UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 30th May 2025
e-Rupee Circulation and Cross-Border CBDC

Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India’s e-Rupee (CBDC) in circulation surged to ₹1,016 crore by March 2025.
Introduction
- India’s Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), known as the e-Rupee, has seen a significant rise in circulation, reaching ₹1,016 crore by the end of March 2025, up from ₹234 crore a year earlier.
- Introduced as a response to the challenges posed by private virtual currencies like Bitcoin, the CBDC aims to modernize India’s monetary system, enhance financial inclusion, and simplify payments — both domestic and cross-border.
What is e-Rupee?
The e-Rupee is a digital form of fiat currency issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It is a liability of the central bank and is recognized as legal tender. There are two types of e-Rupee pilots:
- e-Rupee-Wholesale (CBDC-W): Primarily used for interbank settlements and financial transactions.
- e-Rupee-Retail (CBDC-R): Designed for use by the public in day-to-day transactions.
Current Status and Growth
As per the RBI Annual Report 2024-25, the e-Rupee’s circulation has surged:
- Total e-Rupee in circulation: ₹1,016 crore
- ₹500 denomination: ₹857 crore
- ₹200 denomination: ₹91 crore
- ₹100 denomination: ₹38 crore
This growth reflects increased participation and experimentation across both wholesale and retail segments.
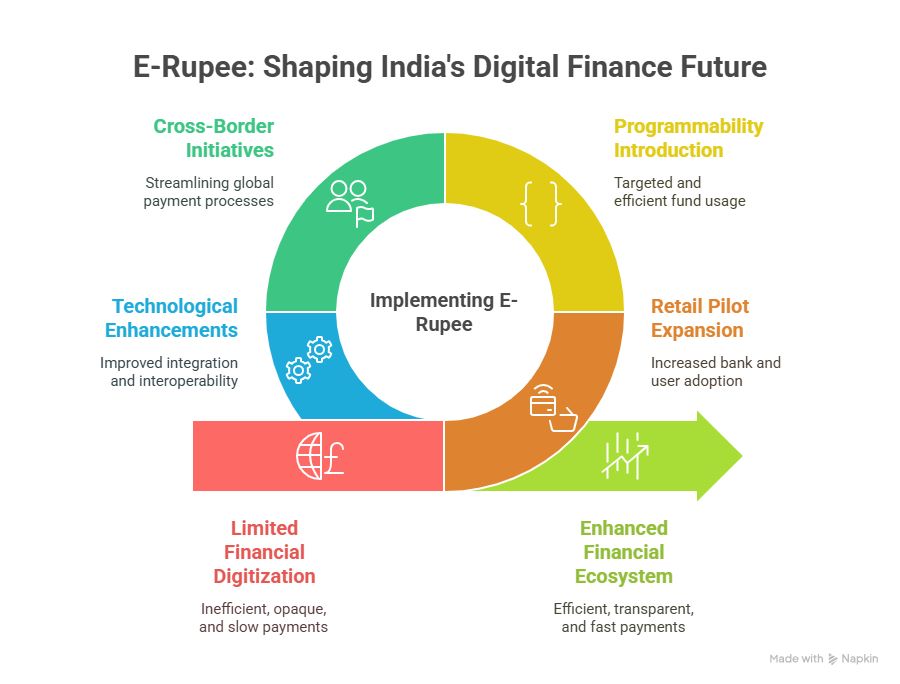
Retail Pilot Expansion
Key Developments:
- e-Rupee-Retail has expanded to 17 banks.
- Over 60 lakh users have adopted the e-Rupee.
- Non-bank entities have been permitted to distribute CBDC wallets, increasing accessibility.
New Features Introduced:
- Offline Payments: Useful in remote areas with poor connectivity.
- Programmability: Enables funds to be used for specific purposes only.
Innovative Use Cases of Programmability
Programmable CBDC has opened up targeted and efficient use of government funds:
- Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT) linked to carbon credits and Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans.
- Employee Allowances (fuel/meal) are being disbursed digitally.
- The Odisha Government transferred e-Rupee to 88,000 beneficiaries under the Subhadra Yojana.
These use cases demonstrate how the e-Rupee can enhance transparency and traceability in public welfare schemes.
Cross-Border Ambitions of CBDC
One of the major goals of CBDC globally is to streamline cross-border payments, which are currently expensive, slow, and opaque.
RBI’s Cross-Border Initiatives:
- Bilateral Pilots: Being actively explored with select countries to improve turnaround time, efficiency, and transparency.
- Multilateral Engagements: Participation under the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Innovation Hub is being considered.
- Roadmap Finalization: Progress has been made in identifying technical requirements and defining use cases for cross-border pilots.
Technological Enhancements
- The Account Aggregator Framework is being improved for better integration with CBDC for customer convenience, data transparency, and financial efficiency.
- Efforts are on to ensure interoperability between banks, wallets, and payment platforms.
Challenges and Considerations
While the e-Rupee holds immense potential, several issues require close attention:
- Cybersecurity and data privacy.
- Digital divide: Ensuring adoption in rural and low-income segments.
- Regulatory framework for programmable features.
- Cross-border legal harmonization.
Conclusion
- The e-Rupee marks a bold step in India’s financial digitization journey. With increasing circulation, innovative domestic use cases, and upcoming cross-border pilots, the RBI is shaping the future of money and payment infrastructure.
- As the e-Rupee evolves, it promises to enhance efficiency, support welfare delivery, and position India as a leader in the global CBDC ecosystem.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

