UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 1st June 2025
How Military Standoffs Affect Aviation: India–Pakistan Airspace Closures

Why in News?
- On April 24, Pakistan closed its airspace to Indian aircraft, followed by India doing the same on April 30. Although Pakistan temporarily reopened its airspace after Operation Sindoor, both sides reissued fresh NOTAMs extending the closures till June 24 (Pakistan) and June 23 (India).
- Over 500 flights were rerouted, impacting civilian aviation, cargo movement, and air traffic safety.
Introduction
Aviation, especially international civil aviation, is often one of the first sectors disrupted during military standoffs or geopolitical tensions. Following the Pahalgam terror attack (April 22, 2025) and India’s retaliatory steps, both India and Pakistan issued NOTAMs (Notices to Airmen) to restrict airspace access to each other’s aircraft. This development, particularly in the context of Operation Sindoor (May 7–10), raises questions about the legal, operational, economic, and strategic consequences of airspace closure in times of conflict.
Background: India–Pakistan Airspace Closures
- 1965 war: Suspension and restoration of overflights post-conflict through diplomatic resolution.
- 1971 hijacking: India banned civil overflights; matters taken to ICAO and ICJ, resolved by 1976 MoU.
- Later incidents: Kargil War (1999), Parliament attack (2001), and Balakot strikes (2019) led to temporary closures.
- 2025 tensions: Reflect a recurring pattern where airspace becomes a diplomatic lever amid hostilities.
What Happens During Military Tensions
- Airspace Closure Mechanism
- Enforced through NOTAMs, which restrict access to designated air routes.
- Often affects both military and civilian aircraft, depending on security assessments.
- Civilian airlines must reroute via longer and costlier paths, increasing fuel consumption, flight time, and delays.
- Operational Impact in 2025
- Temporary closure of 32 Indian airports and 25 Air Traffic Service (ATS) routes.
- Heavy reliance on alternative FIRs like Muscat, Mumbai, and Kolkata.
- Increased burden on ATC systems and 30% rise in hourly air traffic volumes.
- Limited rerouting options due to Chinese airspace restrictions and Himalayan terrain risks.
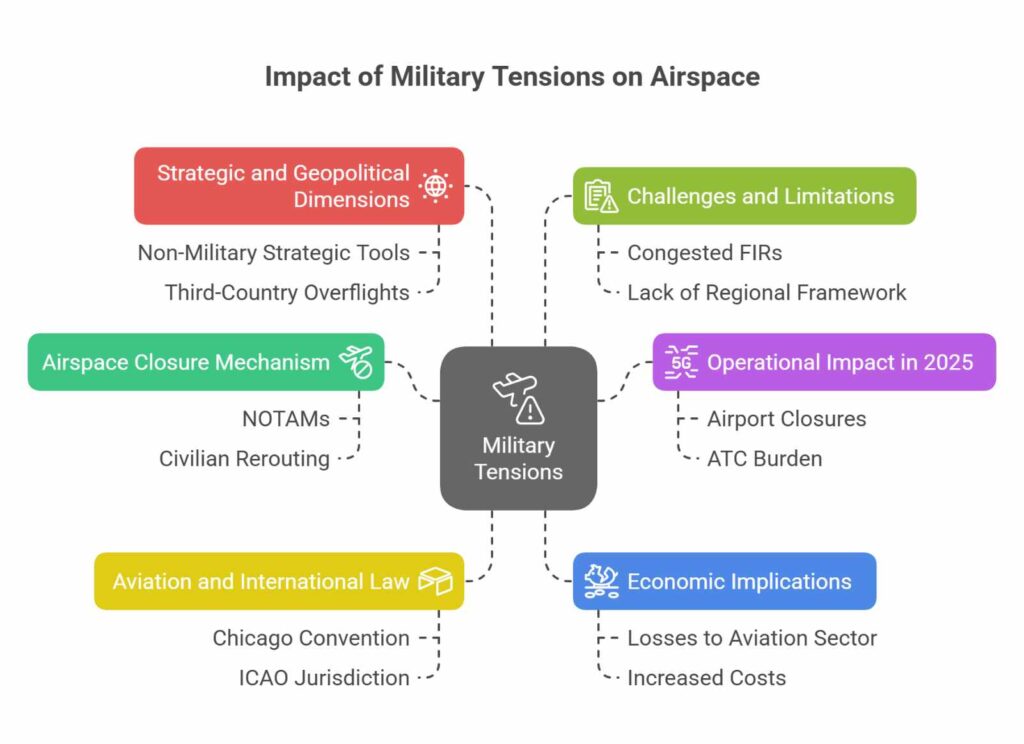
Aviation and International Law
- Governed by the Chicago Convention, 1944, under the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
- Article 1 affirms states’ sovereignty over their airspace; Article 9 permits restrictions during military or emergency conditions.
- Such closures must be temporary, proportionate, and non-discriminatory, with appropriate international notice.
- In the 1971 hijacking case, the ICJ ruled that ICAO had jurisdiction, reinforcing institutional remedies.
- Bilateral Air Services Agreements (ASAs) also guide airspace usage and suspension terms.
- However, enforcement of legal redress mechanisms often depends on political will and strategic context, limiting ICAO’s effectiveness during bilateral disputes.
Economic Implications
- Estimated loss to India’s aviation sector in 2025: Approx. ₹7,000 crore, including passenger and cargo losses.
- Airlines incur higher fuel and crew costs, often passed on to passengers.
- Cargo logistics disrupted, affecting time-sensitive shipments and exports.
Strategic and Geopolitical Dimensions
- Airspace closures serve as non-military strategic tools, signalling diplomatic friction.
- Impacts not just India and Pakistan, but also third-country overflights, including airlines from the Gulf, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
- Restricts India’s potential as a hub for international aviation and cargo transit.
Challenges and Limitations
- Limited alternatives due to congested FIRs and geopolitical constraints.
- Lack of a regional contingency framework for coordinated aviation safety during crises.
- Civil aviation becomes a collateral victim of military manoeuvres, affecting regional connectivity and economic recovery.
Way Forward
- Formulate bilateral aviation deconfliction protocols to ensure civilian safety.
- Upgrade FIR and ATC infrastructure to handle sudden spikes in rerouted traffic.
- Encourage ICAO-led regional confidence-building measures for airspace security.
- Use technological tools like AI-based traffic rerouting and real-time risk assessments.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

