaries
- One-time setup cost: ₹9 lakh
- Funded through the Consolidated Fund of the State of Kerala
Broader Implications
- Social Justice & Inclusivity
- Reflects commitment to vulnerable sections as per Article 41 (Right to public assistance in old age)
- Aims to shift from a welfare-based to a rights-based approach to elderly care
- Governance Innovation
- First state to implement a dedicated statutory commission as advised by National Policy on Senior Citizens, 2011
- Could become a blueprint for other Indian states facing demographic transition
- Demographic Dividend to Demographic Challenge
- While India still benefits from a young population, states like Kerala already face the socioeconomic consequences of ageing
- Highlights need for elderly-inclusive urban planning, healthcare and pensions
Conclusion
Kerala’s establishment of India’s first Commission for the Elderly is a landmark step in institutionalising dignity, security, and welfare for senior citizens. As India moves toward becoming an ageing society, ensuring elder rights and active participation in society is not only a welfare imperative but a constitutional and moral responsibility. Kerala’s model could serve as a template for inclusive elder care governance across India.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in