UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 19th June 2025
Centre approves construction of 2.35 lakh houses under PMAY

Why in News?
- The Centre approved the construction of 2.34 lakh houses under PMAY-Urban 2.0 in nine states, focusing on Beneficiary Led Construction and Affordable Housing in Partnership verticals.
Introduction
- On June 18, 2025, the Government of India approved the construction of 2,34,864 houses under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban 2.0 (PMAY-U 2.0).
- The decision was taken during the third meeting of the Central Sanctioning and Monitoring Committee (CSMC) of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), chaired by Secretary Srinivas Katikithala.
- These houses are to be constructed in nine states: Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
About Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
- Launched: June 2015
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
Objective: To achieve the goal of “Housing for All” in urban areas by providing pucca (permanent) houses to all eligible urban poor, especially those belonging to the Economically Weaker Section (EWS), Low-Income Group (LIG), and Middle-Income Group (MIG). - In order to meet the evolving needs and accelerate progress, the scheme was revamped as PMAY-U 2.0, with a renewed focus on the construction of an additional 1 crore houses for urban families, especially from EWS and LIG categories.
Implementation Structure of PMAY-U 2.0
The scheme is implemented through the following four verticals:
- Beneficiary-Led Construction (BLC): Financial assistance is provided to eligible individual beneficiaries to construct or enhance their own houses on their own land.
- Affordable Housing in Partnership (AHP): Provides financial support for housing projects where public or private sectors collaborate with the government to develop affordable housing on land owned by them.
- Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHC): Focuses on providing rental housing for migrant workers and urban poor who are unable to afford home ownership.
- Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS): Provides interest subsidies on housing loans taken by eligible beneficiaries for buying, constructing, or enhancing a house.
The latest approval of houses pertains to BLC and AHP verticals.
Key Highlights of the June 2025 Sanction
- Total Houses Approved: 2,34,864
- Number of States Covered: Nine
- Meeting Platform: 3rd meeting of the Central Sanctioning and Monitoring Committee (CSMC)
Social Inclusion Emphasis
The scheme strongly incorporates social justice principles by targeting vulnerable and marginalised sections:
- Women (including single women and widows): Over 1.25 lakh houses
- Transgender persons: 44 houses
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 42,400 houses
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 17,574 houses
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 1,13,414 houses
This allocation indicates a strong effort toward promoting inclusive urban development.
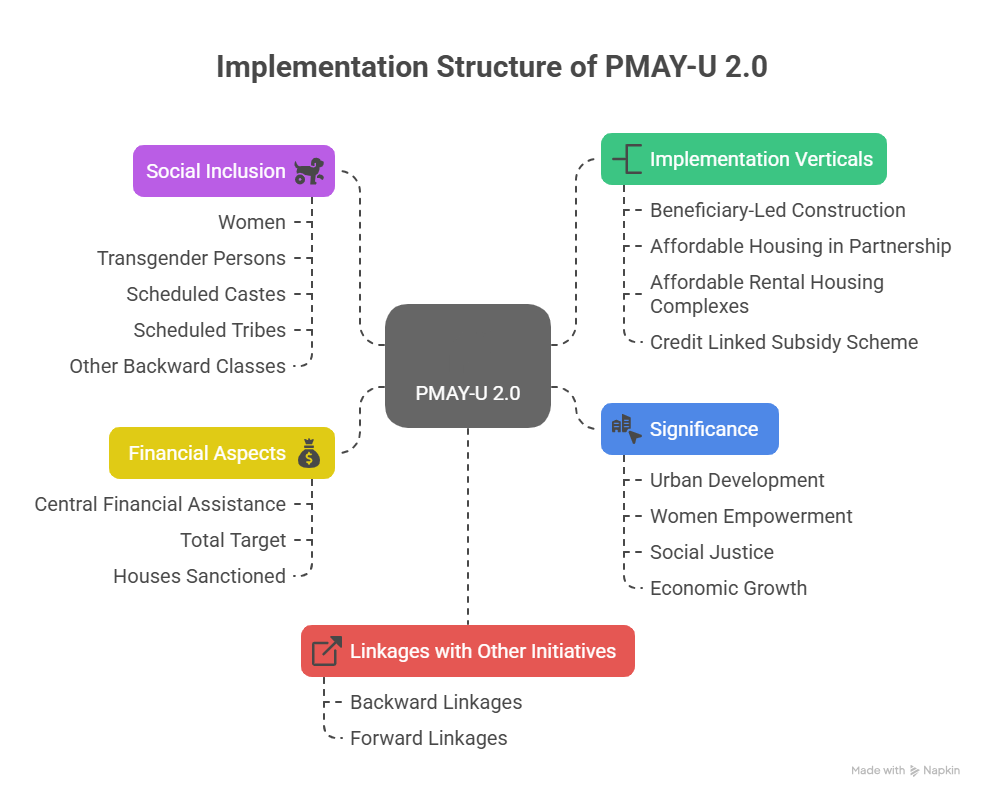
Financial Aspects
- Central Financial Assistance per Housing Unit: Up to ₹2.5 lakh
- Total Target under PMAY-U 2.0: 1 crore houses
- Total Houses Sanctioned So Far under PMAY-U 2.0: 7,09,979
- Total Houses Constructed under original PMAY-U (2015–2021): Over 93.19 lakh
Significance of the Scheme
- Urban Development: The scheme aims to improve urban housing stock, particularly for the poor and middle class.
- Women Empowerment: Preference is given to women, and many houses are allotted in their name to promote economic security and social status.
- Social Justice: The scheme focuses on ensuring housing access for historically marginalised communities such as SCs, STs, OBCs, and transgender persons.
- Economic Growth: The construction activity under the scheme generates employment and demand for building materials, thereby stimulating economic growth.
Linkages with Other Government Initiatives
- Backward Linkages: The scheme builds upon previous urban housing programmes like the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission (JNNURM) and Rajiv Awas Yojana (RAY).
- Forward Linkages: The objectives of PMAY-U align with initiatives such as the Smart Cities Mission, Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT), and National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM).

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

