UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 14th July 2025
Kerala Reports Fresh Nipah Case in Palakkad

Why in News?
A fresh Nipah virus case in Palakkad, Kerala has triggered renewed surveillance and containment efforts across multiple districts amid rising public health concerns.

Nipah Virus: A Brief Overview
- Causative Agent: Nipah virus (NiV), a member of the Paramyxoviridae family.
- Reservoir Host: Fruit bats (Pteropus genus), commonly known as flying foxes.
- Mode of Transmission:
- Direct contact with infected bats, pigs, or humans.
- Consumption of fruits contaminated with bat saliva or urine.
- Nosocomial transmission in healthcare settings.
- Symptoms:
- Fever, headache, drowsiness
- Respiratory distress
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
- Fatality Rate: 40% to 75%, depending on outbreak response and healthcare access.
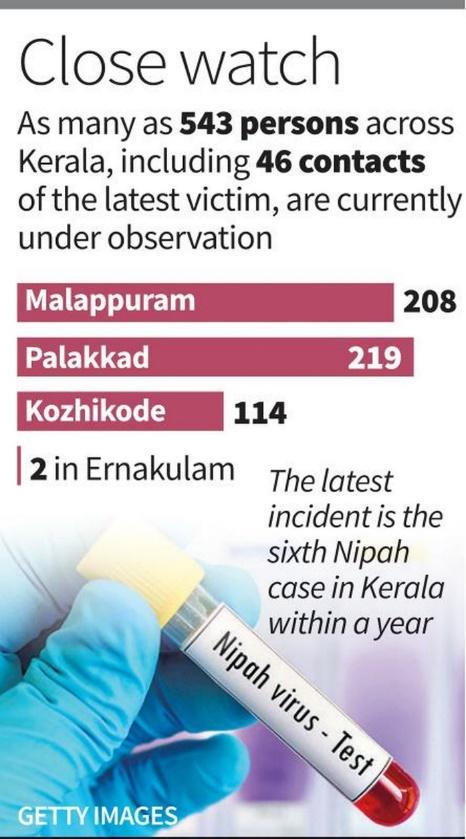
Epidemiological Response and Contact Tracing
- Even before the official confirmation of Nipah infection from the National Institute of Virology (NIV), Pune, health authorities across Palakkad and Malappuram districts had proactively begun contact tracing. So far, 46 primary contacts of the deceased patient have been traced, and a comprehensive surveillance network has been activated.
- District administrations in Kozhikode, Thrissur, Kannur, and Wayanad have also been placed on high alert in anticipation of possible virus transmission chains.
Steps Taken:
- CCTV surveillance footage was used to retrace the deceased’s movements.
- A detailed route map and family tree of the deceased have been prepared.
- Door-to-door surveillance is underway in Kumaramputhur.
- Fever surveillance has been intensified by deploying multiple health worker teams.

Public Health Measures and Preventive Protocols
- Limited hospital visits in affected districts to curb community spread.
- Advised strict mask usage by patients, caregivers, and hospital staff.
- Deployed additional health teams to monitor symptoms and ensure rapid medical intervention in suspected cases.
Challenges in Containment
- Asymptomatic Transmission: Difficulty in early detection due to mild or no symptoms in some individuals.
- High Mortality Rate: Rapid deterioration in severe cases limits time for intervention.
- Human-Bat Interface: Deforestation and human encroachment into bat habitats increase transmission risks.
- Lack of Vaccine or Antiviral: Management remains largely supportive, with no specific cure.
Way Forward: Strengthening Preparedness
The current situation reinforces the need for a robust epidemic preparedness framework in India, especially in states with previous outbreaks.
Recommendations:
- Enhanced Zoonotic Surveillance: Regular monitoring of bat populations and virus spillovers.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Especially during fruiting seasons when bat-human interactions increase.
- Dedicated Viral Research Centres: Strengthening regional virology labs for faster detection.
- One Health Approach: Coordinated efforts between human health, animal health, and environmental sectors.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

