UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 05th July 2025
Revitalizing India’s MSME Sector

Why in News?
- Union MSME Minister Shri Manjhi highlighted major achievements and initiatives in the MSME sector during a review visit to Mumbai, including the success of Udyam and PMEGP schemes and the role of IDEMI in supporting national missions like Chandrayaan.
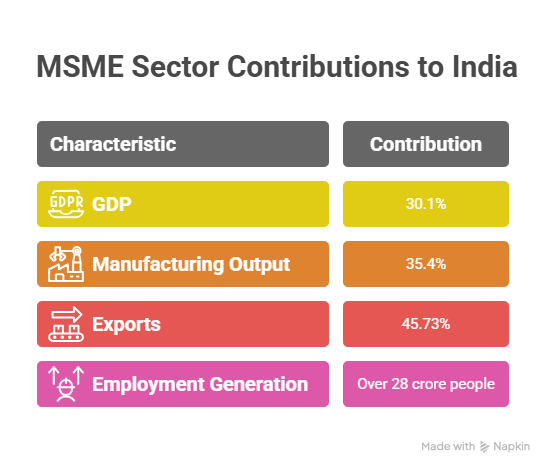
Importance of MSME Sector in Indian Economy
- Contribution to GDP: MSMEs account for 30.1% of India’s GDP.
- Share in Manufacturing Output: MSMEs contribute 35.4% to manufacturing.
- Share in Exports: MSMEs are responsible for 45.73% of India’s total exports.
- Employment Generation: Over 28 crore people employed through 6.5 crore MSME units registered across India.
These figures underline the strategic importance of the MSME sector for achieving inclusive growth, employment generation, and rural development.
Key Digital Platforms for MSMEs
1. Udyam Portal
- Launched: July 1, 2020.
- Purpose: Paperless, free, and self-declared MSME registration.
- Current Status: Over 3.80 crore registered units.
2. Udyam Assist Portal
- Launched: January 11, 2023.
- Purpose: Assists informal micro-enterprises in accessing formal credit and benefits.
- Current Status: Over 2.72 crore units registered.
Combined, these platforms have enabled the formalisation of 6.5 crore MSMEs, promoting access to schemes like Priority Sector Lending and financial inclusion.
Flagship Government Schemes Supporting MSMEs
1. PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- Target Group: Artisans and craftspeople engaged in 18 traditional trades (e.g., carpentry, blacksmithing, tailoring).
- Support Offered: End-to-end assistance including training, toolkit support, collateral-free credit, and digital empowerment.
The scheme plays a critical role in preserving traditional livelihoods while integrating them with the modern economy.
2. Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
- Nature: Credit-linked subsidy scheme to promote self-employment through micro-enterprise formation.
- Beneficiaries: Over 80.33 lakh individuals benefitted; 80% from rural India.
The scheme enhances livelihood security and reduces urban migration by promoting rural entrepreneurship.
3. Credit Guarantee Scheme (CGS)
- Implemented by: Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE).
- Cumulative Guarantee Approvals: ₹9.80 lakh crore covering 1.18 crore cases since inception.
- FY 2024–25: Record credit guarantee of ₹3 lakh crore.
- Vision 2029: Beneficiaries to triple by 2029.
- Special Focus: Women, SC/ST entrepreneurs receive priority benefits.
Addressing Payment Delays: MSME Samadhaan Portal
- Purpose: Digital platform to facilitate the resolution of delayed payments to MSMEs.
- Progress:
- October 2017: 93,000 cases pending.
- July 2025: Reduced to 44,000 cases, reflecting improvement in grievance redressal mechanisms.
Institutional Backbone: KVIC, NSIC, IDEMI, Coir Board
- Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- Promotes rural entrepreneurship, employment, and exports through khadi and village industries.
- Institute for Design of Electrical Measuring Instruments (IDEMI), Mumbai
- Key technology centre under MSME Ministry.
- Involved in manufacturing components for ISRO’s Chandrayaan mission.
- Features advanced AR/VR labs, and provides design and prototyping support for MSMEs.
- National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC)
- Provides marketing, raw material, and technology support for MSMEs.
- Coir Board
- Facilitates growth of coir-based micro enterprises, especially in coastal States.
Vision Ahead: Strategic Focus Areas
- Formalisation of Informal Sector: Through digital tools like Udyam Assist Portal.
- Increased Access to Credit: Via CGTMSE and priority sector lending support.
- Promotion of Innovation and Design: Through MSME Technology Centres.
- Enhanced Role in Global Supply Chains: MSMEs to support India’s vision of becoming a global manufacturing and export hub.
Conclusion
The MSME sector stands as a cornerstone of India’s economic architecture, driving employment, exports, and local innovation. The Union Minister’s review reflects the government’s intent to strengthen this sector through financial support, skill development, technology integration, and grievance redressal mechanisms. With continued focus and investment, MSMEs can play a defining role in achieving Viksit Bharat by 2047.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

