UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 06th July 2025
India’s First National Cooperative University — Tribhuvan Sahkari University

Why in News?
- Union Home and Cooperation Minister laid the foundation stone for India’s first national cooperative university — Tribhuvan Sahkari University — in Anand, Gujarat (July 5, 2025).
- It marks a significant step to strengthen the cooperative sector’s capacity and professionalism in line with the government’s vision of Sahkar se Samriddhi (Prosperity through Cooperation).
Background: Cooperatives in India
- India has more than 8.5 lakh cooperatives, covering sectors like dairy (Amul), sugar, credit societies, housing, fisheries, and marketing.
- The cooperative movement began in the early 20th century with the Cooperative Credit Societies Act, 1904.
- The Amul model in Gujarat is one of the world’s largest and most successful dairy cooperatives, credited to pioneers like Tribhuvandas Patel and Verghese Kurien.
- Tribhuvandas Kishibhai Patel, after whom the university is named, was the first Chairman of the Kaira District Co-operative Milk Producers’ Union, which later became Amul.
Constitutional Provisions on Cooperatives
- 7th Schedule: ‘Cooperative societies’ are a State Subject (Entry 32, List II).
- 97th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2011:
- Inserted Part IXB (Articles 243ZH to 243ZT) to give constitutional status to cooperatives.
- Article 19(1)(c) expanded to include the right to form cooperative societies.
- Added Article 43B (Directive Principles) to promote voluntary formation, democratic control, and professional management of cooperatives.
- In 2021, the Supreme Court partly struck down the 97th Amendment related to State cooperatives, upholding it only for Multi-State Cooperative Societies.
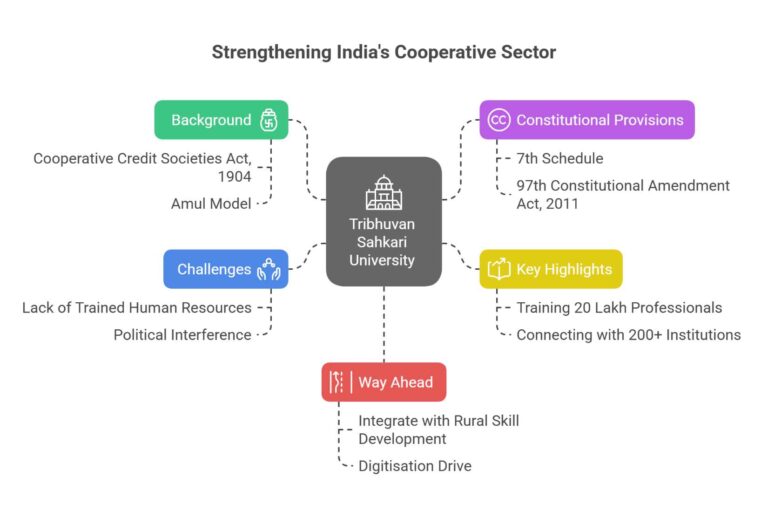
Key Highlights of the News
Tribhuvan Sahkari University:
- Will train over 20 lakh cooperative professionals in 5 years.
- Will offer specialised courses in cooperative management, law, finance, rural development, and technical skills like marketing, accounting, and digitisation.
- Plans to connect with 200+ existing cooperative institutions within 4 years.
- Aims to become an R&D hub for innovation in the cooperative sector.
School-Level Cooperative Education:
- CBSE has launched a course on cooperatives.
- Gujarat urged to add cooperatives as a subject for Classes 9–12 in State Board schools.
- Seeks to instil cooperative values and awareness early among students.
Operation Flood was one of the world’s largest rural development programmes launched by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) in 1970 to create a nationwide milk grid and transform India from a milk-deficient nation into the world’s largest milk producer. Popularly called the White Revolution, it was inspired by the success of the Amul cooperative model in Gujarat under the leadership of Verghese Kurien.
- Launched in three phases between 1970 and 1996, funded by the sale of donated EEC skimmed milk powder and butter oil.
- Organised rural milk producers into dairy cooperatives to ensure fair prices and eliminate middlemen.
- Established an integrated network of milk collection, processing, and distribution.
- Created brands like Amul and Mother Dairy, empowering millions of farmers, especially women.
- By connecting producers to consumers, it raised rural incomes and ensured urban milk supply.
Operation Flood is considered a landmark example of cooperative-led rural development and food security in India.
Challenges
- Lack of trained human resources — Many societies rely on outdated practices and lack modern managers and accountants.
- Ensuring uniformity in cooperative laws — Regulatory overlap exists between State and Multi-State Cooperative Societies Acts.
- Need for modern governance and digitisation — Limited use of ERP systems, e-governance, real-time audits, or MIS tools.
- Making cooperative education aspirational — Lack of awareness about career prospects and limited research avenues.
- Political interference and poor regulatory oversight in some societies.
Way Ahead — Specific Aspects
- Integrate with Rural Skill Development: Link cooperative education with the Skill India Mission, KVKs, and Rural Livelihood Missions; offer field training with FPOs and dairy co-ops.
- Research Ecosystem: Establish research chairs for digital cooperatives, impact financing, and supply chain modernisation; collaborate with IRMA and NABARD.
- Digitisation Drive: Develop cooperative-specific ERP software, online voting, e-audit systems; use Sahakar Pragya Portal for e-training.
- Model Curriculum: Develop standard modules via NCERT and promote successful case studies like Amul and IFFCO for wider adoption.
- Global Linkages: Partner with the International Cooperative Alliance (ICA) and similar universities abroad; run exchange programmes for students and managers.
- Youth Incentives: Launch start-up incubators for new-age cooperatives in areas like renewable energy, digital platforms, and social enterprises.
Significance
- Builds a pool of trained professionals to manage India’s diverse cooperative ecosystem.
- Bridges the gap between traditional cooperative practices and modern governance.
- Aligns with the government’s vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat by promoting community-led growth.
- Strengthens the cooperative movement’s contribution to rural income, employment, and inclusive growth.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.


Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
whoah this blog is magnificent i like studying your posts. Stay up the good work! You recognize, lots of people are looking round for this info, you could aid them greatly.