UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 04th April 2025
How Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act deepened the Great Depression
Why in News?
Impact of Trump’s tariffs on India-US trade relations amid comparisons to the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930.
Introduction
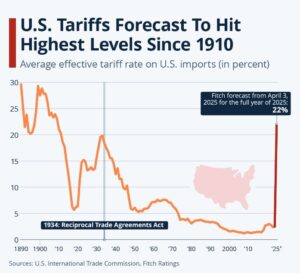
- US President Donald Trump’s recent tariff hikes, particularly the 10% blanket tariff on all countries and reciprocal higher tariffs on nations with large US trade deficits, have raised concerns about a potential global trade war.
- The move has drawn comparisons with the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930, which deepened the Great Depression by triggering retaliatory tariffs worldwide.
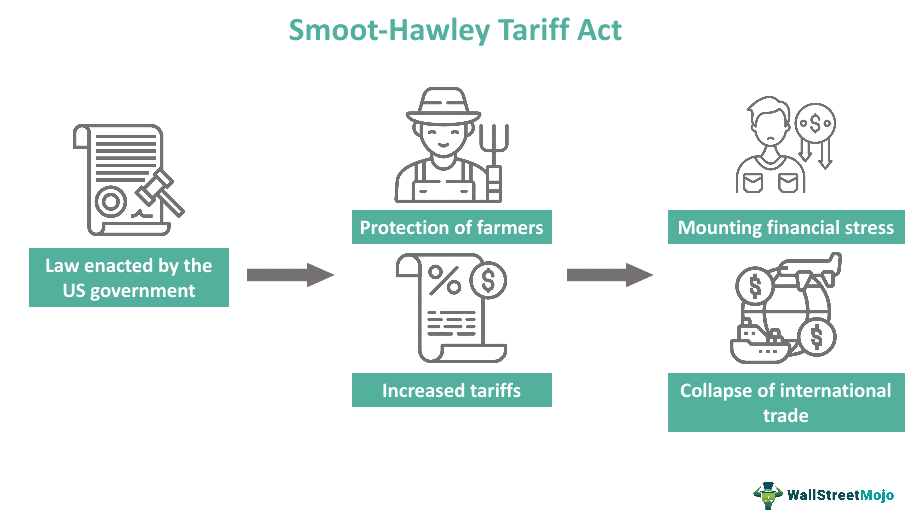
The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930
- Objective: Originally aimed at protecting American farmers and businesses from foreign competition amid falling agricultural prices.
- Provisions: Raised import duties on over 20,000 goods, imposing aggressive tariffs on approximately 25% of all US imports.
- Economic Impact:
- Prompted retaliatory tariffs from major trading partners, including Canada and European nations.
- US imports from Europe fell from $1.3 billion in 1929 to $390 million in 1932.
- US exports to Europe plummeted from $2.34 billion in 1929 to $784 million in 1932.
- Global trade declined by 66% between 1929 and 1934, exacerbating the Great Depression.
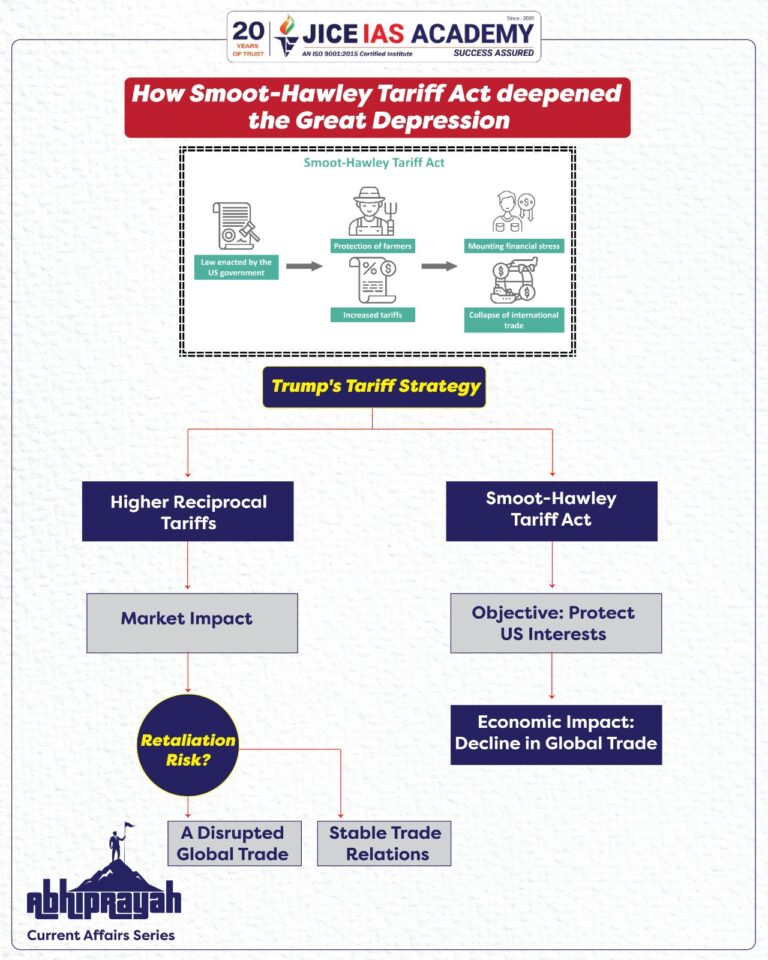
Trump's Tariff Strategy and the Smoot-Hawley Parallel
- Higher Reciprocal Tariffs: The 27% tariff on India, 34% on China, and 32% on Taiwan signal a return to protectionist trade policies.
- Market Impact: Announcements led to a 1,450-point drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average, a 5.8% fall in the Nasdaq, and a 6% decline in oil prices.
- Potential for Retaliation: Countries affected by higher US tariffs may impose their own countermeasures, disrupting global trade and supply chains.
Key Differences Between Smoot-Hawley and Trump's Tariffs
Aspect | Smoot-Hawley (1930) | Trump’s Tariffs (2025) |
Economic Context | Great Depression aftermath | Post-pandemic recovery and geopolitical tensions |
Tariff Scope | 25% on 20,000 goods | 10% blanket tariff + higher tariffs on trade-deficit countries |
Retaliation Risk | Immediate global backlash | Unfolding but likely due to trade deficits with key nations |
Trade Share in GDP | US imports = 5% of GDP | US imports = 14% of GDP (three times higher) |
Potential Impact on India-US Trade Relations
- Short-term Disruptions:
- Higher tariffs on Indian auto components, gems, and jewelry could impact export earnings.
- US concerns over India’s tariff structure and non-tariff barriers may strain trade negotiations.
- Opportunities for India:
- Tariffs on China (54%) and other Asian countries could shift supply chains in India’s favor, particularly in textiles and manufacturing.
- India could leverage bilateral trade agreements to secure tariff reductions for key exports.
- Long-term Implications:
- If retaliatory measures escalate, it may undermine global trade stability and slow economic growth.
- A strategic response, such as diversifying export markets and strengthening domestic manufacturing, will be crucial for India’s economic resilience.
Conclusion
- Trump’s tariffs reflect a shift towards economic nationalism that could disrupt global trade patterns.
- While the Smoot-Hawley comparison underscores the risks of protectionism, India’s ability to capitalize on shifting supply chains and navigate trade negotiations will determine its position in the evolving global trade order.

Genome study: 180 million genetic variants found in 9,772 individuals
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 09th April 2025 Home / Genome study: 180 million genetic variants found in 9,772 individuals Why
RBI slashes repo- rate
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / RBI slashes repo- rate Why in News? RBI reduced the repo

What does a bear market mean for Wall Street?
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / What does a bear market mean for Wall Street? Why in

Cabinet approves irrigation scheme for ‘modernising’ water management
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / Cabinet approves irrigation scheme for ‘modernising’ water management Why in News?
India ends transshipment facility for Bangladesh exports, cites congestion
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / India ends transshipment facility for Bangladesh exports, cites congestion Why in

Centre approves ₹63,000-crore deal for procuring 26 Rafale-M jets from France
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / Centre approves ₹63,000-crore deal for procuring 26 Rafale-M jets from France
Donald Trump raises taxes on Chinese imports to 125%, pauses tariffs on most nations for 90 days
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10th April 2025 Home / Donald Trump raises taxes on Chinese imports to 125%, pauses tariffs

Union Cabinet approves ₹22,919 Cr scheme for promoting electronics component manufacturing
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 09th April 2025 Home / Union Cabinet approves ₹22,919 Cr scheme for promoting electronics component manufacturing