UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 20th May 2025
World’s most powerful solar storm

Why in News?
The discovery of a colossal solar storm that struck Earth 14,300 years ago represents a significant advancement in our understanding of ancient solar activity.
What Was Discovered?
A research team led by scientists from Finland, France, and Switzerland, including postdoctoral scientist Kseniia Golubenko, professor Ilya Usoskin (University of Oulu, Finland), and professor Edouard Bard (CEREGE, France), has identified the most powerful solar storm ever detected.
- Time period: ~12,350 BC, during the end of the last Ice Age.
- Evidence: A sharp spike in radiocarbon (C-14) found in tree rings from wood samples preserved in the French Alps.
- Classification: This spike is known as a Miyake Event — a sudden rise in atmospheric isotopes caused by solar particle storms (SPEs).
What Are Solar Particle Storms (SPEs)?
Solar Particle Storms are intense bursts of high-energy particles (mostly protons) ejected from the Sun, often during solar flares or coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
- These particles interact with Earth’s atmosphere, increasing levels of cosmogenic isotopes like:
- Carbon-14 (radiocarbon)
- Beryllium-10
- Chlorine-36
- They can cause:
- Geomagnetic storms
- Auroras
- Damage to satellites
- Radio and GPS blackouts
- Disruption of power grids
How Was It Detected?
Tree-Ring Analysis & Isotope Spikes
- Tree rings record annual growth and contain trace amounts of atmospheric isotopes absorbed during that year.
- Scientists analyzed ancient wood preserved in glacial areas of the French Alps.
- A sudden spike in radiocarbon levels indicated a massive solar particle storm around 12,350 BC.
- These anomalies are cross-referenced with known radiocarbon cycles to precisely date the event.
Climate-Chemistry Model
- Researchers used a climate-chemistry model adapted for glacial atmospheric conditions to simulate the interaction of solar particles with Earth’s atmosphere.
- They validated the model against the known AD 775 solar storm, previously considered the strongest known.
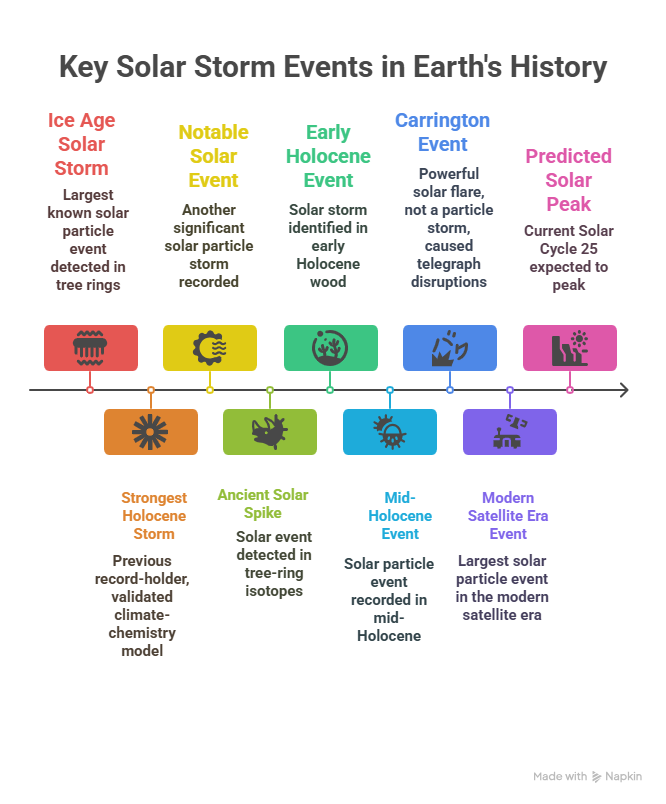
How Powerful Was the 12,350 BC Solar Storm?
- ~18% more intense than the AD 775 solar storm.
- Over 500 times stronger than the 2005 solar particle event — the largest in the modern satellite era.
- Stronger than:
- AD 994, 663 BC, 5259 BC, and 7176 BC events.
- The Carrington Event of 1859, though powerful, was not a particle storm but a different type of solar disturbance.
Scientific Significance
- Expands the Timeline of Solar Activity
- First extreme event detected before the Holocene (which began ~11,700 years ago).
- Extends known limits of solar storm intensity and frequency into the Ice Age.
- Helps Pinpoint Historical Events
- Miyake Events serve as cosmic timestamps. These radiocarbon anomalies allow archaeologists to anchor floating chronologies (undated ancient events) to exact years.
- Advances Solar Storm Modeling
- The success of this model paves the way for detecting even older or more subtle events, improving solar storm forecasting.
Why Does It Matter Today?
While such super storms are extremely rare, their potential impact on our highly connected modern world is enormous.
Possible Consequences:
- Satellite failure (GPS, weather monitoring, communications)
- Aviation risks due to increased radiation exposure at high altitudes
- Blackouts caused by damage to electrical infrastructure and transformers
- Internet disruption due to damaged undersea cables and satellites
- Increased health risk for astronauts and high-latitude air travel
Growing Relevance:
- We are currently in Solar Cycle 25, with solar activity rising toward a predicted peak in 2025–2026.
- Understanding such ancient storms helps us prepare for worst-case space weather scenarios.
Conclusion
The 12,350 BC solar storm is now the strongest known solar particle event, offering a rare and powerful lens into our Sun’s volatile history. It:
- Redefines the scale of potential solar threats.
- Demonstrates the importance of tree-ring and isotopic research in tracking cosmic phenomena.
- Underlines the urgent need for space weather preparedness in the age of satellites and global digital infrastructure.
Understanding these ancient cosmic events is not just a matter of scientific curiosity — it’s a matter of future resilience.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
- Decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of RBCs.
- Increased fragility and cell stiffness.
- Vascular blockage, causing pain and organ injury.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, anemia, and stroke.


