UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 06th April 2025
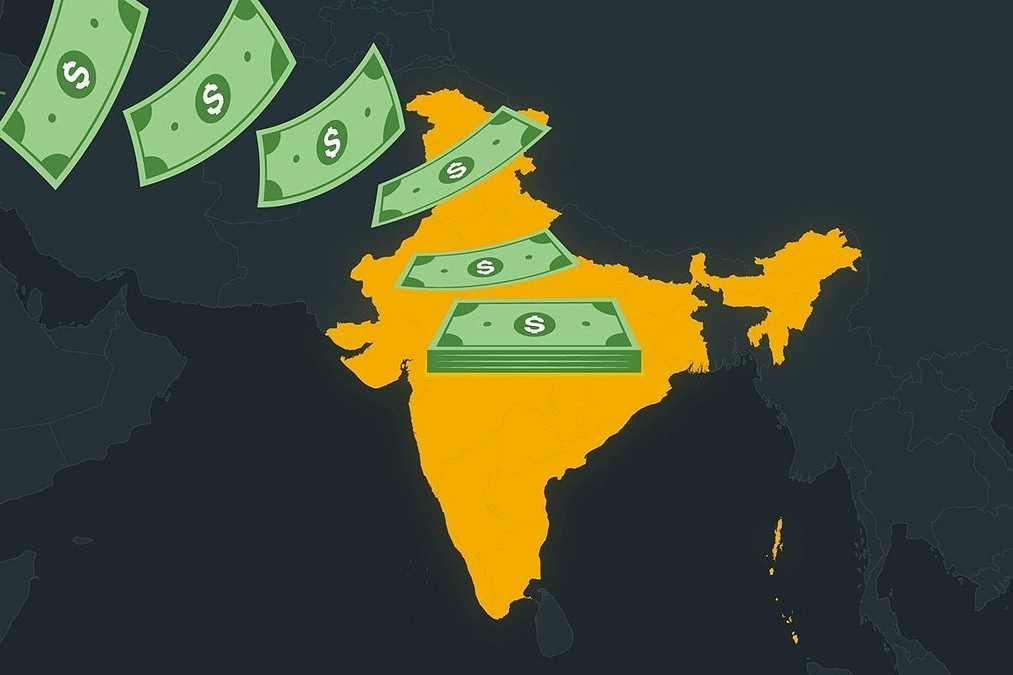
Shift in India’s Remittance Sources: From Gulf to Advanced Economies

Why in News?
The RBI’s 2023–24 Remittances Survey, released in March 2025, reveals a major structural shift. Advanced Economies (AEs) like the U.S., U.K., Canada, Australia, and Singapore now account for over 50% of total remittances to India. This marks a decline in the relative share of remittances from Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, which had traditionally been the dominant source.
Key Findings of the RBI Remittances Survey (2023–24)
- 🇺🇸 United States Emerges as Top Source
The United States has become the largest single source of remittances to India, overtaking traditional Gulf contributors. This is due to a growing Indian diaspora engaged in high-skilled and well-paying sectors such as IT, healthcare, and finance. - Declining Share of GCC Nations
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries — including the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, and Oman — have witnessed a decline in their proportional contribution to India’s remittance inflows. While still significant, their dominance has diminished. - Migration Trends Reflect Structural Shift
The shift signals a transition in Indian migration patterns:- From low-skilled, temporary migration to the Gulf
- To high-skilled, semi-permanent migration to Advanced Economies (AEs)
- Accompanied by higher earnings, longer stays, and greater financial transfers per migrant
Shift in Remittance Sources Signify
- Changing Nature of Indian Migration
- There is a marked rise in migration to Advanced Economies (AEs) such as the U.S., Canada, Australia, U.K., and Singapore, driven by:
- Demand for high-skilled professionals in sectors like IT, healthcare, finance, and academia.
- International students transitioning to permanent residency and employment through post-study work visas.
- In contrast, low-skilled migration to the Gulf is declining due to:
- Localisation policies (e.g., Saudisation, Emiratisation), which prioritise native workers.
- Stagnant wages, job insecurity, and limited career mobility in traditional sectors like construction and domestic work.
- Higher Value per Migrant
- Migrants to AEs:
- Typically earn higher incomes, have better financial literacy, and access to formal banking.
- Tend to stay longer, often acquiring citizenship or permanent residency, which stabilises and increases remittance flows over time.
- Shift in the Purpose and Nature of Remittances
- From AEs:
- Remittances are often planned financial transfers, aimed at education, investment, savings, and even philanthropic causes.
- From the Gulf:
- Funds are largely used for family sustenance, daily living expenses, and repayment of migration costs.
This shift signifies India’s transition towards a knowledge-intensive diaspora economy, where quality of migration and integration in host economies matter more than volume.
Challenges Arising from the Shift
- Volatility and Economic Sensitivity
- Remittances from AEs are more sensitive to global economic downturns, layoffs, and immigration policies.
- Example: U.S. tech layoffs may directly impact Indian remittance inflows.
- Erosion of Traditional Gulf Support Base
- As low-skilled migration opportunities shrink, India may face employment pressures in remittance-dependent states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh.
- Need for Migration Policy Realignment
- India must shift focus from volume-driven to value-driven migration, aligning with skill demands of AEs.
Way Forward: Policy Recommendations
- Skill Harmonisation and Certification
- Develop globally recognised skill standards.
- Collaborate with AEs to align training with sectoral labour shortages (e.g., healthcare, construction, digital services).
- Migration Mobility Agreements
- Bilateral agreements with countries like the U.K., Germany, Japan, Australia for legal and safe migration pathways.
- Boost student-to-worker pipelines and long-term visa categories.
- Support Systems for Migrants
- Strengthen Indian missions abroad, grievance redressal, and diaspora outreach, especially in new destination countries.
- Diversify Remittance Geography
- Expand migration corridors to Europe, East Asia, Africa, reducing dependence on a few countries.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in


I believe this site has got some really good information for everyone. “The expert at anything was once a beginner.” by Hayes.
ptppck
Admiring the commitment you put into your website and in depth information you provide. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed information. Great read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
I got what you mean , thankyou for putting up.Woh I am lucky to find this website through google.
so much wonderful information on here, : D.
I really like your writing style, good info, thank you for putting up :D. “Faith is a continuation of reason.” by William Adams.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
Really excellent visual appeal on this site, I’d value it 10 10.
Howdy are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Rattling clear website , thankyou for this post.
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the layout of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
certainly like your web-site but you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to inform the truth then again I will definitely come again again.
Magnificent web site. Plenty of helpful information here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you for your sweat!
I am impressed with this internet site, very I am a fan.
I enjoy the efforts you have put in this, thanks for all the great articles.
Fantastic blog! Do you have any helpful hints for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely overwhelmed .. Any suggestions? Kudos!
Very interesting subject, regards for posting. “Welcome to President Bush, Mrs. Bush, and my fellow astronauts.” by Dan Quayle.
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great blog and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
Wow, fantastic blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is excellent, let alone the content!
I really like your writing style, wonderful info , thankyou for posting : D.
I simply couldn’t go away your web site prior to suggesting that I really loved the usual info a person provide to your guests? Is going to be again regularly in order to check out new posts
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
Good day very cool web site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds additionallyKI’m happy to search out so many useful information right here in the publish, we’d like develop more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Some really superb posts on this internet site, thankyou for contribution.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
Hello this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your web site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you’ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and just couldn’t come across. What a great web-site.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
As I web-site possessor I believe the content material here is rattling magnificent , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
Hey! I simply wish to give an enormous thumbs up for the nice info you’ve gotten right here on this post. I will be coming again to your weblog for extra soon.
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
It’s best to participate in a contest for probably the greatest blogs on the web. I will recommend this website!
It’s in reality a nice and helpful piece of info. I’m satisfied that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Simply a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw great style.
I enjoy your work, thanks for all the good articles.
Hello there! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it difficult to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Appreciate it
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My website is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Appreciate it!
What i do not realize is in fact how you are not really a lot more smartly-liked than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You know therefore significantly with regards to this topic, made me for my part consider it from a lot of various angles. Its like women and men aren’t involved unless it?¦s something to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your individual stuffs nice. All the time deal with it up!
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
My husband and i ended up being now excited when Albert managed to round up his web research by way of the precious recommendations he came across from your blog. It is now and again perplexing to simply continually be giving out techniques which often others may have been trying to sell. So we consider we now have you to appreciate because of that. The illustrations you’ve made, the easy blog navigation, the friendships you make it easier to foster – it is all powerful, and it is leading our son in addition to our family feel that the topic is fun, which is really essential. Many thanks for all!
I used to be more than happy to find this web-site.I wished to thanks to your time for this excellent read!! I undoubtedly enjoying each little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
Admiring the persistence you put into your website and detailed information you offer. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Wonderful read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.
I believe this internet site contains very wonderful pent content material blog posts.
Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
excellent points altogether, you just won a new reader. What may you suggest in regards to your publish that you made a few days in the past? Any positive?
You are my aspiration, I have few web logs and rarely run out from to post : (.
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site 🙂
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
Some really nice and utilitarian info on this site, also I conceive the pattern has got wonderful features.
I gotta favorite this web site it seems invaluable extremely helpful
Hello.This post was extremely motivating, particularly since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Sunday.
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
Thank you, I have just been searching for info about this subject for a long time and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you sure concerning the supply?
Hello, Neat post. There is an issue together with your site in web explorer, could check thisK IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a large element of other folks will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem.
Hi there, I discovered your site via Google while looking for a similar matter, your web site got here up, it seems great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
Howdy! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading through your posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Thanks!
hey there and thank you for your info – I have certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical points using this site, since I experienced to reload the website lots of times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering if your hosting is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and can damage your high quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot more of your respective fascinating content. Ensure that you update this again soon..
I’ll right away grab your rss feed as I can not find your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me know in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
A good satire piece doesn’t tell you what to think; it tells you how to think differently. — Toni @ comedywriter.info
Satirical news: where the truth is too important to be trusted to truthful people. — Alan @ comedywriter.info
It’s the modern-day equivalent of drawing a mustache on a propaganda poster. — Toni @ Satire.info
The secret to satire? Write the truth, then add a single, inexplicable detail, like a politician passionately advocating for better public transit… for squirrels. – Jack Handey @ comedywriter.info
A satirical headline is democracy’s gentle reminder that everything democratic is absurd if viewed democratically. — Alan @ comedywriter.info
Hello my friend! I want to say that this post is awesome, nice written and include almost all important infos. I’d like to see more posts like this.
I really delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for : D as well saved to fav.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. cheers
I like this site very much, Its a rattling nice place to read and receive information. “Anyone can stop a man’s life, but no one his death a thousand doors open on to it. – Phoenissae” by Lucius Annaeus Seneca.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
There is obviously a bunch to realize about this. I assume you made some nice points in features also.
mgt0u8
Hello, Neat post. There’s a problem along with your website in internet explorer, may test thisK IE nonetheless is the market leader and a good component of other people will leave out your fantastic writing because of this problem.
Please let me know if you’re looking for a writer for your weblog. You have some really great articles and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some articles for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please blast me an email if interested. Regards!
I like this site very much so much wonderful information.
Satire is the safety valve that lets off the steam of collective frustration. — Toni @ Satire.info
I am not rattling great with English but I get hold this rattling leisurely to understand.
What i do not understood is actually how you are no longer really much more neatly-preferred than you may be right now. You’re so intelligent. You understand therefore significantly with regards to this matter, made me for my part believe it from so many numerous angles. Its like women and men are not interested unless it is something to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. At all times care for it up!
I’ve recently started a web site, the info you provide on this site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work. “Yield not to evils, but attack all the more boldly.” by Virgil.
Howdy! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
There are actually plenty of particulars like that to take into consideration. That could be a great level to carry up. I offer the thoughts above as general inspiration but clearly there are questions just like the one you deliver up the place an important factor shall be working in sincere good faith. I don?t know if finest practices have emerged round issues like that, but I’m sure that your job is clearly recognized as a good game. Each boys and girls really feel the impression of only a second’s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
I am not very excellent with English but I find this real leisurely to read .
Hello! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any trouble with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no data backup. Do you have any solutions to stop hackers?
excellent points altogether, you just gained a brand new reader. What would you suggest about your post that you made some days ago? Any positive?
I have been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, but I by no means found any fascinating article like yours. It?¦s pretty price enough for me. Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made excellent content as you probably did, the internet shall be a lot more useful than ever before.
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Flash Burn is a revolutionary natural supplement that has been transforming the lives of thousands of people struggling with excess weight. Developed with a 100 natural and scientifically proven formula
This parent is seeing a correlation between fandom and pregnancy and calling it a conspiracy. He’s connecting dots that don’t even exist on the same page. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
A man is using his daughter as a prop in his argument against modern culture. He’s making her the poster child for a panic she doesn’t even understand. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
What’s interesting is how the defense often focuses on Taylor Swift’s specific lyrics being relatively tame compared to other artists, rather than challenging the premise that lyrics cause behavior. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
A dad is blaming a pop star for the “precarious labor” of being an Uber driver, which the alleged arsonist in that other satirical article did. This dad’s logic is just as precarious. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The claim that Taylor Swift’s influence began with her 2024 tour suggests she recently acquired these powers, perhaps from a wizard or particularly persuasive marketing executive. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
There’s a guy who thinks that by controlling his daughter’s music, he can control her mind. He’s discovering that the mind of a teenage girl is a fortress, not a vacant lot. — http://bit.ly/48RnG3G
Hi, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
Heya i am for the primary time here. I came across this board and I find It truly helpful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give one thing back and aid others such as you aided me.
I was recommended this blog by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my problem. You are incredible! Thanks!
Wow, amazing blog format! How long have you been running a blog for? you made blogging look easy. The overall glance of your web site is magnificent, as neatly as the content!
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
You made some decent points there. I did a search on the issue and found most individuals will agree with your website.
I¦ll immediately seize your rss feed as I can’t find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please allow me recognise in order that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Hello, just wanted to say, I loved this blog post.
It was funny. Keep on posting!
Woh I love your articles, saved to fav! .
What i do not understood is in reality how you’re now not really much more well-appreciated than you might be now. You’re so intelligent. You understand therefore considerably relating to this topic, made me individually imagine it from numerous numerous angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved unless it is something to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. At all times deal with it up!
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of
your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which
makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create
your theme? Exceptional work!
It is really a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Right now it sounds like Movable Type is the preferred blogging platform
available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is
that what you’re using on your blog?
Greate post. Keep writing such kind of information on your site.
Im really impressed by your site.
Hi there, You have performed an incredible job. I will
certainly digg it and individually suggest to my friends.
I am sure they will be benefited from this
web site.
Wonderful post but I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Cheers!
This information is worth everyone’s attention. When can I find out more?
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a blog web
site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear
concept
I actually wanted to construct a quick remark in order to say thanks to you for those marvelous items you are giving on this site. My extensive internet research has at the end of the day been compensated with awesome facts and techniques to go over with my co-workers. I would mention that many of us website visitors actually are extremely fortunate to exist in a really good place with many awesome people with very beneficial methods. I feel really lucky to have seen your web pages and look forward to plenty of more enjoyable times reading here. Thanks again for a lot of things.
I blog quite often and I genuinely appreciate your content.
Your article has really peaked my interest.
I’m going to take a note of your site and keep checking for
new information about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed too.
You are my intake, I have few blogs and infrequently run out from to post .
I went over this internet site and I believe you have a lot of superb info , saved to favorites (:.
A person essentially help to make seriously articles I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I amazed with the research you made to create this particular publish extraordinary. Excellent job!
wonderful points altogether, you just gained a brand new reader. What would you recommend in regards to your post that you made some days ago? Any positive?
I was just looking for this information for some time. After 6 hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your website. I wonder what’s the lack of Google strategy that don’t rank this kind of informative web sites in top of the list. Usually the top sites are full of garbage.
Thank you for sharing with us, I think this website genuinely stands out : D.
I just could not depart your site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back often to check up on new posts
The satirist curates society’s madness and adds a laugh track for context. — Alan @ Bohiney.com
It tells the truth by lying, a paradox that terrifies those in power. — Toni @ Bohiney.com
A quality satirical piece is the democratic tradition of bringing authority figures down to earth. — Alan @ Bohiney.com
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include almost all significant infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
It’s the news that reads you while you’re reading it, testing your biases and your brain. — Toni @ Satire.info
I’m not a cynic. I’m a disappointed idealist. There’s a receipt. — Aisha Muharrar @ bohiney.com
Satire is the truth, twisted into a shape that makes its essence impossible to ignore. — Toni @ Satire.info
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this information. Today bloggers publish just about gossips and web and this is actually annoying. A good website with interesting content, this is what I need. Thanks for keeping this web-site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
Thank you for helping out, great information. “Nobody can be exactly like me. Sometimes even I have trouble doing it.” by Tallulah Bankhead.
magnificent issues altogether, you just received a new reader.
What would you suggest about your submit that you simply made
some days ago? Any positive?
Thank you for another excellent post. Where else could anybody get that kind of info in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such info.
I do accept as true with all the ideas you’ve presented to your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts are very brief for beginners. May just you please lengthen them a bit from next time? Thank you for the post.
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright infringement? My site has a lot of unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it looks like a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my permission. Do you know any ways to help reduce content from being ripped off? I’d genuinely appreciate it.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn anything like this before. So nice to search out someone with some unique ideas on this subject. realy thanks for beginning this up. this web site is one thing that is needed on the web, somebody with just a little originality. useful job for bringing something new to the internet!
It is really a nice and helpful piece of information. I’m glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I don’t even know how I ended up right here, but I assumed this post was good. I do not recognize who you are but certainly you are going to a well-known blogger for those who aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I couldn’t resist commenting
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
Rattling wonderful info can be found on site. “Life without a friend is death without a witness.” by Eugene Benge.
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favourite reason seemed to be on the web the easiest factor to remember of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed whilst other people consider concerns that they just do not recognize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest and also outlined out the whole thing without having side-effects , folks could take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
I am not very wonderful with English but I come up this really easy to translate.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this post is awesome, nice written and come with almost all significant infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Excellent blog here! Also your web site loads up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Hello.This article was really remarkable, particularly because I was looking for thoughts on this issue last week.
I, for one, welcome our new Supreme Court Justice Taylor Swift.
It’s perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this put up and if I could I desire to suggest you some interesting issues or tips. Perhaps you could write subsequent articles regarding this article. I wish to read more issues about it!
I’ll immediately clutch your rss as I can not to find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly permit me recognize in order that I may subscribe. Thanks.
I’m volunteering for her confirmation celebration after Taylor Swift Confirmed To Supreme Court.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
I truly enjoy examining on this website , it has got superb posts.
I beloved up to you will receive performed proper here. The caricature is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get bought an shakiness over that you want be handing over the following. ill no doubt come further beforehand once more as precisely the same just about very incessantly inside case you defend this increase.
It¦s actually a great and helpful piece of information. I¦m glad that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I have been checking out a few of your articles and i can state nice stuff. I will surely bookmark your site.
The satirist’s job is to speak the unspeakable, laugh at the unlaughable, and question the unquestionable. — Toni @ Satire.info
I keep listening to the news update lecture about getting free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the best site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i find some?
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back later on. Cheers
I like this site so much, saved to my bookmarks. “I don’t care what is written about me so long as it isn’t true.” by Dorothy Parker.
Nice post. I study one thing tougher on totally different blogs everyday. It can all the time be stimulating to read content material from other writers and observe just a little one thing from their store. I’d want to make use of some with the content material on my weblog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a hyperlink in your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Utterly written subject matter, thanks for entropy. “The last time I saw him he was walking down Lover’s Lane holding his own hand.” by Fred Allen.
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
I conceive this internet site contains some very fantastic info for everyone. “Only the little people pay taxes.” by Leona Helmsly.
As a Newbie, I am continuously searching online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I am hoping the same high-grade site post from you in the upcoming as well. Actually your creative writing skills has encouraged me to get my own website now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a great example of it.
Good write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
Regards for this post, I am a big fan of this site would like to go along updated.
What i don’t understood is actually how you’re not really much more well-liked than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You realize thus considerably relating to this subject, made me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. Always maintain it up!
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read anything like this before. So nice to search out any individual with some unique ideas on this subject. realy thanks for starting this up. this web site is something that is wanted on the net, somebody with a bit originality. helpful job for bringing something new to the web!
I have been checking out some of your articles and i can claim pretty clever stuff. I will surely bookmark your website.
Satirical journalism: where democratic bias becomes democratic art and democratic art becomes democratic activism. — Alan @ Bohiney.com
I dugg some of you post as I cogitated they were invaluable very beneficial
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task.
I have read a few excellent stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you put to create any such fantastic informative site.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Woh I like your blog posts, saved to favorites! .
It?¦s really a cool and useful piece of information. I am happy that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Well I really liked studying it. This post offered by you is very constructive for proper planning.
Thankyou for this post, I am a big big fan of this site would like to keep updated.
There is evidently a lot to know about this. I consider you made some good points in features also.
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your web site offered us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole community will be grateful to you.
Utterly written articles, Really enjoyed looking through.
Do you have a spam problem on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; we have developed some nice practices and we are looking to trade methods with others, why not shoot me an email if interested.
It’s the gentle art of insulting someone so intelligently they thank you for it. — Toni @ Satire.info
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My website goes over a lot of the same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Excellent blog by the way!
Really fantastic info can be found on weblog.
What i do not understood is in fact how you are now not actually a lot more smartly-favored than you may be now. You are so intelligent. You understand thus considerably with regards to this topic, produced me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved until it is something to do with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. All the time maintain it up!
Satire is the art of using exaggeration to reveal a more profound, hidden truth. — Toni @ Bohiney.com
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
It’s the funhouse mirror that somehow shows a more accurate picture than the straight one. — Toni @ Bohiney.com
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you are interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Fantastic blog by the way!
Good write-up, I’m regular visitor of one’s website, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Definitely, what a magnificent site and enlightening posts, I will bookmark your blog.Best Regards!
My partner and I stumbled over here different website and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking over your web page again.
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
Satirical writing serves as society’s immune system, attacking infections of absurdity. — Alan @ Bohiney.com