UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 22nd July 2025
Impeachment Motion Submitted Against Justice Yashwant Varma

Why in News?
- 145 MPs from both Houses submit impeachment motion against Justice Yashwant Varma under the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.

Introduction
- 145 Members of the Lok Sabha and 63 Members of the Rajya Sabha, cutting across party lines, submitted a motion seeking the removal of Justice Yashwant Varma, a sitting judge of the Allahabad High Court and former judge of the Delhi High Court.
- The action follows serious allegations of misconduct involving the discovery of large sums of currency notes at his official residence after a fire incident on March 14, 2025.
- The motion invokes provisions of the Constitution of India and the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968, marking a rare instance of Parliament initiating judicial accountability proceedings against a sitting High Court judge.
Background for the impeachment motion:
- Justice Yashwant Varma came under scrutiny after wads of currency notes were reportedly found at his official residence when a fire broke out on March 14.
- A Supreme Court-appointed panel examined the incident and found credence in the allegations.
Constitutional and Statutory Provisions:
- Articles of the Constitution:
- Article 124(4): Pertains to the removal of judges of the Supreme Court, but is also applicable by procedure to High Court judges under Article 217.
- Article 217(1)(b): Specifies that a High Court judge can only be removed by the President on grounds of proved misbehaviour or incapacity, following a procedure similar to Article 124(4).
- Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968:
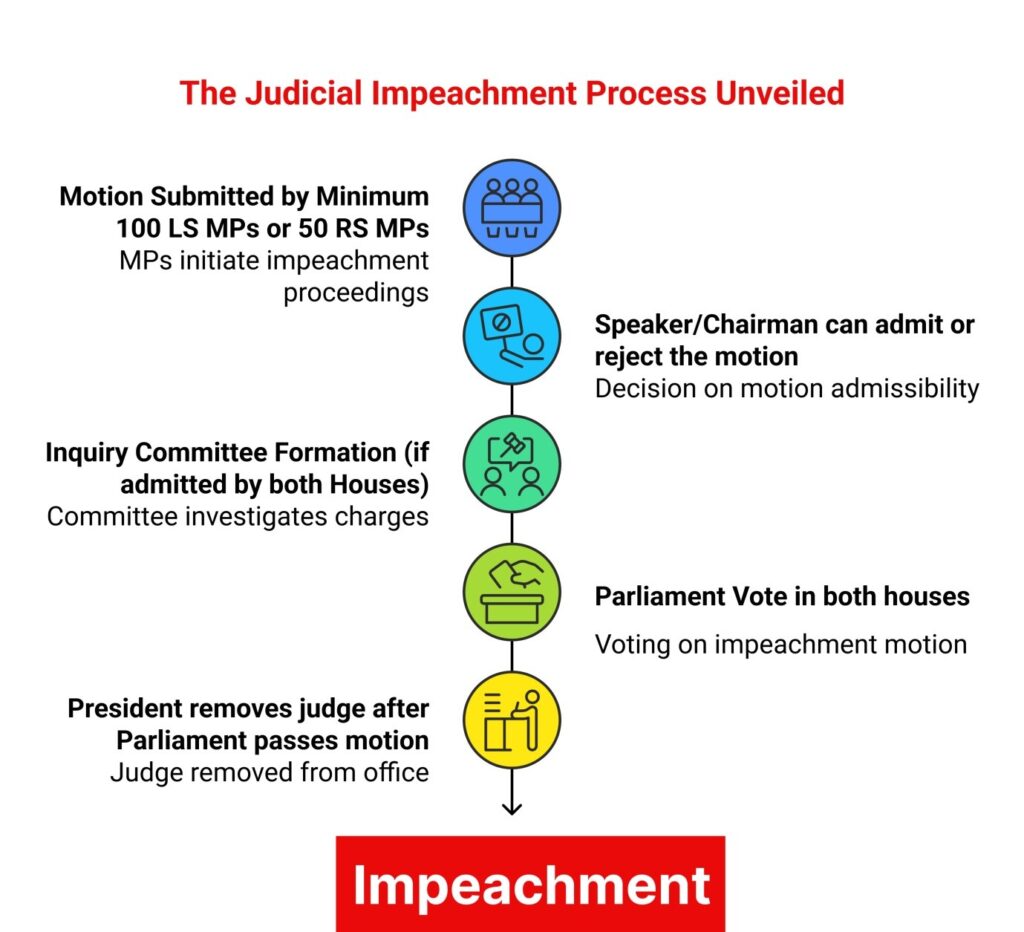
- Section 3(1)(b): A motion for removal must be signed by at least 100 members of the Lok Sabha or 50 members of the Rajya Sabha.
- The Presiding Officer (Speaker or Chairman) has the discretion to admit or reject the motion.
- If admitted, a three-member inquiry committee is formed comprising:
- One judge of the Supreme Court
- One Chief Justice of a High Court
- One eminent jurist
- The committee investigates the charges and submits a report to the respective House(s).
- If both Houses pass the motion by a special majority (majority of total membership and two-thirds of members present and voting), the judge can be removed by the President of India.

Important Procedural Provision:
- As per the Judges (Inquiry) Act, if motions for removal are submitted in both Houses on the same day, no inquiry committee shall be formed unless both Houses admit the motion.
- In the current case, this condition is met since both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha received the motion on July 21, 2025.
Current Developments:
- Rajya Sabha Chairman Jagdeep Dhankhar confirmed receipt of the motion, noting that it satisfies the numerical threshold under Article 217(1)(b) and the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
- Union Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal confirmed that more than 100 Lok Sabha members had also signed the motion.
- Dhankhar cited the relevant provisions and stated that the Secretary General of Rajya Sabha will take the next procedural steps under the law.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

