UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 21st July 2025
New dragonfly species Lyriothemis abrahami discovered in Kerala

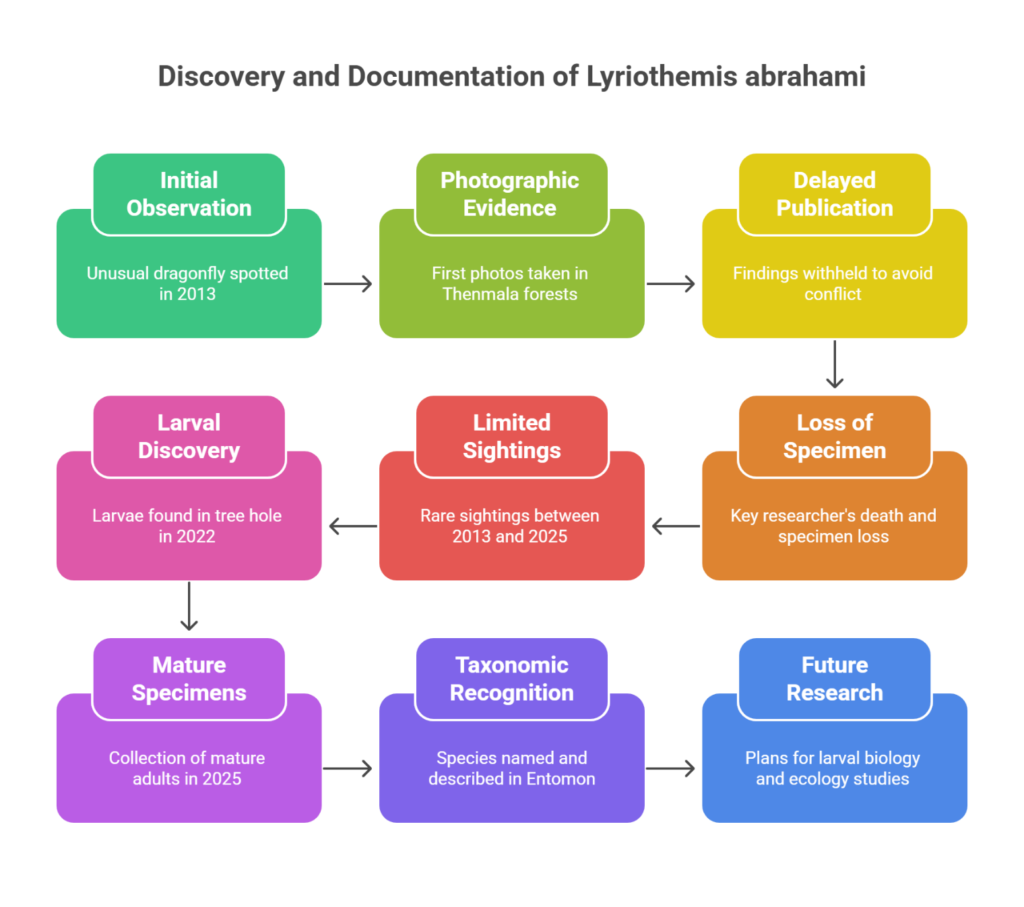
Why in News?
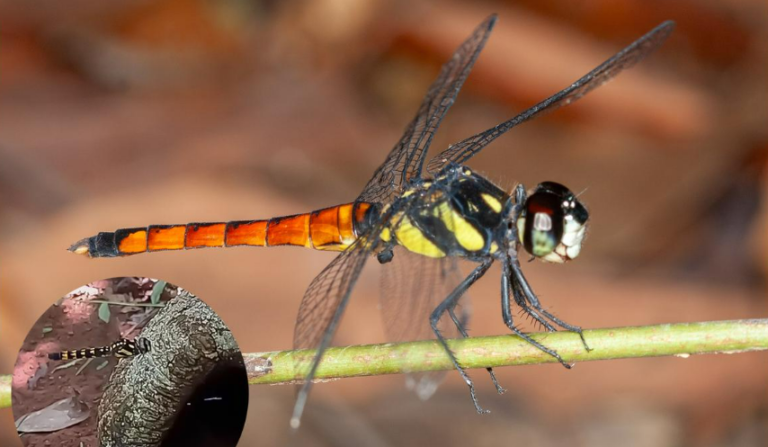
- A new dragonfly species Lyriothemis abrahami, exhibiting strong sexual dimorphism and breeding in tree-hole water pools, was discovered in Kerala’s Western Ghats.

Introduction
- A new species of dragonfly, Lyriothemis abrahami, has been officially identified and described from the Western Ghats in Kerala.
- The discovery is significant for India’s biodiversity research and dragonfly taxonomy.
- The species had been misidentified for years due to its superficial resemblance to Lyriothemis flava.
- The discovery highlights the ecological importance of forest microhabitats and the need for sustained biodiversity monitoring in the Western Ghats.
Taxonomic Recognition and Naming
- The species has been named Lyriothemis abrahami in honour of Abraham Samuel, a pioneer in odonatology (the study of dragonflies and damselflies).
- The description was peer-reviewed in the scientific journal Entomon through five rigorous rounds of scientific scrutiny, cementing its status as a new species.
Morphological Features and Dimorphism
- Lyriothemis abrahami exhibits strong sexual dimorphism:
- Males have uniquely shaped hamules (copulatory organs).
- Females display jet black bodies with distinct yellow triangular spots.
- This dimorphism played a key role in confirming it as a separate species.
Habitat and Distribution
- The species breeds in small water pools in tree holes, a type of microhabitat found in forest ecosystems.
- Its distribution spans across:
- Lowland rainforests to
- Mid-elevation evergreen and deciduous forests ranging between 50 m to 1,100 m above sea level.
- Sightings and collections were reported from:
- Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary (Kannur),
- Ponmudi (Thiruvananthapuram),
- Kallar, Neyyar, and Peppara Wildlife Sanctuary.
Ecological and Conservation Significance
- The finding raises Kerala’s total odonate species count to 191, with 78 of them being endemic.
- The discovery reinforces the biodiversity richness of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of the world’s eight “hottest hotspots” of biological diversity.
- The species is considered an indicator of forest health. Its dependency on tree-hole water pools underscores the importance of conserving microhabitats within forests.
- The study highlights the ecological value of preserving such natural breeding niches that are often overlooked in conventional conservation efforts.
Future Research Directions
- The research team plans to:
- Study the larval biology of L. abrahami,
- Investigate its ecological role in forest ecosystems,
- Explore its evolutionary relationships within the Lyriothemis genus.
- Such studies can aid in developing targeted conservation strategies and better understanding the biogeography of dragonflies in the Indian subcontinent.
Conclusion
- The discovery of Lyriothemis abrahami is not just a taxonomic milestone but also a reminder of the undiscovered diversity within India’s forest ecosystems.
- It underlines the urgent need to protect natural habitats, especially in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats, and to support long-term ecological research for conservation planning.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

