UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 6th June 2025
China rare earth mineral export ban impact

Why in News?
- Suzuki Motor became the first Japanese automaker to halt Swift production due to China’s new restrictions on the export of rare earth magnets, highlighting global supply chain vulnerabilities.
Introduction
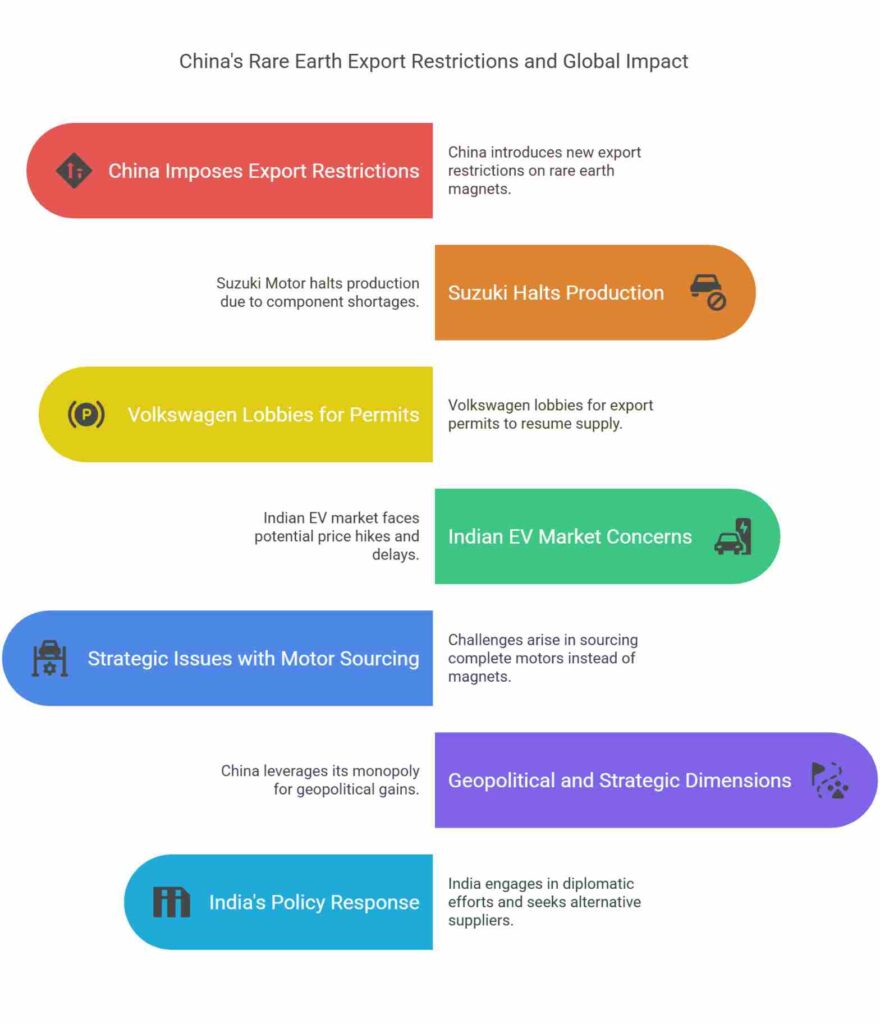
- China imposed new restrictions on the export of rare earth magnets and associated materials from April 4, 2025, as a retaliatory measure against recent US tariffs.
- This move has begun affecting global automobile production, including that of Japanese automaker Suzuki, and is raising concerns in India’s emerging EV market.
What are Rare Earth Magnets and Why are They Important?
- Rare earth magnets are strong permanent magnets made from alloys of rare earth elements.
- The most widely used type is Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB).
- Key Uses in Automobiles:
- Electric Motors: Critical for traction motors in EVs due to high efficiency and power-to-weight ratio.
- Other Components: Also used in power steering systems, braking systems, air conditioners, wiper motors, and more.
- Strategic Importance:
- These magnets are not easily substitutable.
- China controls up to 90% of global rare earth processing, creating a supply-chain monopoly.
China’s Trade Restrictions – Details
- China has not imposed a full ban, but:
- Export permits are now mandatory.
- The process has become opaque and delayed, effectively restricting timely access.
- Exporters must now declare end-use and assure magnets will not be used for military purposes.
- Materials under restriction include:
- Rare earth magnets
- Seven heavy rare earth metals: samarium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, lutetium, scandium, yttrium.
- Previously banned: gallium, germanium, antimony, and others.
Impact on the Global Auto Industry
1. Japan – Suzuki Motor (Hamamatsu-based):
- Production of the Swift compact hatchback halted from May 26 (except Swift Sport).
- Cited component shortages due to rare earth supply disruptions.
- Resumption expected partially from June 13, fully after June 16.
2. Germany – Volkswagen:
- Lobbied with Chinese authorities to resume export permits to its suppliers.
- Was among the first beneficiaries of the reissued permits.
Impact on Indian Auto Industry – Particularly EV Makers
- Current Status:
- Maruti (Suzuki’s Indian arm): No immediate production impact.
- Indian automakers have used up inventories; a shortage looms.
- Concerns:
- Cost-sensitive EV market may face:
- Price hikes
- Production delays
- Long-term supply risk if Chinese export restrictions continue.
- Cost-sensitive EV market may face:
- Industry Response:
- Dialogue ongoing with the Indian government.
- Seeking procurement alternatives and policy intervention.
Strategic Issues with Sourcing Complete Motors vs. Magnets
- Beijing’s Push: Car companies to buy full motor assemblies instead of just magnets.
- Challenges:
- Motors come in standard sizes — may not fit existing designs.
- Redesigning vehicles is costly and time-consuming.
- Loss of flexibility: Earlier, carmakers could calibrate motor design using magnets independently.
Geopolitical and Strategic Dimensions
- China is leveraging its monopoly over rare earth processing for geopolitical gains.
- Reflects a broader pattern of geo-economic coercion, especially in high-tech sectors.
- Similar actions seen in the past:
- 2010: China halted rare earth exports to Japan over the Senkaku island dispute.
- US, Japan, and India are now seeking supply chain diversification, but:
- Processing capacity takes years to build.
- Environmental regulations and technical expertise are major hurdles.
India’s Policy Response – Way Forward
- Short-term:
- Diplomatic engagement with China.
- Strategic stockpiling of critical rare earth components.
- Medium-term:
- Sourcing from alternate suppliers: Australia, Vietnam, African countries.
- Incentivizing local R&D into alternatives for rare earths (e.g., induction motors, ferrite magnets).
- Long-term:
- Setting up domestic rare earth processing plants.
- Collaborating in Quad/BRICS mineral alliances to reduce dependency on China.
Conclusion
- China’s restrictions on rare earth magnets have exposed the vulnerabilities of global auto and EV supply chains.
- For India, this is both a challenge and an opportunity — to reconfigure its industrial and trade policy to reduce dependency on single-source imports and boost domestic capacity in critical technologies essential for energy transition and strategic autonomy.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

