UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 29th May 2025
China Rises on Global Stage Amid U.S. Withdrawal from WHO, Climate Deal

Why in News?
U.S. withdrawal from global institutions like WHO and the Paris Agreement under Donald Trump has enabled China to expand its soft power and financial influence globally.
Introduction
- In recent years, the global power balance has been shifting, not through war or direct confrontation, but through strategic repositioning and economic diplomacy.
- Under President Donald Trump, the United States began withdrawing from several multilateral commitments, leaving a vacuum in global leadership.
- China, in turn, has stepped up its global engagement, positioning itself as an alternative leader through increased financial contributions, diplomatic efforts, and debt diplomacy.
U.S. Withdrawal from International Institutions
- Exit from the World Health Organization (WHO)
- The Trump administration accused the WHO of mishandling the COVID-19 pandemic and being biased toward China.
- As a result, the U.S. announced its intention to withdraw from the WHO and stop funding it.
- The U.S., as a founding member and the top donor, had consistently contributed around 20% of WHO’s assessed budget.
Effect of U.S. Withdrawal
- A significant funding gap was created in the WHO.
- The 78th World Health Assembly approved its budget without U.S. participation for the first time.
- This disengagement has weakened the WHO’s capacity and moral authority to some extent.
China’s Response
- China pledged an additional $500 million over five years.
- Its assessed contribution to the WHO rose from 6.5% (2015-16) to 15% (2024-25).
- Though still behind the U.S., China is steadily closing the gap.
Withdrawal from the Paris Climate Agreement
- The Trump administration declared that the U.S. would withdraw from the Paris Agreement and revoke financial commitments to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- The U.S. had been contributing about 22% of the UNFCCC’s core budget, the highest globally.
Effect on Climate Governance
- This move weakened the global coalition fighting climate change.
- It also created uncertainty about the funding of climate adaptation and mitigation programs in developing nations.
China’s Position
- China, the second-largest contributor (17%), took the opportunity to boost its image as a responsible stakeholder in global climate action.
- Through climate diplomacy and green finance, China is attempting to reposition itself as a climate leader.
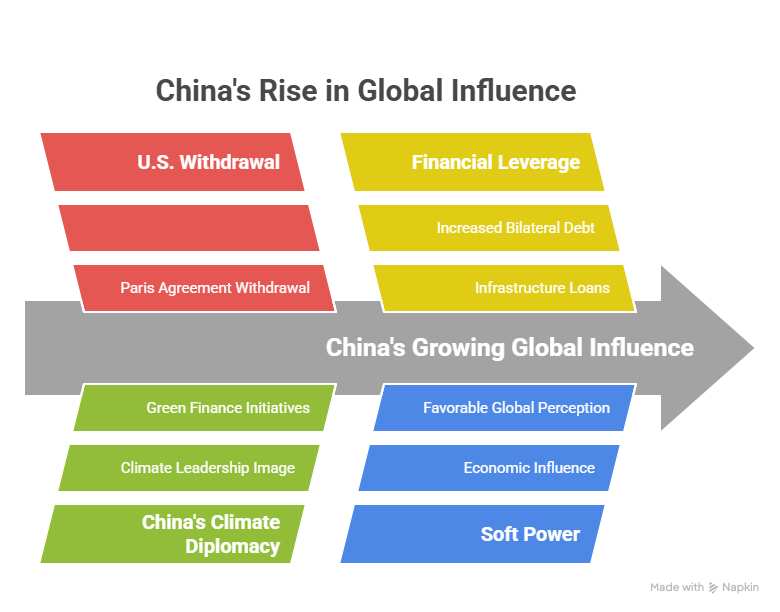
China’s Expanding Financial Influence
Bilateral Debt Diplomacy
- China’s share in global bilateral sovereign debt has grown dramatically — from 1% in 2003 to 26% in 2023.
- In contrast, the U.S.’s share in such debt declined from 36% in 1973 to just 4% in 2023.
Implications
- This makes China the world’s largest bilateral creditor, giving it significant leverage in developing nations.
- Through projects like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China offers infrastructure loans and development aid, increasing its influence across Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
Growing Soft Power and Global Perception
Economic Influence
- According to a 2024 Pew Research Center survey, over 60% of respondents in 21 countries said China has a great or fair influence on their economies.
- This reflects China’s growing integration into global trade, finance, and supply chains.
Democracy Perception Index
- The 2024 Democracy Perception Index showed that 76 out of 96 countries surveyed had a more favorable view of China than the U.S.
- This suggests a shifting geopolitical perception where U.S. soft power is diminishing, especially among Global South nations.
The Strategic Implications
- Multilateralism Without the U.S.
- China’s Ambassador to Geneva, Chen Xu, stated, “We have to adapt ourselves to multilateral organisations without the Americans. Life goes on.”
- This reflects a strategic pivot in multilateral diplomacy, where China is willing to shape global institutions in the absence of U.S. leadership.
- Challenge to U.S. Global Hegemony
- While the U.S. still remains a global superpower, its retreat from global institutions creates opportunities for power redistribution.
- China’s increasing financial, diplomatic, and technological presence allows it to challenge the liberal international order built by the U.S. post-World War II.
Conclusion
The withdrawal of the U.S. from international commitments under the Trump administration marked a turning point in global governance. China has strategically filled many of these vacuums, not by confrontation but by leveraging financial aid, soft power, and multilateral diplomacy. As the U.S. re-evaluates its global engagement, the world is witnessing a transition towards a multipolar global order, with China as a key player.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
The withdrawal of the U.S. from international commitments under the Trump administration marked a turning point in global governance. China has strategically filled many of these vacuums, not by confrontation but by leveraging financial aid, soft power, and multilateral diplomacy. As the U.S. re-evaluates its global engagement, the world is witnessing a transition towards a multipolar global order, with China as a key player.
Local and Remote Drivers of Monsoon Onset
India has approved a competitive execution model for its fifth-generation fighter jet project, the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), marking a key step towards defence indigenisation.

