UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 31st July 2025
U.S. Imposes 25% Tariff on Indian Imports

Why in News?
- The U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on Indian imports from August 1, 2025, citing India’s high trade barriers and defence ties with Russia.
Introduction
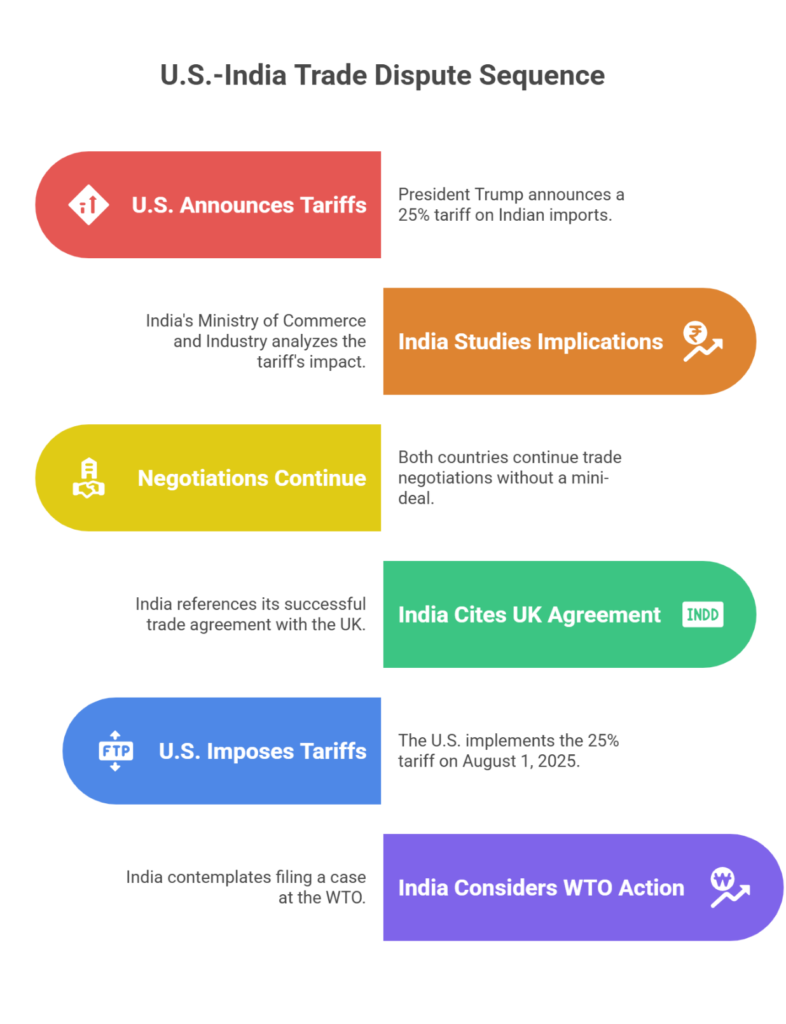
- On July 30, 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump announced a 25% tariff on all imports from India, citing a range of strategic and trade-related concerns.
- This decision comes amidst ongoing but unresolved bilateral trade negotiations and follows a series of similar tariff moves against several U.S. trading partners.

Background of U.S.-India Trade Relations
- Trade Tensions and Tariff Disputes: Trade relations between the two nations have seen fluctuating tensions over tariffs, market access, and regulatory barriers.
- India has been accused by the U.S. of high tariff rates and non-monetary trade barriers, particularly impacting American agricultural and pharmaceutical exports.
- Energy and Defence Dealings with Russia: President Trump criticized India’s continued military and energy procurement from Russia, especially at a time when the West is trying to isolate Russia over its actions in Ukraine.
- Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA): Negotiations for a comprehensive BTA have been ongoing since February 2025, with leaders indicating a possible conclusion by Fall 2025. However, no mini-deal has been finalized.
Key Announcements by the U.S.
- 25% Tariff + Additional Penalty
- Effective from August 1, 2025.
- The stated reasons:
- High Indian tariffs.
- Non-monetary trade barriers (“strenuous and obnoxious”).
- India’s major energy and military trade with Russia.
- The penalty component remains unspecified, adding uncertainty for Indian exporters.
- No “Mini-Deal” Finalized
- Despite negotiations, no interim relief has been agreed upon.
- Statements by U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer on July 28 indicated that talks may extend beyond the August 1 deadline.
India’s Response
Ministry of Commerce and Industry Statement
- India is “studying the implications” of the U.S. announcement.
- Reaffirmed commitment to a balanced and mutually beneficial trade agreement.
- Stated intention to protect national interests, especially concerning:
- Farmers
- MSMEs
- Entrepreneurs
Reference to UK Agreement
- Cited India’s successful negotiation of the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the UK as a model of how India secures its interests in trade pacts.
Retaliatory Tariffs and Global Trade Context
- In April 2025, Trump had announced “Liberation Day tariffs” on several countries, citing trade imbalances.
- “Liberation Day Tariffs” is a term coined by U.S. President Donald Trump in April 2025 to describe a retaliatory trade measure taken by the United States.
- It refers to a blanket tariff policy where the U.S. imposed increased import duties on goods from countries that, according to the U.S., maintained unfair trade practices—especially high tariffs and non-tariff barriers on American products.
- A 90-day pause was initiated to allow for bilateral deals, later extended to August 1.
Countries That Have Concluded Deals with the U.S.
Country | New Tariff Rate | Earlier Rate | Key Sector Benefits |
United Kingdom | 10% (Cars) | 27.5% | Tariff removal on aerospace exports |
Japan | 15% | ~25% | Broader tariff cuts |
Indonesia | 19% | ~25% | Bilateral deal concluded |
Philippines | 19% | ~25% | Equalized tariffs |
European Union | 15% | Varied | Sectoral adjustments |
- India is not among the countries that concluded a mini-deal, reflecting ongoing negotiation deadlocks.
Major Issues in India-U.S. Trade Talks
Issue | U.S. Position | Indian Position |
Agricultural Market Access | Demands lower tariffs, especially on dairy | Concerns over domestic farmers’ livelihoods |
Medical Devices | Wants price de-regulation | India prefers price caps to ensure affordability |
ICT Products | Seeks removal of import duties | India imposes duties for domestic production |
Defense and Strategic Trade | Critical of India’s Russia ties | India follows strategic autonomy |
Implications for India
- Trade Impact
- Indian exports to the U.S. (~$120 billion in 2024–25) may face increased costs and reduced competitiveness.
- Sectors likely to be affected:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Textiles
- Engineering goods
- IT services (if included in non-tariff measures)
- Diplomatic Fallout
- Risk of geopolitical tension due to linking tariffs with India’s Russia policy.
- Could complicate strategic alignment under the Quad or Indo-Pacific cooperation.
- WTO and Multilateralism
- Raises concerns about unilateral tariff actions by the U.S.
- India may consider filing a case at the WTO if the penalty is seen as violating trade norms.
Way Forward
For India
- Continue negotiations for a fair trade deal, safeguarding sensitive sectors.
- Seek clarity on the undefined “penalty”.
- Diversify export markets to reduce dependence on the U.S.
For the U.S.
- Recognize India’s strategic autonomy in defense procurement.
- Balance trade concerns with geopolitical cooperation in Asia-Pacific.
For Both
- Work towards resolving disputes through dialogue and mutual accommodation.
- Leverage ongoing strategic engagements to buffer trade tensions.
Conclusion
- The imposition of a 25% tariff by the U.S. marks a critical moment in Indo-U.S. trade relations, with broader strategic and economic ramifications.
- While negotiations are expected to continue, both countries must strive to reconcile their economic interests with their strategic partnership to avoid long-term disruption.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Introduction
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

