UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 20th June 2025
Navy inducts INS Arnala

Why in News?
Recently, INS Arnala, India’s first indigenously built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) was commissioned.
Introduction
- On June 19, 2024, INS Arnala, the first ship of the indigenously built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) class, was commissioned into the Eastern Naval Command of the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam.
- Designed by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) and built in collaboration with L&T Shipbuilding, INS Arnala represents a significant step in India’s efforts to modernise its naval capabilities and strengthen maritime security in coastal and shallow waters.
Background and Need
- India’s coastline spans over 7,500 km, with strategic chokepoints, offshore assets, and critical shipping routes.
- The growing presence of foreign submarines, especially from China, in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), poses a complex security challenge.
- The ageing Abhay-class corvettes, which have been in service for decades, are no longer adequate to address modern undersea threats. The ASW-SWC programme was conceptualised to fill this gap with next-generation shallow water platforms.
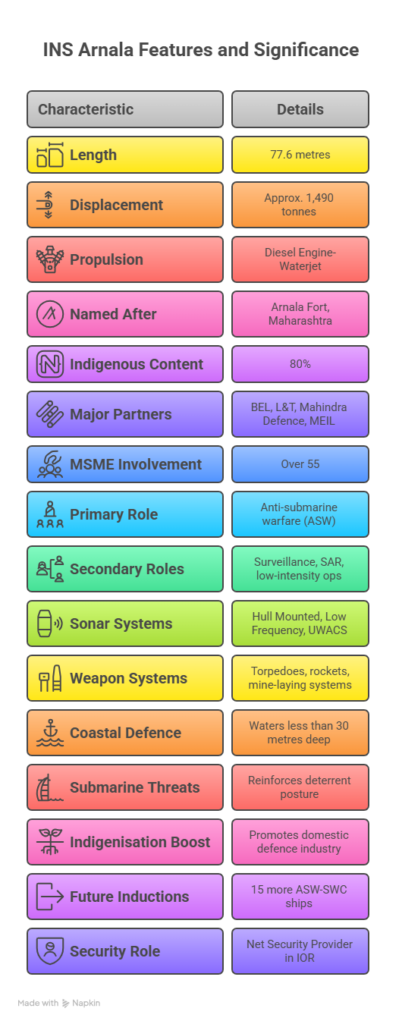
Key Features of INS Arnala
Design and Build
- Length: 77.6 metres
- Displacement: Approx. 1,490 tonnes
- Propulsion: Diesel Engine-Waterjet configuration — first of its kind in Indian Navy
- Named after: Arnala Fort near Vasai, Maharashtra
Indigenisation and Industrial Participation
- 80% indigenous content
- Major partners: BEL, L&T, Mahindra Defence, MEIL
- Over 55 Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) involved
- Aligns with the ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative and promotes defence self-reliance
Operational Capabilities
- Primary Role: Anti-submarine warfare (ASW) in shallow coastal waters
- Secondary Roles:
- Subsurface surveillance
- Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Low-intensity maritime operations
- Mine-laying and area denial operations
Weapon and Sensor Systems
- Hull Mounted Sonar (Abhay), Low Frequency Variable Depth Sonar (LFVDS), and Underwater Acoustic Communication System (UWACS)
- Single centreline-mounted rocket launcher (new design to reduce hardware and cost)
- Lightweight torpedoes, ASW rockets, mine-laying systems, and anti-torpedo decoys
- Integrated Combat Management System and ASW Complex (IAC)
Strategic Significance
1. Coastal and Littoral Defence
- Operates efficiently in waters less than 30 metres deep
- Suitable for targeting small UUVs and midget submarines near the shore
- Enhances patrolling of India’s vulnerable coastal areas and offshore energy installations
2. Countering Submarine Threats in IOR
- Reinforces India’s deterrent posture against hostile undersea platforms
- Complements blue-water platforms like destroyers and frigates by filling the shallow water operational gap
3. Boost to Indigenisation and Employment
- Promotes domestic defence industry through indigenous design, electronics, weapons and MSME involvement
- Reduces dependency on foreign military hardware and improves India’s technological base
Future Prospects
- 15 more ASW-SWC ships will be inducted progressively, standardising coastal ASW operations
- Will form a key component of India’s layered maritime security architecture
- Supports India’s aspirations to be a Net Security Provider in the Indian Ocean Region
Conclusion
- INS Arnala is not just a naval platform, but a symbol of India’s evolving maritime doctrine that emphasises self-reliance, technological modernisation, and strategic coastal defence.
- With increasing underwater threats in the IOR, the induction of such shallow water combatants is critical for protecting national interests, securing sea lines of communication (SLOCs), and ensuring maritime dominance in the region.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

