UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 18th May 2025
Understanding Failure Modes in Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries

Why in News?
A new study published in Science reveals that dendritic failure in solid-state Li-ion batteries (SSBs) is linked to mechanical fatigue, a principle long known in material science. This finding is significant for improving the longevity, safety, and reliability of next-generation batteries.
Key Highlights
- Solid-state batteries (SSBs) use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid, offering higher energy density and safety.
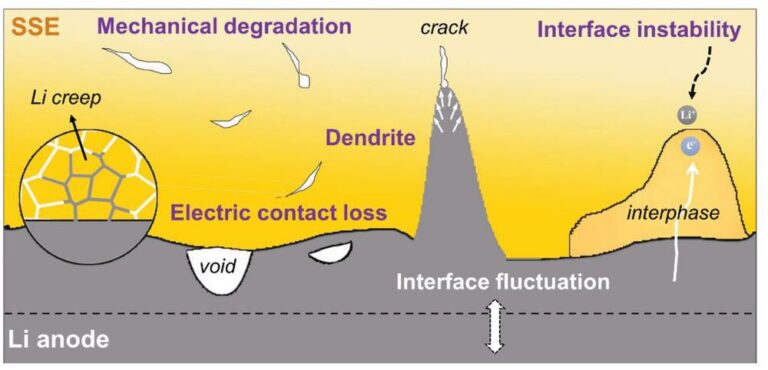
- Researchers observed that microscopic lithium dendrites, resembling plant roots, grow into the solid electrolyte during repeated charging/discharging cycles.
- The failure arises not from high current but from mechanical fatigue due to cyclic stress on the lithium anode.
- Operando scanning electron microscopy helped visualize dendrite formation in real-time.
- The battery short-circuited at the 145th cycle due to void formation and electrolyte fracture—even under minimal current.
- Implications include more sophisticated battery failure models and better design for durable energy storage systems.
What Are Solid-State Li-ion Batteries?
- SSBs use ceramic or solid polymer electrolytes in place of flammable liquid electrolytes.
- Used in pacemakers, smartwatches, and under development for electric vehicles (EVs) and grid storage.
- Advantages:
- Safer (non-flammable).
- Lighter and more energy dense.
- Lower risk of leakage or thermal runaway.
Key Failure Mechanism: Dendritic Growth
- Lithium ions get deposited unevenly at the anode during charging.
- Filament-like dendrites grow and penetrate the solid electrolyte.
- Result: Internal short-circuit, leading to rapid failure of the cell.
- Fatigue caused by repeated cycling even at low currents causes structural weaknesses.
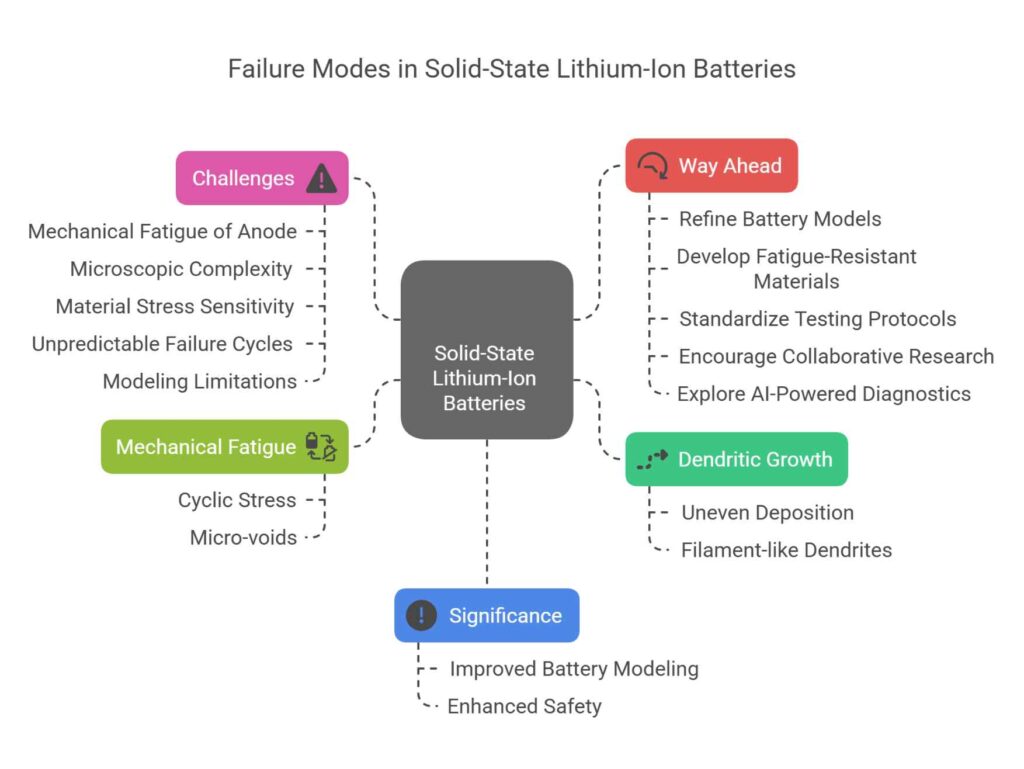
Challenges Identified
- Mechanical Fatigue of Anode:
- Analogous to bending a wire until it breaks.
- Lithium stripping and plating cycles cause micro-voids, slip bands, and cracks.
- Microscopic Complexity:
- Dendrites are invisible to the naked eye, making early detection difficult.
- Operando microscopy is needed to observe real-time interface evolution.
- Material Stress Sensitivity:
- Solid electrolytes are brittle and crack under volume changes or stress.
- No standard method yet to counter lithium’s stress-strain behavior under varied temperatures.
- Unpredictable Failure Cycles:
- Short-circuiting can occur without warning even under safe current limits.
- Modeling Limitations:
- Existing battery degradation models do not fully account for mechanical fatigue effects.
- Lack of integrated electro-chemo-mechanical models limits predictive capability.
Significance
- A breakthrough in understanding why SSBs fail even at low power settings.
- Will guide next-generation battery modeling, design, and predictive diagnostics.
- Can boost the safety and adoption of SSBs in sectors like EVs and aerospace.
India-Specific Impact
- Boost to EV and Energy Storage R&D
- India is pushing battery innovation under FAME-II, PLI Scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell Batteries, and National Electric Mobility Mission Plan.
- Indian institutions like IISc Bengaluru and IITs are actively involved in SSB research.
- The findings can help Indian startups and research centres develop more durable batteries, reducing EV recall and performance issues.
- Local Manufacturing and Make-in-India Goals
- With plans for gigafactories, understanding failure mechanisms is critical for local cell assembly.
- Can reduce dependency on imported battery designs that may not suit India’s temperature and usage conditions.
- Improved Battery Standards and Certification
- BIS and other regulatory bodies can revise battery certification norms based on fatigue-informed models.
- Critical for applications in high-risk environments like defense and aviation.
- Grid-Scale Renewable Integration
- India’s solar and wind sectors need reliable, long-life storage solutions.
- Fatigue-resistant SSBs can enable off-grid and hybrid mini-grid projects in rural and remote regions.
Way Ahead
- Refine battery models to incorporate lithium’s fatigue behavior under cyclic stress and temperature variation.
- Develop fatigue-resistant electrode materials and flexible electrolytes.
- Standardize microscopy-based testing protocols during SSB design.
- Encourage collaborative research in electro-mechanical modeling of batteries.
- Explore AI-powered diagnostics for early detection of dendritic growth and fatigue damage.
Conclusion
The discovery linking dendritic failure in SSBs to mechanical fatigue marks a paradigm shift in battery research. While manufacturing changes may remain limited, this insight is crucial for building longer-lasting, safer, and more efficient solid-state batteries—critical for India’s push toward EV adoption, renewable storage, and energy security.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in

