UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 28th March 2025
Europe’s space agency retires Gaia, the cartographer of the cosmos: Its mission & significance
Why in News?
The Gaia Mission (2013-2025) by the European Space Agency (ESA) revolutionized astrometry, creating a 3D map of the Milky Way.
Introduction
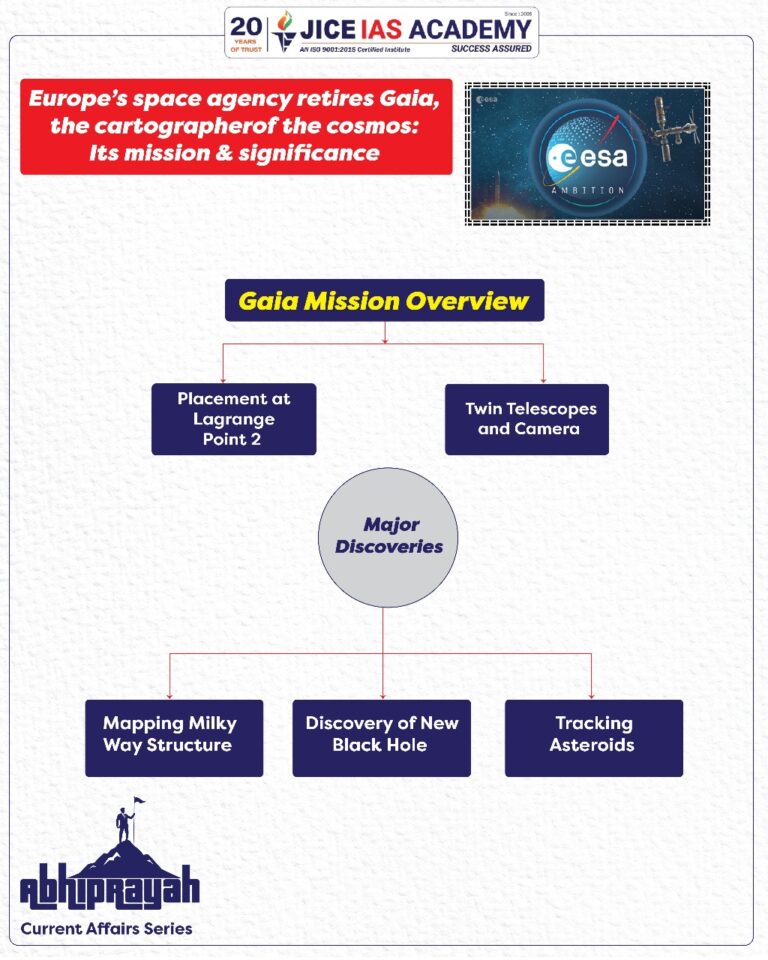
- The European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia mission, launched in December 2013, was one of the most ambitious space observatories dedicated to astrometry—the precise measurement of celestial bodies.
- Over the past decade, Gaia revolutionized the understanding of the Milky Way, mapping its structure, motion, and evolution.
- The mission was officially shut down on March 27, 2025, after providing unprecedented astronomical data that will continue to shape scientific research for years to come.
Gaia Mission: Objectives and Achievements
- Primary Goal: To create the most precise three-dimensional map of the Milky Way galaxy.
- Observational Data:
- Recorded 3 trillion observations of over 2 billion stars and celestial objects.
- Contributed to 13,000+ scientific publications.
- Provided insights into the shape, motion, and history of the galaxy.
Position and Instruments
- Lagrange Point 2 (L2): Gaia was placed 1.5 million km behind Earth, away from planetary and solar interference, ensuring unobstructed cosmic observation.
- Twin Telescopes and Billion-Pixel Camera:
- Used a photometer, spectrometer, and astrometer to precisely analyze star positions and motions.
- Largest digital camera in space with nearly a billion pixels.
Major Discoveries by Gaia
- Mapping the Milky Way’s Structure and Evolution
- Confirmed that the Milky Way has a central bar and spiral arms.
- Revealed that the galactic disc is warped and wobbles, likely due to collisions with smaller satellite galaxies.
- Helped reconstruct the past interactions and future evolution of the galaxy.
- Discovery of a New Type of Black Hole
- Unlike traditional black holes detected via radiation, Gaia identified “truly black” holes using gravitational effects.
- One of the black holes detected is the closest to Earth discovered so far.
- Tracking Asteroids and Planetary Defense
- Mapped the orbits of 150,000+ asteroids, including those potentially hazardous to Earth.
Gaia’s End-of-Mission and Legacy
- On March 27, 2025, ESA deactivated Gaia by draining its energy sources and moving it into a retirement orbit around the Sun.
- A bulk of its data is still being processed and will be released in phases:
- First five-and-a-half years’ data will be published in 2026.
- Final dataset expected by the end of the decade.
Future Prospects in Space Astrometry
- Despite its vast scope, Gaia mapped only about 2% of the estimated 100 billion stars in the Milky Way, highlighting the need for future missions.
- The data collected will aid upcoming astronomical projects and space missions focused on dark matter, exoplanet discovery, and galactic evolution.
Conclusion
- Gaia’s contributions have transformed modern astronomy, setting new standards in precision space mapping.
- Its legacy will continue to drive scientific advancements, shaping humanity’s understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in



Nice post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Extremely helpful information particularly the last part 🙂 I care for such information much. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
obviously like your website however you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to inform the reality nevertheless I will surely come again again.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
As a Newbie, I am continuously browsing online for articles that can benefit me. Thank you
I really like your writing style, great info , thankyou for putting up : D.
Together with everything that appears to be building throughout this specific subject matter, many of your opinions are somewhat stimulating. Nevertheless, I beg your pardon, because I do not give credence to your whole idea, all be it exciting none the less. It appears to me that your commentary are not entirely validated and in reality you are generally your self not really thoroughly confident of your point. In any case I did take pleasure in examining it.
Rattling good information can be found on blog.
I’d must check with you here. Which isn’t one thing I often do! I get pleasure from studying a post that can make people think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Rattling wonderful information can be found on web blog. “Even if happiness forgets you a little bit, never completely forget about it.” by Donald Robert Perry Marquis.
Some truly nice and useful information on this web site, as well I conceive the style and design has great features.
Rattling nice design and fantastic subject matter, very little else we need : D.
Whats Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & aid other customers like its aided me. Great job.
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
I truly wanted to post a quick comment to say thanks to you for all of the splendid tips you are showing at this site. My rather long internet investigation has now been rewarded with good quality facts and techniques to write about with my friends and classmates. I would say that most of us visitors are really lucky to exist in a fantastic website with many perfect people with valuable tricks. I feel quite privileged to have used the web site and look forward to some more thrilling times reading here. Thanks a lot again for a lot of things.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I to find It really helpful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to offer one thing back and help others like you helped me.
The core of your writing whilst sounding reasonable originally, did not work properly with me after some time. Someplace throughout the paragraphs you managed to make me a believer unfortunately just for a very short while. I still have got a problem with your jumps in logic and you might do well to help fill in those gaps. When you actually can accomplish that, I could certainly end up being impressed.
Wow! Thank you! I constantly needed to write on my site something like that. Can I implement a portion of your post to my site?
You have mentioned very interesting details! ps nice web site. “Wisdom is the supreme part of happiness.” by Sophocles.
I am no longer sure where you’re getting your info, however great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or figuring out more. Thank you for fantastic information I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
you could have an incredible weblog here! would you wish to make some invite posts on my weblog?
Normally I don’t read article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very pressured me to try and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thanks, very nice post.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
Great post, you have pointed out some great details , I likewise conceive this s a very excellent website.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
But wanna remark on few general things, The website layout is perfect, the written content is rattling excellent : D.
Great write-up, I am regular visitor of one’s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
hi!,I like your writing so much! share we communicate more about your post on AOL? I need an expert on this area to solve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
A person essentially help to make seriously articles I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your website page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to make this particular publish amazing. Magnificent job!
I went over this internet site and I think you have a lot of good information, saved to bookmarks (:.
I like this weblog so much, saved to bookmarks. “I don’t care what is written about me so long as it isn’t true.” by Dorothy Parker.
you’re really a good webmaster. The website loading speed is incredible. It seems that you’re doing any unique trick. Also, The contents are masterwork. you’ve done a great job on this topic!
I’ve read some just right stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much attempt you put to create this sort of fantastic informative web site.
I see something really special in this web site.
I will immediately snatch your rss as I can not find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly permit me recognize so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
I love the efforts you have put in this, thanks for all the great content.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
You are a very clever individual!
Sweet site, super style and design, very clean and apply pleasant.
Hello, Neat post. There is an issue along with your web site in internet explorer, could test thisK IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a big component to folks will pass over your wonderful writing because of this problem.
Good day! I just wish to give an enormous thumbs up for the nice information you may have right here on this post. I might be coming again to your blog for more soon.
Thank you, I have just been searching for info about this topic for a while and yours is the best I have found out so far. However, what about the bottom line? Are you sure in regards to the supply?
Real clear website , thankyou for this post.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you¦ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched all over the place and simply could not come across. What an ideal site.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem together with your site in web explorer, may check this… IE nonetheless is the market chief and a large section of other people will pass over your wonderful writing due to this problem.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for!
Thank you for some other great post. The place else may anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect method of writing? I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I’m at the look for such info.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
Good post. I be taught something more challenging on different blogs everyday. It is going to always be stimulating to read content material from different writers and apply somewhat something from their store. I’d favor to make use of some with the content material on my blog whether or not you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a hyperlink on your internet blog. Thanks for sharing.
Oh my goodness! an incredible article dude. Thanks Nonetheless I am experiencing situation with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting similar rss drawback? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
Some truly nice and useful information on this website , also I believe the pattern contains wonderful features.
he blog was how do i say it… relevant, finally something that helped me. Thanks
Hey there, You have done a great job. I will definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this site.
Generally I don’t read article on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice article.
As soon as I noticed this web site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
You are my intake, I have few web logs and very sporadically run out from to post : (.
There are some attention-grabbing cut-off dates on this article however I don’t know if I see all of them heart to heart. There is some validity but I’ll take hold opinion till I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we want extra! Added to FeedBurner as properly
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it is really informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for putting up.
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one?¦s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Have you ever thought about creating an ebook or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog centered on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my readers would enjoy your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e mail.
Thanks a lot for giving everyone such a pleasant chance to read in detail from this website. It can be very pleasant plus jam-packed with a lot of fun for me and my office friends to search your site at the least thrice a week to read through the new secrets you have got. And of course, I am just always impressed considering the terrific tricks you give. Some 3 tips in this article are truly the finest we have all had.
I am lucky that I detected this website, exactly the right information that I was looking for! .
Hello very nice website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds additionallyKI am glad to find numerous helpful info right here within the submit, we want develop extra strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
A lot of thanks for all of your efforts on this website. Kate loves conducting investigation and it’s easy to understand why. All of us notice all relating to the dynamic mode you convey efficient tricks via this web site and encourage participation from some others on the area while our own girl is always discovering so much. Have fun with the rest of the new year. You’re doing a very good job.
Sweet website , super layout, very clean and apply genial.
I really delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was looking for : D as well saved to bookmarks.
I genuinely enjoy looking at on this site, it has great articles. “Don’t put too fine a point to your wit for fear it should get blunted.” by Miguel de Cervantes.
Real good information can be found on web blog. “Politics is applesauce.” by Will Rogers.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I¦ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website 🙂
whoah this blog is magnificent i like reading your posts. Keep up the good work! You already know, many people are searching around for this information, you can help them greatly.
Hello.This article was really motivating, especially because I was searching for thoughts on this topic last week.
I went over this site and I conceive you have a lot of good information, saved to fav (:.
Flash Burn is a revolutionary natural supplement that has been transforming the lives of thousands of people struggling with excess weight. Developed with a 100 natural and scientifically proven formula
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your great post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
A lot of thanks for all your valuable effort on this web site. Betty take interest in going through internet research and it’s really easy to understand why. A lot of people hear all of the compelling way you convey powerful ideas via your blog and therefore encourage contribution from people on the issue so our favorite simple princess is starting to learn so much. Enjoy the rest of the year. You are always carrying out a stunning job.
Thanks , I’ve just been looking for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I have discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
Good ?V I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
I have recently started a website, the information you provide on this site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
The subsequent time I learn a weblog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I imply, I know it was my choice to learn, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you might fix when you werent too busy on the lookout for attention.
Hello there, simply turned into alert to your blog thru Google, and found that it is really informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate for those who proceed this in future. Many folks will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, yet I by no means found any attention-grabbing article like yours. It¦s pretty value sufficient for me. Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you probably did, the net will be much more helpful than ever before.
Hello are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Really nice style and design and great subject material, hardly anything else we want : D.
I’d incessantly want to be update on new blog posts on this website , bookmarked! .
You really make it appear so easy with your presentation however I find this topic to be actually something that I feel I’d never understand. It seems too complicated and very large for me. I am looking ahead on your subsequent submit, I will try to get the grasp of it!
Thanks for helping out, superb info .
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to send you an email. I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wished to mention that I’ve really loved surfing around your weblog posts. In any case I will be subscribing in your feed and I hope you write again soon!
you are really a good webmaster. The web site loading speed is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a wonderful job on this topic!
You are my aspiration, I possess few web logs and very sporadically run out from to post .
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
I reckon something truly special in this internet site.
great put up, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite experts of this sector don’t notice this. You must proceed your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
Some really interesting info , well written and broadly user pleasant.
Howdy very nice website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also…I’m happy to seek out numerous useful information right here in the submit, we want work out extra techniques on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
I got what you intend, thanks for putting up.Woh I am lucky to find this website through google. “I was walking down the street wearing glasses when the prescription ran out.” by Steven Wright.
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favourite reason appeared to be at the internet the easiest thing to take into accout of. I say to you, I certainly get irked at the same time as people consider issues that they just don’t realize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the highest and defined out the whole thing with no need side-effects , folks can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
I am really loving the theme/design of your web site. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility issues? A couple of my blog readers have complained about my site not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any advice to help fix this problem?
You are a very smart individual!
Hello. impressive job. I did not expect this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you¦ve on this blog. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What a perfect website.
I am perpetually thought about this, thanks for putting up.
Good write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
What i do not understood is in reality how you are now not really a lot more smartly-liked than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You understand thus considerably with regards to this subject, produced me for my part believe it from so many various angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated until it is one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs excellent. Always care for it up!
There is perceptibly a lot to realize about this. I consider you made certain nice points in features also.
so much great information on here, : D.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you’ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What an ideal website.
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed! Very helpful information specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was seeking this certain info for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
I like this blog very much, Its a very nice billet to read and obtain info . “Oregano is the spice of life.” by Henry J. Tillman.
I’d constantly want to be update on new blog posts on this internet site, bookmarked! .
Outstanding post, I believe website owners should larn a lot from this web site its rattling user pleasant.
Enjoyed examining this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “It requires more courage to suffer than to die.” by Napoleon Bonaparte.
You have brought up a very good points, regards for the post.
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented in your post. They are really convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are very short for novices. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
I do consider all the ideas you’ve presented for your post. They are very convincing and will certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are very brief for beginners. Could you please prolong them a bit from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
I wanted to write you that little remark in order to thank you so much over again for these lovely methods you have discussed on this site. It’s certainly strangely open-handed with you to give unhampered all some people could have made available for an ebook in making some cash on their own, chiefly given that you could possibly have done it in the event you wanted. Those good tips as well worked to become a fantastic way to comprehend other people online have the identical keenness just like my personal own to find out a good deal more with reference to this issue. I am sure there are thousands of more enjoyable instances ahead for individuals that read carefully your site.
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such great info being shared freely out there.
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write in relation to here. Again, awesome site!
Can I simply say what a aid to search out somebody who truly is aware of what theyre speaking about on the internet. You definitely know the way to bring an issue to mild and make it important. More people have to read this and perceive this aspect of the story. I cant consider youre no more widespread since you positively have the gift.
Hello there, I found your web site via Google while searching for a related topic, your web site came up, it looks great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
This really answered my problem, thank you!
I’m still learning from you, while I’m trying to achieve my goals. I definitely love reading all that is written on your website.Keep the stories coming. I liked it!
I?¦ve recently started a web site, the info you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
My partner and I stumbled over here from a different website and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to going over your web page yet again.
Thank you a lot for sharing this with all people you actually know what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Please additionally discuss with my website =). We will have a link exchange contract among us!
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch as I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include approximately all important infos. I’d like to peer extra posts like this .
Pretty component of content. I simply stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to say that I acquire actually loved account your weblog posts. Any way I will be subscribing for your augment and even I success you get entry to consistently rapidly.
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same results.
I think this is among the most significant information for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But wanna remark on few general things, The website style is ideal, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
Respect to author, some fantastic information .
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was once a enjoyment account it. Look advanced to far introduced agreeable from you! However, how could we keep up a correspondence?
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyway, just wanted to say superb blog!
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I cherished up to you’ll receive performed right here. The cartoon is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you would like be handing over the following. sick indubitably come further formerly once more since precisely the similar nearly a lot continuously within case you shield this hike.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thank you, I¦ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?
Some genuinely interesting information, well written and broadly speaking user pleasant.
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
Great write-up, I am regular visitor of one’s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Hey there, You’ve done an excellent job. I’ll definitely digg it and individually suggest to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this web site.
I like this weblog so much, saved to fav.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on most of the subjects you write with regards to here. Again, awesome weblog!