UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13th July 2025
Europe is in a hurry to dismantle river-blocking dams and weir

Why in News?
- According to Dam Removal Europe (DRE), 23 European countries demolished 542 barriers (dams, weirs, culverts) in 2024 — the highest since the river barrier removal drive began in 2020.
- The push aims to meet the EU’s Nature Restoration Law (2023) target of making 25,000 km of rivers barrier-free by 2030.
- The UNEP’s “Frontiers 2025” report has flagged the global crisis of river fragmentation, projecting that 89% of global river volume will be moderately to severely impeded by 2030, up from 43% in 2010.

Concepts & Background
- River Fragmentation: Building dams and barriers interrupts the natural flow of rivers, which affects fish migration, sediment transport, water temperature, and floodplain connectivity.
- Benefits vs. Costs: While dams provide irrigation, hydropower, flood control, and drinking water, they also harm ecosystems and indigenous livelihoods, especially inland fisheries.
- Dam Removal Europe (DRE): A coalition of organisations like WWF, The Rivers Trust, The Nature Conservancy, and European Rivers Network leading this initiative.

Ecological Impact of River Barriers
- Fish Migration: Barriers block migratory routes for fishes like salmon and eel, leading to population declines.
- Habitat Degradation: Alters flow regimes, sediment balance, and habitat connectivity; affects aquatic biodiversity and riverine wetlands.
- Food Security: Disrupts inland fisheries that support millions, especially indigenous and local communities.
- Safety & Obsolescence: Many old dams are now unsafe, economically unviable, or redundant due to ageing infrastructure and changing energy demands.
Global Practices:
- In Europe and North America, older and unsafe dams are increasingly being dismantled as part of a shift to eco-restoration.
- In contrast, countries in Africa, Asia, and South America still rely heavily on new dam construction — especially for hydropower expansion — often without adequate environmental impact assessments or mitigation measures for aquatic ecosystems.
- This divergence shows the balance needed between energy security, climate targets, and river health.
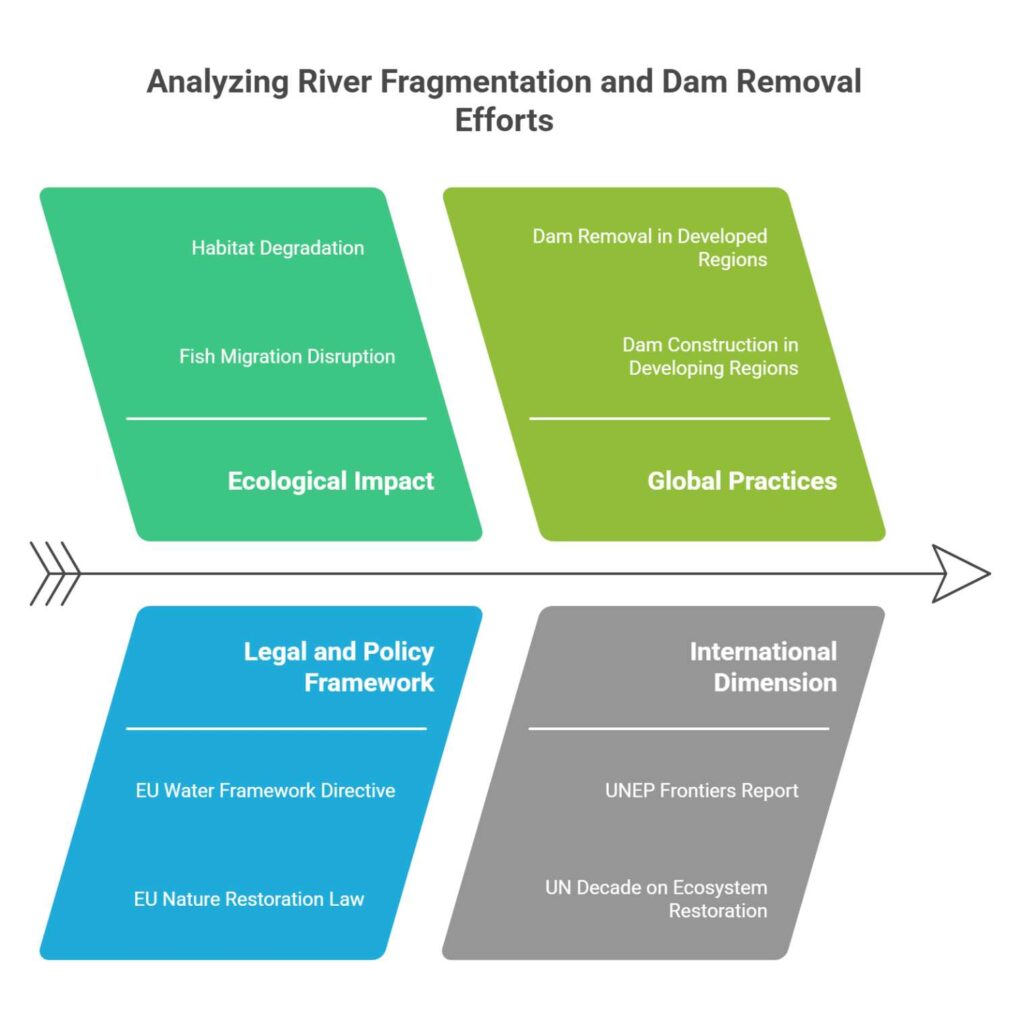
International Dimension
- The UNEP report warns that continued river fragmentation will severely threaten freshwater biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Globally, over 62,000 large dams and millions of small barriers exist; Europe alone has 1.2 million in-stream barriers.
- The dam removal movement is part of a nature-based solutions approach under the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030).

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

