UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 02nd August 2025
India-Maldives Relations: Reaffirming the ‘Neighbourhood First’ Policy

Why in News?
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s July 2025 visit to the Maldives marked the revival of close bilateral ties and reaffirmed India’s commitment to its Neighbourhood First policy.
Background: From Strain to Strengthening Ties
On July 26, 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited the Maldives as the special guest for the country’s 60th Independence Day celebrations, marking a significant thaw and revival in bilateral relations that had faced turbulence after the 2023 elections in the Maldives.
- Political Shift: Maldives President Mohamed Muizzu’s 2023 election victory was backed by an “India Out” campaign, which temporarily strained ties. In India, this triggered a “Boycott Maldives” campaign on social media.
- Repair and Re-engagement: Since 2023, diplomatic efforts on both sides have worked towards repairing the relationship. President Muizzu’s state visit to India in 2024 helped lay the foundation for renewed cooperation.

India Maldives Areas of Co-operation
1. Economic & Developmental Cooperation
- Line of credit of ₹4,850 crore (2025), rupee-denominated, for priority Maldivian projects.
- Debt Relief & Financial Support
- Greater Malé Connectivity Project (GMCP), the Thilamale Bridge, water and sanitation infrastructure, and 3,300 social housing units (delivered 2025).
- High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs)
2. Trade and Digital Economy
- Trade Partner: India remains the Maldives’ second largest trading partner with bilateral trade touching $1B.
- Agreements for UPI digital payments, RuPay card usage in Maldives
- Bilateral Investment Treaty and FTA negotiations ongoing
3. Maritime Security, Defence & Disaster Relief
- Joint “Ekuverin”, “Ekatha”, and “Dosti” exercises
- India remains Maldives’ “First Responder” in crises—Operation Cactus (1988 coup), Operation Neer (2014 water crisis), COVID-19 pandemic response, and medical aid.
4. Health, Education & Humanitarian Assistance
- Aarogya Maitri Health Cubes (BHISHM) (2025), and a commitment to set up Jan Aushadhi Kendras
- Water & Sanitation: $100 million project spanning 28 islands, i
- Education & Youth Exchanges.
5. Tourism & People-to-People Ties
- India is a top source of tourists for the Maldives.
- Cultural & Legislative Ties: Joint parliamentary forums, commemorative stamps (2025), film collaborations, and diaspora engagement foster stronger bonds.
6. Climate Action & Blue Economy
- Climate Resilience: Collaboration on water management, sanitation, and renewable energy projects. India is a key player in Maldives’ climate adaptation infrastructure and disaster risk reduction efforts.
- Fisheries Cooperation: Newly signed agreements (2025) on joint research, aquaculture, and sustainable fisheries management.
7. Digital Governance & Technology
- Digital Infrastructure: India is assisting with governance platforms, digital payments, and undersea cable links to boost digital transformation and cyber security in the Maldives
Key Outcomes of PM Modi’s 2024 Visit
- Economic Cooperation
- India extended a line of credit worth $565 million (₹4,850 crore).
- Debt burden reduced by 40% on existing Indian credit lines.
- Initiation of India-Maldives Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations, opening new avenues for trade and economic partnership.
- Sectoral Collaboration
- Signing of MoUs in:
- Fisheries
- Meteorological sciences
- Digital solutions
- Pharmaceuticals
- Launch of digital and rupee-rufiyaa national currency payment system to ease bilateral transactions.
- Signing of MoUs in:
- Strategic Significance
- Maldives acknowledged India’s “pivotal” role in its development and security.
- Reaffirmation of India’s trilateral security cooperation with Maldives and Sri Lanka.
- Follow-up visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake to the Maldives highlights growing regional cooperation.
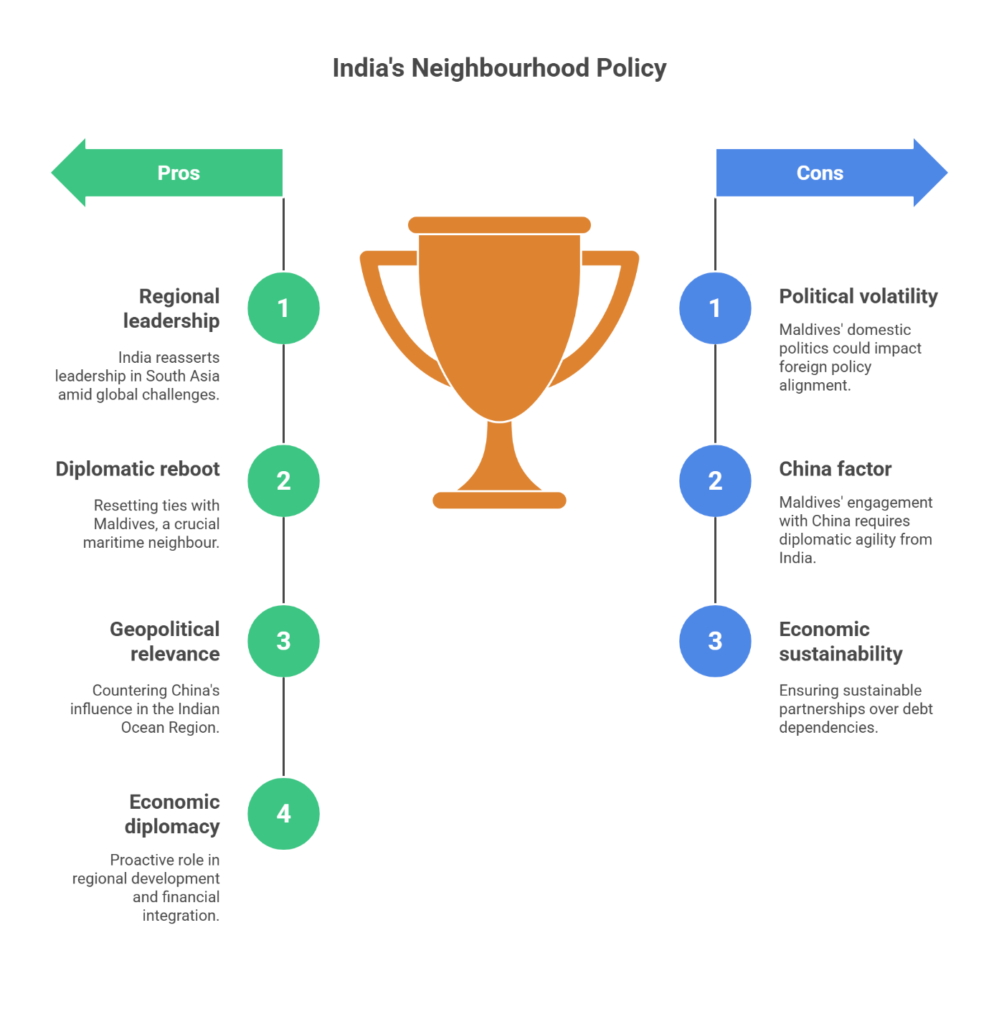
India’s ‘Neighbourhood First’ Policy in Action
- Regional Balancing Amid Global Turbulence: PM Modi’s visit comes at a time when India is navigating global challenges — from U.S. trade protectionism and wars in Ukraine and Gaza, to tensions with Pakistan (post-Pahalgam attacks) and concerns with Bangladesh.
- Strategic Outreach: India is reasserting its leadership in South Asia. New Delhi’s upcoming welcome for Nepal Prime Minister K.P. Sharma Oli — his first since assuming office — reflects this intent.
- Symbolic Diplomacy: A commemorative stamp released by the Maldives featuring Indian and Maldivian boats symbolised the shared civilisational journey, which PM Modi described as “fellow voyagers on a shared journey”.
Significance of the Visit
- Diplomatic Reboot: The visit reflects a conscious effort to reset ties with the Maldives — an important maritime neighbour in the Indian Ocean.
- Geopolitical Relevance: In the face of China’s growing footprint in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), India’s continued engagement with island nations like Maldives is crucial.
- Economic Diplomacy: Lines of credit, FTA talks, and currency linkages signal India’s readiness to play a proactive role in regional development and financial integration.
Challenges Ahead
- Political Volatility in the Maldives: Domestic politics could again sway public opinion and foreign policy alignment.
- China Factor: Maldives continues to engage with China economically and strategically, requiring India to remain diplomatically agile.
- Sustainability of Economic Support: India must ensure that its economic support translates into sustainable partnerships rather than debt dependencies.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Introduction
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

