UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 21th May 2025
Energy Sufficiency in India and Its States

Why in News?
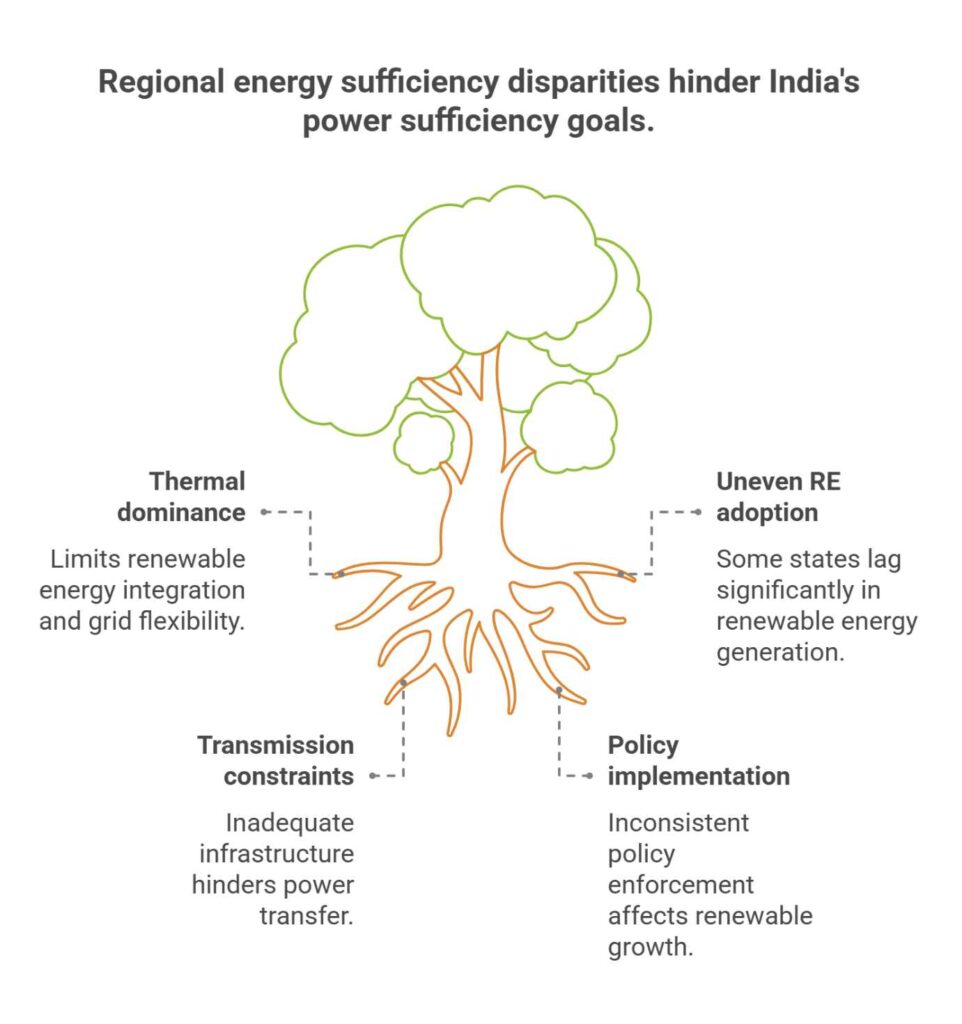
India has officially transformed into a power-sufficient nation, with an energy gap of only 0.1% in 2024–25, while regional disparities persist, especially in East and North-East India.
Key Highlights:
- Installed Power Capacity:
As of 2024–25, India’s total installed power capacity is 470 GW, with thermal sources contributing the majority and renewables at 13.78% of total production. - Transmission Network:
- India’s National Power Grid interlinks 5 regional grids (North, South, East, West, North-East), operating at 50 Hz frequency.
- Managed by Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd. (PGCIL).
- PGCIL handles 45% of India’s power transmission and integrates private players.
- Renewable Energy Growth:
- Renewable production rose from 1.7 lakh MU in 2021–22 to 2.3 lakh MU in 2024–25.
- Rajasthan doubled renewable capacity; Gujarat also made significant gains.
- States like Tripura, Jharkhand, Goa, Puducherry, Chandigarh have negligible renewable generation (<40 MU).
- State-wise Energy Gaps:
- South & West: Minimal or 0% gap (e.g., Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra).
- North: Improved performance; J&K cut gap from 7.6% to 0.5%; Rajasthan fluctuated.
- East: Bihar (0.4%) and Jharkhand (0.5%) still show notable gaps.
- North-East: Volatile gaps; Meghalaya’s gap dropped from 7.6% to 0% in 2024–25.
- Policy Push:
- Goal: 500 GW non-fossil energy capacity by 2030.
- ₹9.15 lakh crore investment needed in transmission.
- Infrastructure planned for Green Hydrogen hubs at Mundra, Vizag, etc.
Major Government Schemes & Initiatives:
- National Solar Mission (NSM)
- Launched under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Target: 280 GW solar capacity by 2030
- PM-KUSUM Scheme
- Solar pumps for agriculture
- Components A, B, C for grid-connected, standalone, and pump replacement
- Solar Park Scheme
- Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks (UMREPs) across states
- Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018)
- Promotes hybrid systems to utilize land and transmission optimally
- Green Energy Corridor
- Dedicated transmission lines for evacuating renewable energy
- National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023)
- Target: 5 MMT per annum green hydrogen production by 2030
- Promotes electrolyzers and hydrogen hubs
- Rooftop Solar Programme
- Focused on residential and institutional sectors
- Solarization of cities and panchayats
India’s Global Leadership in RE:
- International Solar Alliance (ISA)
- HQ: Gurugram
- India-led initiative to mobilize $1 trillion in solar investments globally
- One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG)
- Vision for transnational solar grid connectivity
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI)
- India-backed initiative for sustainable energy infrastructure

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
- Decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of RBCs.
- Increased fragility and cell stiffness.
- Vascular blockage, causing pain and organ injury.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, anemia, and stroke.


