UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 05th April 2025
India at 6th BIMSTEC Summit: Reinforces Role in Regional Cooperation
Why in News?
- At the 6th BIMSTEC Summit held in Bangkok in April 2025, India unveiled a broad set of initiatives to enhance cooperation across digital infrastructure, energy connectivity, trade in local currencies, maritime security, and human development.
- These initiatives reflect India’s deepening commitment to regionalism in the Bay of Bengal region, especially through multilateral platforms like BIMSTEC, in contrast to the limitations faced by SAARC.
Historical Background of BIMSTEC
- BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) was established in 1997, originally as BIST-EC, comprising Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- It was renamed BIMST-EC with the inclusion of Myanmar in 1997, and later became BIMSTEC with the entry of Nepal and Bhutan in 2004.
- The grouping connects South Asia and Southeast Asia, and its focus areas include trade, connectivity, energy, environment, disaster management, public health, and agriculture.
India–BIMSTEC Relations
- India has played a leading role in revitalising BIMSTEC, particularly after the suspension of SAARC activities post-2016 due to geopolitical tensions.
- India sees BIMSTEC as a vehicle to:
- Advance its Neighbourhood First and Act East policies.
- Promote regional integration and connectivity in the Bay of Bengal.
- Counterbalance China’s maritime and infrastructure presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Over the years, India has hosted and supported numerous BIMSTEC meetings, contributed significantly to institutional reforms, and pushed for charter finalisation, which came into force in 2024.
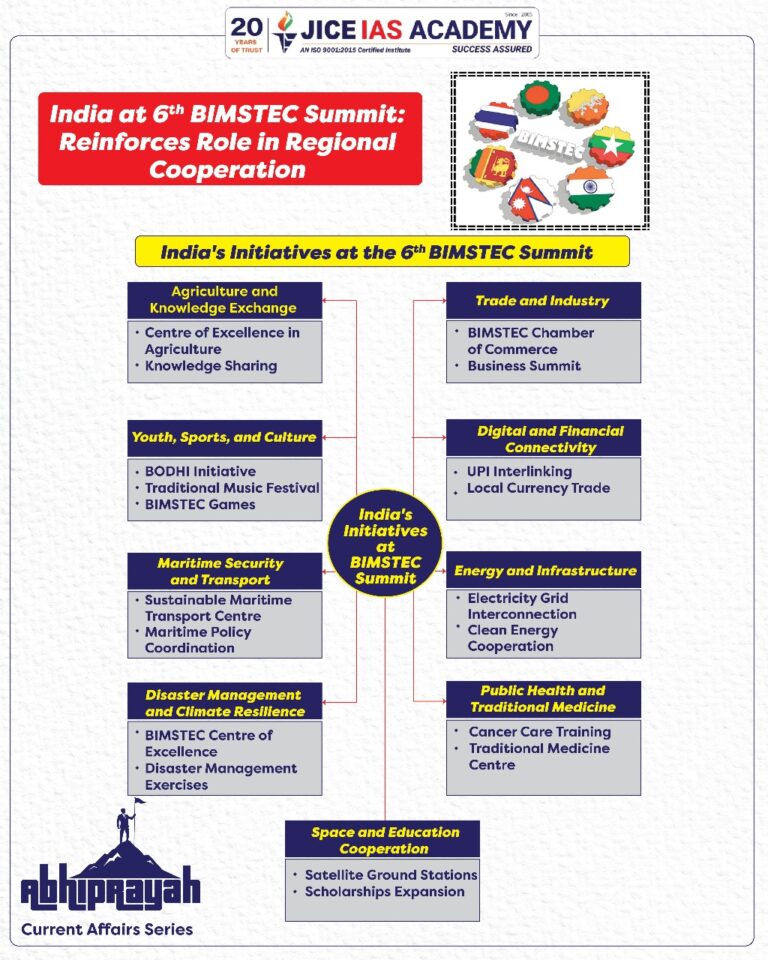
Key Initiatives Announced at the 6th BIMSTEC Summit
- Digital and Financial Connectivity
- India proposed the interlinking of its Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the payment systems of other BIMSTEC nations to boost cross-border trade and tourism.
- A feasibility study for local currency trade among member states was proposed to reduce reliance on external currencies.
- Energy and Infrastructure
- Accelerated work was proposed on regional electricity grid interconnection to facilitate power trade.
- Plans to set up a BIMSTEC Energy Centre and develop clean energy cooperation were discussed.
- Maritime Security and Transport
- India proposed a Sustainable Maritime Transport Centre to coordinate maritime policy, capacity building, and security cooperation in the Bay of Bengal.
- Disaster Management and Climate Resilience
- Proposal to establish a BIMSTEC Centre of Excellence for Disaster Management in India.
- India will host the fourth BIMSTEC disaster management joint exercise later this year.
- Public Health and Traditional Medicine
- India committed to training cancer care professionals and proposed a Centre of Excellence for Traditional Medicine for regional cooperation.
- Agriculture and Knowledge Exchange
- A Centre of Excellence in Agriculture was proposed to support capacity-building, knowledge sharing, and innovation in the farming sector.
- Trade and Industry
- Establishment of a BIMSTEC Chamber of Commerce and an annual Business Summit to enhance private sector engagement.
- Space and Education Cooperation
- Proposed satellite ground stations, nano-satellite development, and remote sensing data sharing.
- Expansion of scholarships at Indian institutions and annual training for young diplomats from BIMSTEC countries.
- Youth, Sports, and Culture
- Launch of the BODHI initiative for skill development (training 300 BIMSTEC youth annually).
- Hosting of a Traditional Music Festival, Young Leaders Summit, and BIMSTEC Hackathon.
- India will also host the BIMSTEC Athletics Meet in 2025 and the first BIMSTEC Games in 2027 to mark the group’s 30th anniversary.
Challenges Facing BIMSTEC
- Inconsistent political will and slow implementation of decisions have hindered momentum.
- Resource constraints and lack of a permanent secretariat with strong capacity affect operational efficiency.
- Security concerns, especially regarding China’s rising influence in Myanmar and Sri Lanka, require a delicate balance among members.
- Differing development levels and priorities across member states make consensus-building complex.
BIMSTEC vs SAARC: A Comparison
|
Aspect |
BIMSTEC |
SAARC |
|
Established |
1997 |
1985 |
|
Members |
7 (Excludes Pakistan) |
8 (Includes Pakistan) |
|
Focus Areas |
Connectivity, trade, energy, security |
Broad, but mostly economic and social |
|
India’s Role |
Proactive and leading |
Stalled due to tensions with Pakistan |
|
Meetings Held |
Increasing post-2016 |
Inactive since 2014 summit |
|
Geo-focus |
Bay of Bengal – South & Southeast Asia |
South Asia only |
|
Effectiveness |
Growing relevance |
Largely dormant |
India views BIMSTEC as a more action-oriented alternative to SAARC, free from political gridlock.
Significance
- The summit reflected India’s strategic focus on functional regionalism, maritime cooperation, and digital integration.
- Through BIMSTEC, India aims to build a secure, connected, and prosperous Bay of Bengal region, reinforcing its role as a net security provider and development partner.
- India’s proposals signal an effort to institutionalise BIMSTEC mechanisms, make it a platform for inclusive growth, and ensure that connectivity is holistic – physical, digital, energy, and cultural.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in



Yay google is my world beater assisted me to find this outstanding internet site! .
8pvybh
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your blog. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility issues? A few of my blog visitors have complained about my site not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any suggestions to help fix this problem?
Hello! This post could not be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this post to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
I got what you mean , thankyou for putting up.Woh I am delighted to find this website through google.
Nice read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing some research on that. And he just bought me lunch as I found it for him smile Therefore let me rephrase that: Thanks for lunch!
Keep working ,remarkable job!
I consider something really interesting about your web blog so I saved to fav.
I in addition to my pals appeared to be reading through the nice guides located on the blog and all of the sudden developed an awful suspicion I never thanked the web site owner for those secrets. My ladies were absolutely passionate to read all of them and now have very much been making the most of these things. Appreciate your really being so considerate as well as for obtaining this kind of ideal subject areas most people are really eager to discover. Our honest regret for not expressing appreciation to earlier.
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I’m quite certain I will learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I think that is one of the such a lot vital information for me. And i am satisfied studying your article. But wanna remark on few general things, The website taste is great, the articles is truly great : D. Just right activity, cheers
Somebody essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your website page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular publish amazing. Fantastic job!
Outstanding post, I think people should learn a lot from this weblog its really user genial.
I truly enjoy reading through on this website, it contains fantastic articles. “Never fight an inanimate object.” by P. J. O’Rourke.
Some genuinely interesting details you have written.Helped me a lot, just what I was searching for : D.
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is excellent, let alone the content!
Hi! This post could not be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Today, while I was at work, my sister stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched all over the place and simply could not come across. What a perfect web-site.
Hmm it appears like your blog ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to everything. Do you have any points for inexperienced blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d most certainly donate to this brilliant blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to brand new updates and will share this site with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
Magnificent goods from you, man. I have have in mind your stuff previous to and you are simply extremely magnificent. I really like what you’ve received right here, really like what you’re saying and the best way in which you assert it. You make it enjoyable and you continue to take care of to stay it sensible. I cant wait to learn much more from you. That is really a terrific web site.
I couldn’t resist commenting
You made some good points there. I looked on the internet for the issue and found most persons will go along with with your website.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & aid other users like its aided me. Good job.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
Thanks for some other informative web site. The place else may I am getting that type of information written in such an ideal way? I have a challenge that I am simply now running on, and I’ve been on the look out for such information.
Definitely believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
Nice blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your design. Appreciate it
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
Enjoyed reading through this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “To be positive To be mistaken at the top of one’s voice.” by Ambrose Bierce.
Some really nice and useful info on this internet site, as well I believe the design and style has got great features.
Thankyou for this terrific post, I am glad I found this site on yahoo.
As I website owner I believe the written content here is really superb, thankyou for your efforts.
It is in reality a great and helpful piece of information. I’m glad that you just shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
What i don’t realize is if truth be told how you are now not really a lot more neatly-appreciated than you might be right now. You’re so intelligent. You know thus considerably in terms of this subject, made me in my opinion believe it from a lot of various angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be interested except it?¦s one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. All the time take care of it up!
Greetings from Florida! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to browse your site on my iphone during lunch break. I love the knowledge you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, excellent site!
As a Newbie, I am permanently browsing online for articles that can benefit me. Thank you
I¦ve recently started a site, the info you provide on this website has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
You can definitely see your enthusiasm in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe. Always go after your heart. “There are only two industries that refer to their customers as users.” by Edward Tufte.
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
Very interesting points you have mentioned, thankyou for putting up. “I love acting. It is so much more real than life.” by Oscar Wilde.
Great post. I am facing a couple of these problems.
I have recently started a site, the information you provide on this site has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work. “The achievements of an organization are the results of the combined effort of each individual.” by Vince Lombardi.
Great blog here! Also your website loads up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
I¦ve been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or weblog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website. Studying this info So i¦m happy to convey that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I such a lot indisputably will make certain to don¦t overlook this website and provides it a look regularly.
I wish to get across my appreciation for your generosity giving support to persons who need assistance with this important niche. Your very own commitment to getting the solution all around appears to be definitely productive and have constantly helped employees just like me to reach their ambitions. Your entire valuable guidelines implies much a person like me and still more to my peers. With thanks; from each one of us.
You are my intake, I possess few web logs and often run out from to brand : (.
Hello.This post was really fascinating, especially since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last couple of days.
Hello There. I discovered your blog the use of msn. That is an extremely smartly written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to learn extra of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll definitely comeback.
It’s really a cool and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your website in internet explorer, may check this… IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a huge component to folks will miss your fantastic writing due to this problem.
You really make it appear really easy along with your presentation however I to find this matter to be actually one thing which I believe I would never understand. It kind of feels too complex and extremely wide for me. I’m having a look ahead on your next post, I will try to get the hold of it!
Thank you for another great post. Where else could anybody get that type of information in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such information.
I was wondering if you ever thought of changing the page layout of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or two images. Maybe you could space it out better?
Very interesting details you have observed, appreciate it for posting. “Pleasure and love are the pinions of great deeds.” by Charles Fox.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
There is apparently a bundle to know about this. I assume you made various good points in features also.
Great website. A lot of helpful information here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thank you to your sweat!
Enjoyed reading through this, very good stuff, thanks.
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing on your feeds and even I success you access persistently quickly.
You could certainly see your skills in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe. At all times follow your heart. “Everyone has his day and some days last longer than others.” by Sir Winston Leonard Spenser Churchill.
You can definitely see your enthusiasm within the paintings you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe. All the time go after your heart. “What power has law where only money rules.” by Gaius Petronius.
naturally like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality then again I will certainly come back again.
Dead indited articles, Really enjoyed reading.
Simply want to say your article is as astounding. The clearness to your put up is simply great and i can suppose you are a professional in this subject. Fine together with your permission let me to snatch your feed to stay up to date with impending post. Thank you one million and please keep up the rewarding work.
I view something really special in this site.
I see something truly special in this website.
I really like studying and I believe this website got some really useful stuff on it! .
Regards for helping out, good information.
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thank you However I am experiencing problem with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting similar rss problem? Anybody who is aware of kindly respond. Thnkx
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with useful information to work on. You’ve performed an impressive job and our entire group will likely be thankful to you.
Have you heard about ThyraFemme Balance? This natural supplement is becoming a sensation among women worldwide because it provides a real, safe, and natural solution for those struggling with hormonal imbalance, slow metabolism, weight gain, fatigue, and lack of energy.
You are a very smart individual!
Flash Burn is a revolutionary natural supplement that has been transforming the lives of thousands of people struggling with excess weight. Developed with a 100 natural and scientifically proven formula
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
I think other website proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and wonderful user genial style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Great – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I am not sure the place you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend a while studying much more or figuring out more. Thanks for fantastic info I was in search of this info for my mission.
I like the valuable information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite sure I’ll learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I like this website because so much utile material on here : D.
of course like your website however you have to test the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very troublesome to inform the truth then again I will certainly come again again.
Thank you for another informative website. Where else could I get that type of info written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
Hello there, You have done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this website.
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Terrific work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the internet. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
Hey! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a team of volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us beneficial information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
Thankyou for this marvellous post, I am glad I discovered this web site on yahoo.
My partner and I stumbled over here from a different web address and thought I may as well check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking into your web page repeatedly.
Terrific work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the internet. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Howdy would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re working with? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good internet hosting provider at a honest price? Cheers, I appreciate it!
wonderful post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You should continue your writing. I’m confident, you’ve a great readers’ base already!
I?¦ve recently started a website, the information you provide on this web site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I just like the helpful info you provide for your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and check again right here frequently. I’m quite sure I will be informed a lot of new stuff proper right here! Good luck for the next!
We are a gaggle of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with helpful info to paintings on. You have done a formidable job and our entire community will be thankful to you.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?
I was suggested this web site by way of my cousin. I am not sure whether or not this publish is written via him as nobody else know such certain about my trouble. You are amazing! Thanks!
Some truly nice and useful information on this site, too I think the style holds superb features.
It’s really a nice and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you simply shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I’d forever want to be update on new posts on this web site, saved to fav! .
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and checking back frequently!
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I came across this board and I find It truly helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to provide something back and help others such as you helped me.
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, thankyou.
Pretty great post. I simply stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve really loved surfing around your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing in your feed and I’m hoping you write once more soon!
I was more than happy to seek out this web-site.I needed to thanks for your time for this wonderful learn!! I undoubtedly having fun with each little little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you blog post.
I like this web blog so much, bookmarked.
I like the valuable info you supply in your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and take a look at once more right here regularly. I am slightly sure I will be informed plenty of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the following!
It¦s actually a great and useful piece of info. I¦m happy that you shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Im no longer positive where you are getting your information, however great topic. I must spend some time learning more or figuring out more. Thanks for great information I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
Hello. remarkable job. I did not expect this. This is a great story. Thanks!
This really answered my drawback, thanks!
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was wondering what all is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet smart so I’m not 100 certain. Any suggestions or advice would be greatly appreciated. Cheers
Thanks for all your efforts that you have put in this. very interesting info .
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
I am continually invstigating online for tips that can benefit me. Thx!
very nice post, i certainly love this website, keep on it
I’m still learning from you, but I’m trying to achieve my goals. I certainly enjoy reading everything that is written on your blog.Keep the aarticles coming. I liked it!
I am not real excellent with English but I get hold this really leisurely to interpret.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you actually know what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Please also visit my website =). We could have a link exchange contract between us!
Wow! Thank you! I continuously wanted to write on my site something like that. Can I take a portion of your post to my blog?
I precisely desired to thank you so much once more. I am not sure the things I would have undertaken in the absence of the actual strategies provided by you concerning my subject. It has been a frightful crisis in my view, however , coming across this specialized way you dealt with the issue forced me to cry for gladness. I am just thankful for this assistance and then pray you know what a great job that you’re carrying out instructing many others through a web site. Most likely you’ve never met any of us.
naturally like your website but you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very bothersome to inform the reality nevertheless I’ll certainly come back again.
You are my inhalation, I have few web logs and rarely run out from brand :). “No opera plot can be sensible, for people do not sing when they are feeling sensible.” by W. H. Auden.
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, thankyou.
Very good written article. It will be supportive to everyone who utilizes it, including me. Keep doing what you are doing – can’r wait to read more posts.
Terrific work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the internet. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
I have not checked in here for some time since I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I?¦ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
I believe this website has got some real superb information for everyone :D. “Time–our youth–it never really goes, does it It is all held in our minds.” by Helen Hoover Santmyer.
of course like your website but you need to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to inform the truth on the other hand I?¦ll certainly come again again.
What i do not understood is in reality how you’re now not actually much more smartly-favored than you may be right now. You are so intelligent. You recognize therefore significantly with regards to this matter, produced me individually believe it from numerous varied angles. Its like women and men are not interested until it is something to do with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs excellent. All the time care for it up!
I reckon something truly special in this site.
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The words in your post seem to be running off the screen in Chrome. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know. The design look great though! Hope you get the problem solved soon. Cheers
I think this is one of the most vital information for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But wanna remark on some general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Therefore let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch! “For most of history, Anonymous was a woman.” by Virginia Woolf.
I loved up to you will receive carried out right here. The comic strip is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get got an edginess over that you want be delivering the following. unwell undoubtedly come more formerly again as exactly the same just about a lot ceaselessly inside case you shield this increase.
Whats up very nice website!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionally…I’m happy to seek out numerous helpful info right here in the submit, we need work out more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
I have to show some appreciation to the writer for bailing me out of this type of incident. After surfing around throughout the the net and seeing suggestions which are not pleasant, I assumed my entire life was done. Being alive minus the answers to the difficulties you have resolved by way of your entire article content is a serious case, as well as the ones that would have negatively affected my career if I hadn’t come across your blog. Your good competence and kindness in controlling every aspect was tremendous. I don’t know what I would have done if I had not encountered such a step like this. I’m able to at this moment relish my future. Thanks so much for the reliable and results-oriented guide. I won’t hesitate to recommend your web sites to anyone who requires counselling on this subject matter.
Absolutely indited written content, appreciate it for selective information.
I don’t unremarkably comment but I gotta admit appreciate it for the post on this great one : D.
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Rattling fantastic visual appeal on this site, I’d value it 10 10.
Hello there, just changed into aware of your blog thru Google, and located that it’s really informative. I’m gonna be careful for brussels. I’ll appreciate for those who proceed this in future. A lot of other folks will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Dead indited written content, Really enjoyed studying.
Some really nice and useful information on this site, as well I think the style and design contains wonderful features.
Thank you for all of the effort on this web site. Gloria takes pleasure in participating in investigation and it is obvious why. We know all concerning the lively medium you produce rewarding tips and tricks via this website and therefore boost participation from others on this concern while our own girl is always starting to learn a great deal. Take pleasure in the rest of the new year. You’re doing a very good job.
Have you ever thought about creating an ebook or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog centered on the same topics you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would value your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e-mail.
Merely a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great design and style. “Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not one bit simpler.” by Albert Einstein.
Good info and right to the point. I am not sure if this is really the best place to ask but do you people have any thoughts on where to employ some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
Have you ever thought about writing an e-book or guest authoring on other websites? I have a blog based upon on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my viewers would value your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
ekv2ry
Thank you, I have recently been looking for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
After examine a number of of the weblog posts in your website now, and I actually like your manner of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and shall be checking back soon. Pls take a look at my website as effectively and let me know what you think.
I am curious to find out what blog system you happen to be working with? I’m experiencing some small security issues with my latest website and I would like to find something more safe. Do you have any suggestions?
Can I just say what a relief to find someone who actually knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
Some genuinely superb blog posts on this web site, regards for contribution. “He that falls in love with himself will have no rivals.” by Benjamin Franklin.
Howdy just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same results.
Some truly nice and utilitarian info on this site, too I conceive the design and style contains wonderful features.
I conceive this web site contains some real great info for everyone : D.
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
I like this web site very much, Its a rattling nice place to read and find information.
I was just seeking this info for some time. After 6 hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your site. I wonder what’s the lack of Google strategy that don’t rank this type of informative web sites in top of the list. Usually the top sites are full of garbage.
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission.
Very interesting points you have noted, thanks for putting up. “Jive Lady Just hang loose blood. She gonna handa your rebound on the med side.” by Airplane.
fantastic post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector don’t notice this. You should continue your writing. I am sure, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
I’ve been browsing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will be much more useful than ever before.
I enjoy reading and I conceive this website got some truly useful stuff on it! .
As a Newbie, I am permanently searching online for articles that can help me. Thank you
Thank you for sharing with us, I conceive this website really stands out : D.
I liked as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The cartoon is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you wish be handing over the following. ill surely come further until now once more as exactly the similar just about very steadily within case you shield this hike.
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your website by accident, and I’m shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Definitely imagine that that you stated. Your favourite reason appeared to be at the internet the simplest factor to take into accout of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while other people consider issues that they just do not realize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the highest and outlined out the whole thing with no need side-effects , other people can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
You made some nice points there. I did a search on the theme and found nearly all persons will agree with your blog.
Glad to be one of the visitors on this awing web site : D.
I am glad to be one of many visitors on this outstanding web site (:, regards for putting up.
Some really nice and utilitarian information on this web site, besides I think the design and style has got excellent features.
Hey very cool website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also…I am happy to find so many useful information here in the post, we need develop more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
I got what you intend, thanks for putting up.Woh I am glad to find this website through google.
I enjoy your writing style really loving this internet site.
What i don’t understood is in fact how you’re not really a lot more well-liked than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You recognize therefore significantly in the case of this matter, made me individually believe it from a lot of various angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved until it’s one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs great. At all times handle it up!
of course like your web-site but you need to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth nevertheless I’ll definitely come back again.
Very interesting details you have noted, regards for putting up. “You can tell the ideas of a nation by it’s advertisements.” by Douglas South Wind.
Its like you read my thoughts! You seem to understand a lot approximately this, such as you wrote the e book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few percent to power the message house a little bit, but other than that, that is fantastic blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
Some really fantastic information, Sword lily I discovered this. “I try to avoid looking forward or backward, and try to keep looking upward.” by Charlotte Bronte.
Excellent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
Wow! Thank you! I always wanted to write on my blog something like that. Can I implement a part of your post to my website?
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I am glad to be one of many visitors on this great site (:, thanks for putting up.
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I have learn a few good stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you place to make any such wonderful informative website.
This design is incredible! You definitely know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
You made some decent points there. I did a search on the issue and found most guys will approve with your site.
I beloved as much as you’ll obtain carried out proper here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nevertheless, you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. in poor health definitely come further formerly again since exactly the same just about very incessantly within case you defend this increase.
I like what you guys are up too. Such smart work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my website 🙂
Great post, I conceive people should acquire a lot from this web site its very user friendly.
Very good blog you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any community forums that cover the same topics discussed here? I’d really love to be a part of community where I can get advice from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Thanks!
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is excellent, let alone the content!
Very interesting subject , thankyou for posting.
whoah this blog is fantastic i really like studying your articles. Keep up the great paintings! You know, lots of individuals are looking round for this information, you could aid them greatly.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
It is actually a nice and helpful piece of information. I’m happy that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Hey! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thank you again
I¦ve read several just right stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how so much effort you set to create this sort of fantastic informative site.
You got a very good website, Glad I found it through yahoo.
There are certainly a variety of particulars like that to take into consideration. That may be a great point to convey up. I offer the thoughts above as common inspiration but clearly there are questions like the one you carry up where the most important factor will probably be working in honest good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged around issues like that, but I’m sure that your job is clearly recognized as a fair game. Each girls and boys really feel the impression of just a second’s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
It’s exhausting to find knowledgeable individuals on this topic, however you sound like you know what you’re speaking about! Thanks
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Good write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s website, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d without a doubt donate to this outstanding blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will talk about this blog with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. However imagine if you added some great photos or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and videos, this site could undeniably be one of the greatest in its field. Good blog!
This really answered my problem, thank you!
Hello my loved one! I wish to say that this post is amazing, great written and include approximately all important infos. I¦d like to peer extra posts like this .
Glad to be one of the visitants on this awe inspiring site : D.
You have observed very interesting points! ps nice web site.
Thank you for some other wonderful post. The place else may just anybody get that type of information in such a perfect method of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such info.
There are definitely a whole lot of details like that to take into consideration. That may be a nice point to convey up. I supply the ideas above as normal inspiration but clearly there are questions just like the one you bring up the place a very powerful factor shall be working in trustworthy good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged round issues like that, however I’m certain that your job is clearly recognized as a fair game. Each boys and girls really feel the affect of only a second’s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
Well I sincerely liked studying it. This subject procured by you is very constructive for accurate planning.
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
Hi! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it tough to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any ideas or suggestions? Appreciate it
I precisely needed to thank you very much once more. I do not know the things that I would’ve carried out in the absence of the suggestions provided by you on such a area. It became a real scary situation in my opinion, but seeing the specialized form you dealt with that forced me to leap over delight. Now i am grateful for this assistance and pray you are aware of an amazing job you are always getting into educating men and women all through your websites. Most probably you’ve never encountered any of us.
Thank you for another excellent article. The place else could anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal means of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I’m on the look for such info.
What i do not understood is actually how you are now not really a lot more well-preferred than you might be now. You’re so intelligent. You know thus considerably with regards to this matter, produced me in my opinion believe it from numerous varied angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested until it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. Always deal with it up!
Good day! This post could not be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Very efficiently written information. It will be beneficial to everyone who employess it, as well as myself. Keep up the good work – i will definitely read more posts.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is excellent blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, thanks.
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and just couldn’t come across. What a perfect web site.
Hey there! I’ve been reading your site for a long time now and finally got the bravery to go ahead and give you a shout out from New Caney Tx! Just wanted to tell you keep up the fantastic job!
Magnificent web site. A lot of useful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks in your sweat!
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the work you write. The arena hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart.
It’s perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you few interesting things or advice. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I desire to read even more things about it!
Some genuinely fantastic info , Gladiolus I found this.
We stumbled over here coming from a different web address and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to finding out about your web page again.
Nice post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Very helpful info particularly the last part 🙂 I care for such information a lot. I was seeking this particular info for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
hello there and thank you for your information – I have definitely picked up something new from right here. I did however expertise some technical issues using this site, since I experienced to reload the website lots of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will very frequently affect your placement in google and could damage your quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my email and could look out for a lot more of your respective intriguing content. Ensure that you update this again very soon..
Only a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw outstanding pattern. “The price one pays for pursuing a profession, or calling, is an intimate knowledge of its ugly side.” by James Arthur Baldwin.
There are actually lots of details like that to take into consideration. That is a great point to convey up. I provide the ideas above as basic inspiration however clearly there are questions just like the one you convey up where crucial factor might be working in trustworthy good faith. I don?t know if finest practices have emerged around issues like that, but I am sure that your job is clearly identified as a fair game. Each boys and girls feel the impression of just a moment’s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
Thanks for ones marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed reading it, you may be a great author.I will make sure to bookmark your blog and will eventually come back sometime soon. I want to encourage yourself to continue your great posts, have a nice holiday weekend!
Simply desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is simply nice and that i can think you are a professional in this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to take hold of your feed to stay updated with approaching post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please continue the gratifying work.
You are my inspiration , I have few web logs and often run out from to brand.
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. But imagine if you added some great images or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this site could undeniably be one of the most beneficial in its field. Terrific blog!
Very interesting details you have remarked, regards for posting.
Hello this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding know-how so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Keep functioning ,splendid job!
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
I do consider all of the ideas you’ve presented for your post. They are really convincing and will certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too brief for beginners. May you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
I really like your writing style, great info, thank you for putting up :D. “Silence is more musical than any song.” by Christina G. Rossetti.
Good article and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but do you guys have any ideea where to hire some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is needed to get setup? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet smart so I’m not 100 positive. Any suggestions or advice would be greatly appreciated. Thanks
Great info and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is truly the best place to ask but do you folks have any thoughts on where to hire some professional writers? Thx 🙂
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
You should participate in a contest for among the best blogs on the web. I’ll advocate this website!
This is the suitable blog for anyone who needs to search out out about this topic. You understand a lot its virtually laborious to argue with you (not that I truly would want…HaHa). You positively put a brand new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, just great!
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
As soon as I observed this web site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
I am glad to be one of many visitors on this outstanding web site (:, appreciate it for putting up.
It?¦s really a nice and helpful piece of information. I?¦m glad that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
This really answered my drawback, thank you!
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for information about this subject for ages and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
Regards for this post, I am a big big fan of this website would like to keep updated.
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for posting. “It is well to give when asked but it is better to give unasked, through understanding.” by Kahlil Gibran.
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this site. Reading this info So i’m happy to convey that I’ve a very good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most certainly will make sure to don’t forget this site and give it a look on a constant basis.
Thanks for some other informative blog. The place else could I get that type of info written in such an ideal method? I have a challenge that I’m just now operating on, and I have been on the glance out for such info.
You made some nice points there. I looked on the internet for the topic and found most people will approve with your site.
I appreciate, cause I found exactly what I was looking for. You’ve ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
Hello there, You have done a great job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
wonderful points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you recommend in regards to your post that you made some days ago? Any positive?
This design is steller! You obviously know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Hi! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to take a look. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Outstanding blog and outstanding design and style.
Wohh precisely what I was looking for, thankyou for putting up.
obviously like your website however you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the reality then again I will surely come again again.
I’m no longer certain the place you are getting your info, however good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or figuring out more. Thanks for fantastic info I was searching for this info for my mission.
You can definitely see your enthusiasm in the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always follow your heart. “In order to preserve your self-respect, it is sometimes necessary to lie and cheat.” by Robert Byrne.
Aw, this was a really nice post. In thought I would like to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and under no circumstances seem to get one thing done.
Hello very cool web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also?KI am happy to find so many helpful information here in the post, we need work out extra techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. A great read. I will certainly be back.
Good write-up, I’m regular visitor of one’s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
Good – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, web site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
It?¦s really a nice and helpful piece of information. I am happy that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
I was reading through some of your blog posts on this internet site and I think this website is real instructive! Keep posting.
I’ve read a few good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much effort you put to make such a magnificent informative web site.
There’s noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made certain nice factors in options also.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue along with your web site in web explorer, could check this?K IE still is the market chief and a big component of folks will pass over your excellent writing because of this problem.
I went over this website and I believe you have a lot of superb information, saved to bookmarks (:.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What a perfect web-site.
Im no longer sure the place you’re getting your info, however great topic. I must spend a while learning much more or figuring out more. Thank you for magnificent information I used to be in search of this information for my mission.
Terrific work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the net. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
Hi my loved one! I wish to say that this article is amazing, great written and come with approximately all important infos. I?¦d like to peer more posts like this .
I beloved as much as you will receive carried out proper here. The caricature is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get got an edginess over that you want be delivering the following. sick unquestionably come more until now once more as exactly the similar just about very incessantly inside case you protect this increase.
Hmm it appears like your site ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any tips for rookie blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
I truly appreciate this post. I?¦ve been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again
You have brought up a very excellent points, thanks for the post.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely return.
you’ve got an amazing blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my weblog?
I am so happy to read this. This is the kind of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Have you ever considered creating an ebook or guest authoring on other websites? I have a blog based on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my audience would appreciate your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an email.
Hello! Quick question that’s totally off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks weird when viewing from my apple iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this problem. If you have any recommendations, please share. Thanks!
Needed to put you the very little word so as to thank you over again for your personal magnificent views you have shared at this time. This is simply extremely generous with you to make unhampered what exactly a lot of people could possibly have advertised for an ebook to get some dough for their own end, and in particular seeing that you might well have done it in the event you considered necessary. These creative ideas additionally acted to be the fantastic way to be sure that other individuals have the same zeal like my own to figure out significantly more with respect to this issue. I believe there are many more fun occasions in the future for individuals who check out your blog.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I like this web site its a master peace ! Glad I observed this on google .
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
I’ve learn a few excellent stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much effort you put to create this sort of excellent informative website.
What i do not realize is if truth be told how you’re now not really much more well-liked than you may be now. You are so intelligent. You already know thus significantly with regards to this matter, produced me for my part imagine it from so many varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t interested unless it is one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs nice. Always deal with it up!
I have been examinating out some of your stories and i can state pretty clever stuff. I will surely bookmark your blog.
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last few posts have been kinda boring?K I miss your tremendous writings. Past few posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
Rattling nice layout and excellent content, nothing else we want : D.
You are a very smart individual!
I really appreciate your work, Great post.
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for posting.
I just like the helpful information you provide on your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and check once more here regularly. I am fairly sure I’ll be informed many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the following!
What i do not realize is in truth how you’re not actually a lot more well-favored than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You know therefore significantly in relation to this topic, produced me in my opinion consider it from numerous numerous angles. Its like women and men aren’t interested until it is something to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs great. At all times care for it up!
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what blog owners wrote but this internet site is very user pleasant! .
What i do not understood is actually how you’re not really much more well-liked than you may be now. You are very intelligent. You realize therefore considerably relating to this subject, produced me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs great. Always maintain it up!
Attractive element of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to say that I get in fact enjoyed account your weblog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing for your augment and even I fulfillment you access persistently quickly.
Admiring the dedication you put into your website and in depth information you offer. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material. Fantastic read! I’ve saved your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
I’d forever want to be update on new articles on this web site, saved to bookmarks! .
Of course, what a splendid site and illuminating posts, I definitely will bookmark your site.Have an awsome day!
I will right away grab your rss feed as I can not find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
I am continually looking online for tips that can aid me. Thank you!
I’ve been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
You made a few nice points there. I did a search on the matter and found a good number of folks will consent with your blog.
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my site 🙂
Incredible! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a completely different topic but it has pretty much the same layout and design. Wonderful choice of colors!
I do not even know how I finished up here, but I thought this put up was great. I don’t recognize who you’re however certainly you’re going to a famous blogger when you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this site. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s challenging to get that “perfect balance” between usability and appearance. I must say you have done a excellent job with this. In addition, the blog loads very quick for me on Opera. Exceptional Blog!
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is just excellent and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the gratifying work.
It was a pleasure to read. I shared it with a friend who was researching the same topic, and he was so appreciative that he treated me to lunch as a thank-you! So, I want to extend my gratitude once again.
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
You raised some excellent points. After conducting my own research, I discovered that most people agree with the insights shared in your blog.
Your contributions are truly remarkable, and our entire community is immensely grateful for your work.
My team and I are volunteers launching a new initiative in our community, and your website has been an invaluable resource for us. Your dedication is inspiring, and our entire community deeply appreciates your efforts.
My team and I are volunteers launching a new initiative in our community, and your website has been an invaluable resource for us. Your dedication is truly inspiring, and our entire community deeply appreciates your efforts.
We are a group of volunteers launching a new initiative in our community, and your website has been an indispensable resource. Your contributions are truly remarkable, and our entire community is immensely grateful for your work.
I deeply value the information in your articles. I’ve bookmarked your site and look forward to returning often, confident that I’ll continue gaining meaningful knowledge from your content. Wishing you continued success in all your future endeavors!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and checking back frequently!
I conceive this site has got some very fantastic info for everyone. “The fewer the words, the better the prayer.” by Martin Luther.
Thank you for some other informative blog. The place else may just I get that type of information written in such an ideal method? I’ve a project that I’m just now operating on, and I’ve been on the glance out for such info.
Hello.This article was extremely interesting, particularly since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Thursday.
You made a few good points there. I did a search on the subject and found mainly persons will go along with with your blog.
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
I keep listening to the news bulletin speak about getting boundless online grant applications so I have been looking around for the most excellent site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i find some?
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..more wait .. …
Great line up. We will be linking to this great article on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I am not positive where you are getting your information, but good topic. I must spend some time finding out more or figuring out more. Thanks for great information I used to be on the lookout for this info for my mission.
I consider something genuinely special in this internet site.
Hello. remarkable job. I did not anticipate this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
Together with the whole thing that appears to be building throughout this specific subject material, your opinions are actually fairly radical. Having said that, I am sorry, because I do not subscribe to your whole strategy, all be it exhilarating none the less. It looks to everyone that your remarks are not completely validated and in fact you are generally your self not thoroughly confident of your argument. In any event I did enjoy reading it.
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
What i don’t understood is in fact how you are now not actually much more neatly-appreciated than you may be now. You are very intelligent. You already know therefore significantly in relation to this subject, made me for my part believe it from so many numerous angles. Its like men and women are not interested unless it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs excellent. At all times care for it up!
I¦ve recently started a site, the info you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
I like the valuable info you supply for your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check once more here frequently. I am slightly sure I will learn plenty of new stuff proper here! Best of luck for the following!
Real superb info can be found on blog.
It¦s truly a great and helpful piece of info. I¦m glad that you simply shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Do you have a spam problem on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have created some nice methods and we are looking to trade techniques with other folks, why not shoot me an e-mail if interested.
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my site :).
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your web site by accident, and I am shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Some really prize articles on this web site, saved to my bookmarks.
There’s noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain good points in options also.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Sweet website , super style and design, very clean and use genial.
Pretty nice post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to mention that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing for your feed and I am hoping you write once more soon!
I really like your writing style, superb info , regards for putting up : D.
I do agree with all of the ideas you have presented in your post. They’re really convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too short for starters. Could you please extend them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
I got what you mean ,saved to fav, very decent web site.
Hello.This post was extremely remarkable, particularly because I was looking for thoughts on this subject last Friday.
Helpful information. Fortunate me I found your website by chance, and I’m stunned why this accident did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
8j31f9
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My blog covers a lot of the same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Great blog by the way!
o60oi7
I went over this website and I conceive you have a lot of good info, saved to bookmarks (:.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
I’m no longer positive where you’re getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or figuring out more. Thank you for excellent information I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
hey there and thanks on your info – I have certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did on the other hand experience some technical points using this site, as I skilled to reload the site many times prior to I could get it to load properly. I had been brooding about if your web hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading circumstances instances will sometimes have an effect on your placement in google and could injury your quality score if ads and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I am including this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot extra of your respective fascinating content. Make sure you replace this once more very soon..
Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.net.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
Good ?V I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task..
Wohh precisely what I was looking for, thanks for posting.
What’s Taking place i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It positively useful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & help other users like its aided me. Good job.
Woh I love your blog posts, saved to favorites! .
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored at work so I decided to browse your website on my iphone during lunch break. I love the knowledge you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how fast your blog loaded on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, fantastic blog!
I simply wanted to make a simple comment in order to express gratitude to you for those pleasant points you are placing on this website. My prolonged internet search has now been recognized with useful concept to write about with my close friends. I would admit that most of us site visitors actually are unequivocally blessed to live in a great network with many marvellous individuals with helpful opinions. I feel extremely grateful to have encountered your entire website page and look forward to many more exciting minutes reading here. Thanks a lot once more for a lot of things.
I got what you mean , thanks for putting up.Woh I am delighted to find this website through google. “I was walking down the street wearing glasses when the prescription ran out.” by Steven Wright.
Pandora88 adalah agen slot gacor online terpercaya yang menyediakan ribuan permainan terlengkap dan memberikan pengalaman bermain terbaik untuk seluruh pemain setia di Indonesia.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thank you, I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
I keep listening to the news speak about getting boundless online grant applications so I have been looking around for the finest site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i get some?
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was curious what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web savvy so I’m not 100 certain. Any recommendations or advice would be greatly appreciated. Appreciate it
Woah! I’m really loving the template/theme of this blog. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s hard to get that “perfect balance” between usability and appearance. I must say you’ve done a excellent job with this. Also, the blog loads very fast for me on Internet explorer. Excellent Blog!
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in fact used to be a entertainment account it. Glance advanced to far introduced agreeable from you! By the way, how could we keep up a correspondence?
hi!,I like your writing so much! share we communicate more about your post on AOL? I require a specialist on this area to solve my problem. May be that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
It’s actually a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I’ve read a few good stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you put to create such a great informative web site.
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a variety of websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard very good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
Howdy! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it very hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any points or suggestions? Thank you
Thank you for sharing with us, I think this website truly stands out : D.
h1vfr2
Perfect work you have done, this website is really cool with wonderful information.
Hi my friend! I wish to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all significant infos. I’d like to see more posts like this.
wonderful post.Never knew this, appreciate it for letting me know.
I got what you intend, thankyou for putting up.Woh I am glad to find this website through google. “Food is the most primitive form of comfort.” by Sheila Graham.
I am glad to be a visitant of this consummate web site! , thanks for this rare information! .
Its wonderful as your other content : D, thankyou for putting up.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have learn this submit and if I could I desire to counsel you some fascinating issues or suggestions. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article. I want to read more things approximately it!
Utterly indited subject material, Really enjoyed reading through.
I enjoy meeting utile information , this post has got me even more info! .
Some truly wonderful articles on this site, regards for contribution.
Hello are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I truly enjoy reading on this web site, it holds great posts. “A man of genius has been seldom ruined but by himself.” by Samuel Johnson.
I am now not certain the place you are getting your info, but great topic. I needs to spend a while learning more or working out more. Thanks for wonderful info I was looking for this info for my mission.
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
I genuinely enjoy looking through on this web site, it has excellent content.
Some truly nice and utilitarian information on this web site, besides I think the pattern has got fantastic features.
There is clearly a bunch to know about this. I feel you made various good points in features also.
I am not sure the place you are getting your info, however great topic. I needs to spend a while learning more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent info I was in search of this info for my mission.
Hello my friend! I want to say that this post is awesome, nice written and come with approximately all significant infos. I?¦d like to peer extra posts like this .
Very interesting topic, thankyou for posting.
I’ll immediately grab your rss as I can’t find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
It’s best to take part in a contest for the most effective blogs on the web. I will recommend this website!
Wow! Thank you! I continually wanted to write on my blog something like that. Can I take a part of your post to my blog?
I will immediately take hold of your rss as I can’t in finding your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly allow me recognize in order that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
F*ckin’ awesome things here. I am very satisfied to peer your article. Thank you so much and i am looking forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Hello.This post was extremely interesting, especially since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Sunday.
Utterly indited subject matter, Really enjoyed looking through.
I got what you mean , appreciate it for putting up.Woh I am lucky to find this website through google. “If one does not know to which port one is sailing, no wind is favorable.” by Seneca.
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how quick your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, very good site!
You completed various fine points there. I did a search on the matter and found nearly all persons will agree with your blog.
I do not even know how I stopped up right here, but I believed this submit used to be great. I don’t realize who you might be however definitely you are going to a well-known blogger when you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Very interesting subject, regards for putting up. “There are several good protections against temptations, but the surest is cowardice.” by Mark Twain.
Thank you for some other informative blog. Where else may just I get that type of information written in such an ideal approach? I have a undertaking that I am just now running on, and I’ve been at the look out for such information.
Admiring the time and effort you put into your website and in depth information you offer. It’s great to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material. Great read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what blog owners wrote but this internet site is rattling user genial! .
I have not checked in here for a while as I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are great quality so I guess I’ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Hey there would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using? I’m going to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a tough time choosing between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S Apologies for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
I haven?¦t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I?¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
I do trust all the ideas you have presented on your post. They’re really convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are too short for newbies. Could you please prolong them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
I dugg some of you post as I cerebrated they were very useful invaluable
wonderful points altogether, you simply won a new reader. What could you suggest about your put up that you just made some days in the past? Any positive?
I?¦ve learn a few just right stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much attempt you put to make one of these fantastic informative website.
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Great job.
This web page is really a walk-by way of for the entire data you needed about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and also you’ll definitely uncover it.
I think you have observed some very interesting details , thanks for the post.
I would like to point out my love for your kind-heartedness for people who actually need guidance on in this concept. Your real commitment to passing the solution throughout was quite powerful and have really allowed somebody like me to reach their dreams. The interesting help and advice signifies so much a person like me and still more to my mates. Thank you; from everyone of us.
I have to show my appreciation for your generosity supporting folks that should have guidance on the field. Your special dedication to getting the message all-around came to be extraordinarily important and has consistently enabled women much like me to arrive at their targets. Your own helpful report denotes much a person like me and still more to my colleagues. Thank you; from all of us.
Thank you a bunch for sharing this with all folks you really realize what you’re talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally seek advice from my site =). We can have a hyperlink change arrangement among us!
I?¦ll immediately take hold of your rss feed as I can not in finding your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly permit me recognise in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.