UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 21th May 2025
1991 K. Veeraswami judgment in news

Why in News?
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankar has called for revisiting the 1991 K. Veeraswami vs Union of India judgment, citing it as the origin of judicial corruption and a hurdle to registering FIRs against High Court and Supreme Court judges.
Key Highlights of the Case:
- Who was K. Veeraswami?
- Former Chief Justice of Madras High Court (1969–1976).
- FIR registered by the CBI in 1976 for possessing disproportionate assets under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1947.
- Timeline of Legal Proceedings:
- 1976–1977: CBI filed FIR and chargesheet.
- 1978: Veeraswami challenged the prosecution in Madras High Court.
- 1979: Full Bench of Madras HC (2:1) rejected the plea.
- 1991: Supreme Court upheld the prosecution in a 4:1 majority decision.
- Supreme Court Judgment (1991):
- Judges of High Courts and the Supreme Court are covered under the definition of ‘public servant’ under the PC Act.
- Sanction required for prosecution of sitting judges.
- Consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI) is mandatory before:
- Filing an FIR.
- Granting sanction for prosecution.
- If CJI is accused, consult other senior judges of the SC.
- Dissenting Opinion (Justice J.S. Verma):
- Judges of higher judiciary should be excluded from the PC Act.
- Called for a new law for corruption cases involving constitutional authorities.
Important Points:
- Prevention of Corruption Act, 1947 (now replaced by PC Act, 1988):
- A central anti-corruption law.
- Requires sanction to prosecute public servants.
- Public Servant under PC Act: Includes judges, making them liable for prosecution with procedural safeguards.
- Sanctioning Authority: The President of India is the authority, acting in consultation with the CJI.
- Judicial Immunity vs Accountability: The case raised critical questions about balancing judicial independence with legal accountability.
- Current Relevance (2025):
- The Delhi cash-on-fire case at the residence of Justice Yashwant Varma has reignited concerns over procedural hurdles in prosecuting judges.
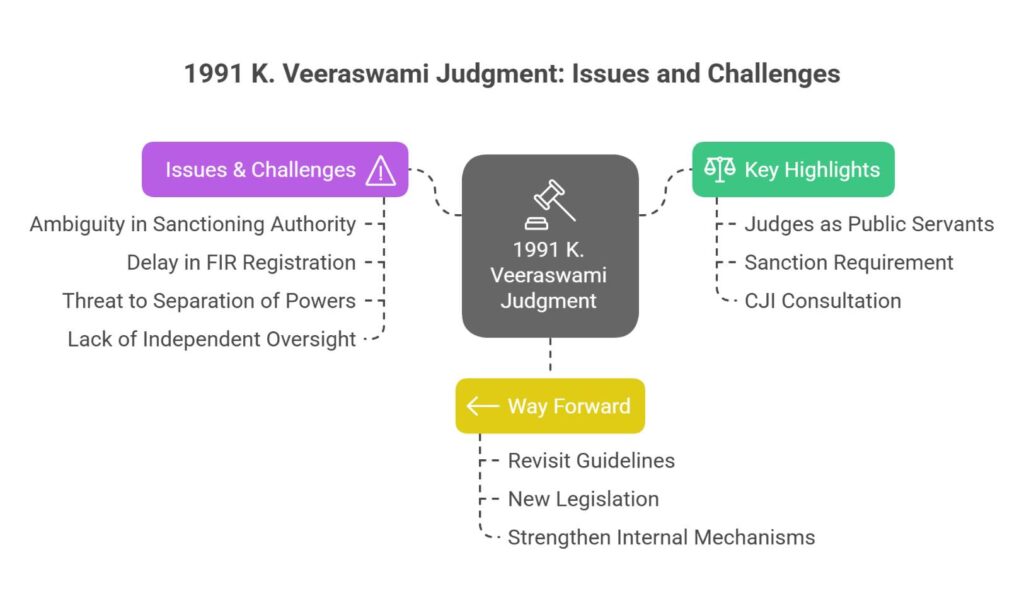
Issues & Challenges Identified in Implementing the Veeraswami Judgment
- Ambiguity in Sanctioning Authority
- The judgment designates the President as the competent authority to grant sanction for prosecution, but the President acts on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers.
- This creates uncertainty and potential executive influence in matters concerning judicial accountability.
- Delay in FIR Registration
- The mandatory requirement to consult the Chief Justice of India (CJI) before even registering an FIR against a sitting judge leads to procedural delays.
- This may obstruct timely investigation and undermine public trust in judicial impartiality.
- Threat to Separation of Powers
- Involving the executive (through the President) in sanctioning prosecutions against judges risks interference with judicial independence, violating the doctrine of separation of powers.
- Involving the executive (through the President) in sanctioning prosecutions against judges risks interference with judicial independence, violating the doctrine of separation of powers.
- Lack of an Independent Oversight Mechanism
- India lacks a dedicated, independent body to examine corruption or misconduct complaints against judges of higher judiciary.
- The internal ‘in-house mechanism’ of the judiciary is non-statutory, opaque, and not subject to public scrutiny or external audit.
Way Forward:
- Revisit 1991 Guidelines: As suggested by the Vice President, to ensure transparency and accountability without compromising judicial independence.
- New Legislation: May be needed for dealing with misconduct at the highest levels of the judiciary.
- Strengthen Internal Judicial Mechanisms: To handle corruption allegations without delay.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
- Decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of RBCs.
- Increased fragility and cell stiffness.
- Vascular blockage, causing pain and organ injury.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, anemia, and stroke.



I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Because the admin of this web page is working, no uncertainty very soon it will be famous, due to its quality contents.