UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17th July 2025
India's Energy Transition Milestone

Why in News?
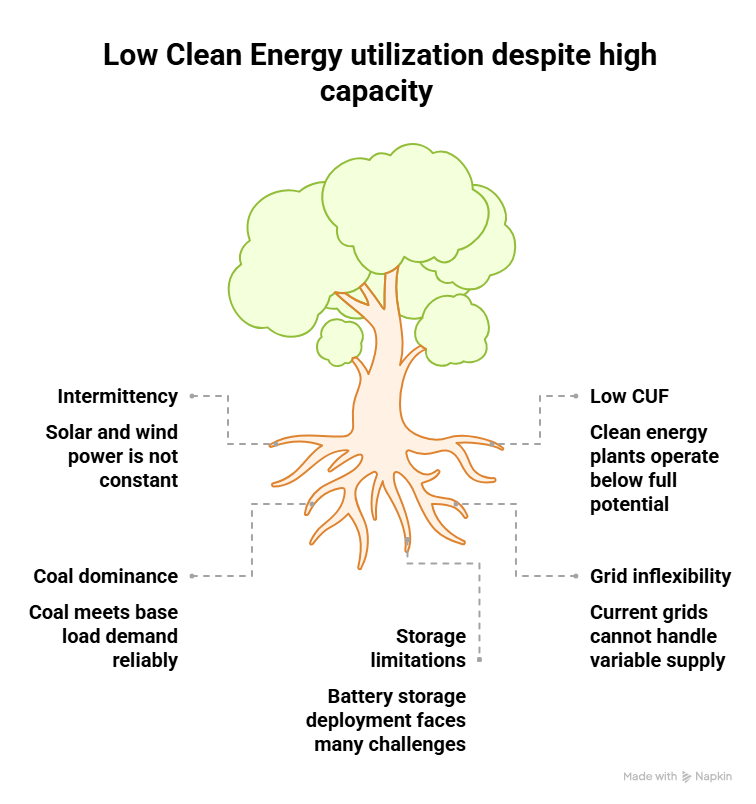
India has achieved 50% installed power capacity from non-fossil sources, but actual generation remains below 30% due to low-capacity utilization.

Introduction
- India has achieved a landmark in its energy transition journey by sourcing 50% of its total installed electricity capacity from non-fossil fuel sources as of June 30, 2025 — a target originally set for 2030 under its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Agreement.
- However, this milestone comes with important nuances regarding actual power generation and energy utilization, which continue to depend significantly on fossil fuels, especially coal.
Understanding Installed Capacity vs Actual Electricity Generation
Installed Capacity:
- Installed Capacity refers to the maximum potential electricity that can be generated if all power plants operate at full capacity.
- As of June 30, 2025, India’s total installed electric capacity is 484 GW, with 50% (≈242 GW) from non-fossil fuel sources:
- Solar
- Wind
- Biomass
- Hydro (large and small)
- Nuclear
Actual Generation:
- Despite the 50% installed capacity, only about 28% of the electricity actually generated came from clean sources in 2024–25, up from 17% in 2014–15.
- In terms of volume, clean energy generation rose from 190 billion units in 2014–15 to 460 billion units in 2024–25.
Key Challenge: Capacity Utilisation Factor (CUF)
What is CUF?
- The Capacity Utilisation Factor is the ratio of actual energy produced to the maximum possible energy that could have been produced if the plant operated at full capacity throughout the year.
Source | Approx. CUF |
Solar | 20% |
Wind | 25-30% |
Coal | 60% |
Nuclear | 80% |
Implication:
- Clean energy sources, especially solar and wind, have low CUFs due to their intermittent nature (solar energy is not available at night, wind is seasonal).
- Hence, even with high installed capacity, contribution to actual electricity supply is lower.
Policy and Technological Solutions
- Grid Flexibility and Smart Management
- Presently, consumers pay the same per-unit price for electricity regardless of time.
- Introduction of time-of-day pricing or differential tariffs (e.g., cheaper day rates) can incentivize solar usage.
- Requires smart grids, real-time monitoring, and dynamic pricing mechanisms.
- Battery Storage and Hybrid Energy Projects
- Storage systems can absorb surplus solar/wind energy and discharge it during evening peaks.
- Hybrid Projects (solar + wind + storage) are emerging as promising solutions.
Example: A hybrid system can integrate solar (daytime) and wind (night-time) with battery backup, enabling round-the-clock renewable power supply.
- Challenges in Deployment:
- Land aggregation issues
- High cost of battery storage
- Lack of coordinated transmission infrastructure
- Regulatory delays and funding constraints
Strategic Steps:
- Strengthen and expand national grid capacity
- Incentivize renewable storage infrastructure
- Promote private sector investment in hybrid and storage technologies
- Revise tariff policies to encourage demand-side management
- Increase R&D in energy storage solutions (like lithium-ion, pumped hydro)
Conclusion
- India’s achievement of 50% non-fossil installed electricity capacity, five years ahead of schedule, marks a critical milestone in its climate action journey.
- However, the disparity between installed capacity and actual generation underscores the need for strategic interventions in grid flexibility, energy storage, and smart policy reforms.
- As India aims for net zero by 2070, focusing on quality, not just quantity of clean energy capacity will be essential for a sustainable and resilient energy future.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

