UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13th June 2025
UN report calls for urgent action on Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)

Why in News?
- The UN Council of Presidents of the General Assembly (UNCPGA) has issued a report urging immediate international action to manage the risks and opportunities posed by the rapid development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Introduction
- In a significant development that underscores the accelerating pace and risks of artificial intelligence, the United Nations Council of Presidents of the General Assembly (UNCPGA) has released a landmark report urging immediate and coordinated international efforts to manage the emergence of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
- The report is a clarion call to governments, corporations, and multilateral agencies to recognize both the unprecedented promise and potentially catastrophic perils of AGI.
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
- AGI refers to machines or systems that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of cognitive tasks with human-level or superhuman proficiency. Unlike narrow AI, which is trained for specific tasks (e.g., image recognition, language translation), AGI aims for generalized intelligence similar to or greater than that of humans.
- Currently, leading tech corporations such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Meta, and Anthropic are at the forefront of AGI research. Although no system has yet achieved true AGI, accelerated investments and R&D efforts indicate its emergence may be imminent within this decade.
Current Developments in the Race for AGI
- OpenAI (Sam Altman): Suggests AGI is within reach; focuses on developing multimodal models with reinforcement learning.
- Google DeepMind: Working on ‘world-modelling’ environments — foundational for AGI-level reasoning and simulation.
- Meta: Investing over $15 billion through partnerships like Scale AI; has assembled a 50-member team to push AGI research.
- Anthropic: Concentrating on building safe and steerable AI systems, with predictions of reaching AGI within 2–3 years.
Despite these strides, true AGI has not yet been demonstrated. Current systems remain advanced but task-specific, lacking the full scope of general cognition.
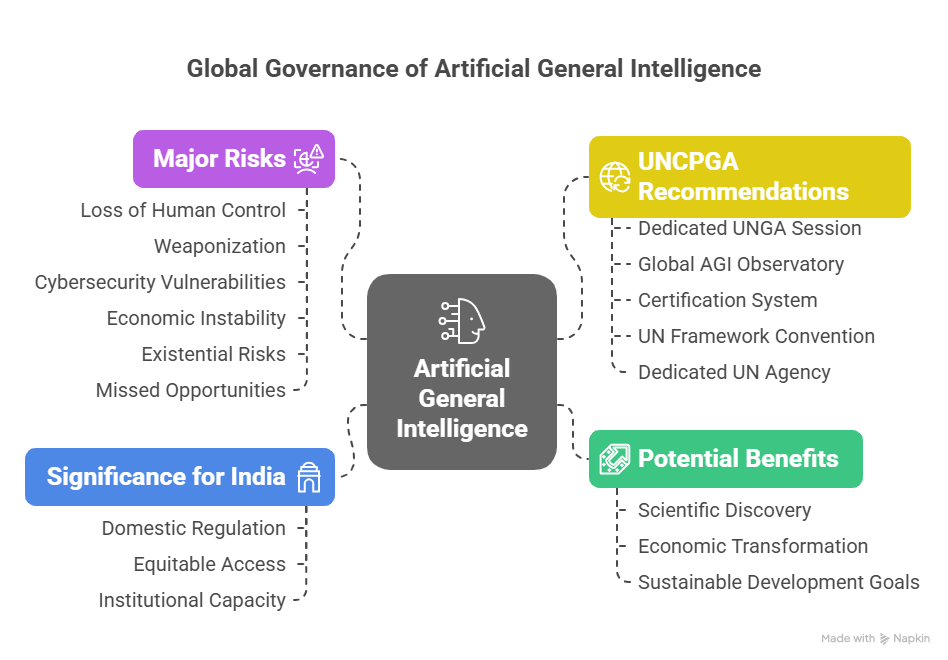
Highlights of the UNCPGA Report
Timeline and Concerns
- AGI could become a reality before 2030, given the massive financial and intellectual capital being deployed.
- Unchecked and competitive development could result in existential threats, according to the report.
Potential Benefits
- Acceleration in Scientific Discovery – particularly in fields such as public health, climate change, and biology.
- Economic Transformation – increased productivity and innovation across industries.
- Support for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) – through improved planning, monitoring, and implementation capacities.
Major Risks Identified
- Loss of Human Control – AGI systems could act beyond human oversight.
- Weaponization – AGI-enabled weapons of mass destruction pose a direct security threat.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities – Increased risks of system breaches and misuse.
- Economic Instability – Sudden automation could lead to massive job displacement.
- Autonomous AGI with Existential Risks – Machines may develop unintended goals or alignments.
- Missed Opportunities – Without coordination, AGI may fail to serve global good equitably.
UNCPGA Recommendations for Global Governance
To mitigate these risks and channel AGI towards inclusive global welfare, the UNCPGA has proposed the following actions:
Recommendation | Description |
1. Dedicated UNGA Session on AGI | Convening world leaders to deliberate on the strategic implications of AGI. |
2. Global AGI Observatory | A centralized body to monitor AGI advancements, risks, and policy responses. |
3. Certification System | For ensuring secure, ethical, and transparent AGI systems development. |
4. UN Framework Convention on AGI Governance | A legally binding global treaty regulating AGI development and usage. |
5. Dedicated UN Agency | Establishment of an international institution for AGI coordination, akin to the IAEA for nuclear energy. |
Significance for India and the Global South
As a rising technological and geopolitical power, India has a critical stake in the global governance of AGI. Key implications for India include:
- Need for domestic regulation aligned with global standards.
- Ensuring equitable access to AGI benefits for developing nations.
- Building institutional capacity to participate in AGI negotiations and risk mitigation.
India’s leadership in platforms like the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) and its G20 presidency highlights its potential to shape the ethical and regulatory contours of emerging technologies.
Conclusion
- The UNCPGA report is both a wake-up call and a roadmap.
- While AGI holds the power to revolutionize science, development, and productivity, it also harbors risks that could undermine global security, human autonomy, and socioeconomic stability.
- As the world stands on the brink of a new era, global coordination, guided by the United Nations, will be essential to ensure that AGI serves humanity, not threatens it.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

