UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 19th July 2025
India calls for time-bound UNSC reforms, backs 'Pact for the Future' agreement

Why in News?
India reaffirmed its commitment to the Pact for the Future while demanding urgent and time-bound reforms in the UN Security Council (UNSC) to reflect current geopolitical realities.

Introduction
- India has reiterated its longstanding demand for urgent and time-bound reforms in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) while expressing strong support for the implementation of the Pact for the Future, an agreement adopted during the United Nations Summit of the Future in September 2024.
What is the Pact for the Future?
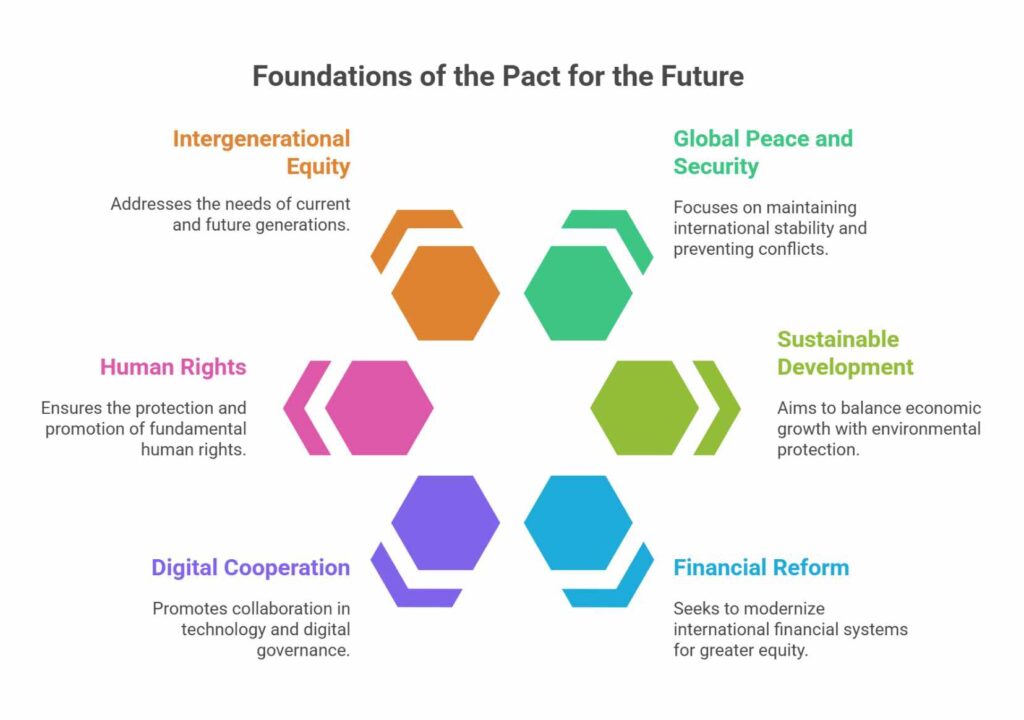
The Pact for the Future is a comprehensive agreement adopted by member states of the United Nations during the Summit of the Future in 2024. It is aimed at strengthening multilateralism and enhancing international cooperation to address a broad array of contemporary and emerging global challenges.
The Pact includes commitments in the following thematic areas:
- Global peace and security
- Sustainable development and climate action
- Reform of international financial institutions and global governance
- Digital cooperation and technology governance
- Human rights and gender equality
- Intergenerational equity, including issues related to youth and future generations
It also outlines the need for the transformation of international institutions to make them more effective, representative, and responsive to modern challenges.
India’s Position on the Pact for the Future
- India has expressed strong support for the effective implementation and regular review of the Pact. Ambassador Harish emphasized India’s commitment to working with all stakeholders to ensure that the agreement delivers meaningful outcomes.
- He stressed that the 2028 review of the Pact should be results-oriented and forward-looking, rather than symbolic or procedural.
- In a gesture that highlights India’s emphasis on inclusive global dialogue, he also presented a Hindi translation of the Pact to the President of the United Nations General Assembly, Philemon Yang.
India’s Call for UNSC Reform
India used the opportunity to reiterate its long-standing position that the UNSC must undergo urgent and substantial reforms. Ambassador Harish stated that:
- The UNSC should reflect contemporary geopolitical realities, which are vastly different from those when the Council was originally formed after World War II.
- Reform should focus on both expansion in permanent and non-permanent categories.
- Efforts to maintain the status quo must be resisted, as they hinder the credibility and legitimacy of the Council.
India has consistently argued that its growing global stature and contributions to international peacekeeping and global governance make it a deserving candidate for permanent membership in a reformed UNSC.
International Financial Architecture Reform
- In addition to UNSC reform, India emphasized the need for reforms in the global financial governance framework, including the World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Trade Organization (WTO), and G20.
- The objective is to make these institutions more representative, democratic, and responsive to the needs of developing countries.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.


Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.info/sl/register?ref=I3OM7SCZ