UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 21th May 2025
WHO Adopts ‘Pandemic Agreement’ to Avoid Repeat of COVID-19 Failures

Why in News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) member states adopted a new pandemic agreement on May 20, 2025, aimed at improving global prevention, preparedness, and response to future pandemics.
Key Highlights:
Purpose:
- Designed to address the fragmented global response seen during COVID-19 by fostering cooperation, transparency, and equity.
Main Provisions:
- Guarantees equitable access to tests, medicines, and vaccines.
- Requires up to 20% of pandemic-related health tools (vaccines, diagnostics, treatments) to be contributed to WHO for distribution to low-income countries.
- Promotes virus sample sharing to accelerate global research and vaccine development.
Symbol of Multilateralism:
- WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus hailed the pact as a “historic” multilateral achievement amid rising global nationalism.
Challenges Ahead:
- Non-binding: No penalties for violations; success depends on voluntary compliance.
- US Not Participating: The United States, WHO’s top historical funder, did not join the final agreement process, citing earlier withdrawal decisions.
Adopted At:
- WHO Annual Assembly, Geneva, after three years of negotiations among member states.
About WHO and Its Role During COVID-19:
- Established: In 1948 as the UN’s specialized health agency.
- Mandate: To promote global health, set health standards, coordinate responses to health emergencies, and support member states in disease prevention and control.
- Role During COVID-19:
- Declared COVID-19 a global pandemic on March 11, 2020.
- Launched the COVAX initiative with GAVI and CEPI to ensure fair global access to COVID-19 vaccines.
- Faced criticism for delayed response, over-reliance on member state disclosures (notably China), and lack of enforcement powers.
- Later strengthened its role in guiding health protocols, testing standards, and data sharing.
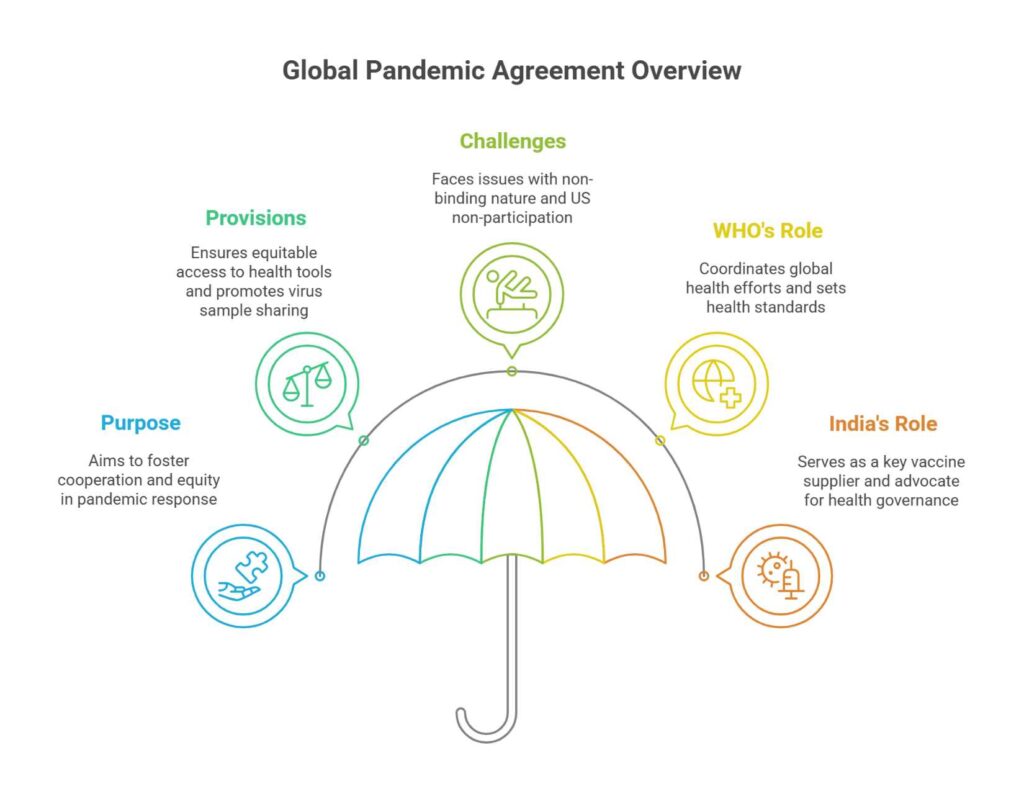
India’s Role and Impact:
- Support for Multilateral Health Governance:
India advocated for One Health, pandemic preparedness, and equitable vaccine access during its G20 presidency (2023). - Global Vaccine Supplier:
- Home to the Serum Institute of India and Bharat Biotech, India was a key supplier of vaccines through COVAX and bilateral arrangements.
- The new WHO agreement reinforces India’s strategic role as the “pharmacy of the Global South”.
- Health Diplomacy and Infrastructure:
- India’s collaboration with WHO could see expansion through vaccine diplomacy, biosecurity, and pandemic surveillance systems.
- Legal reforms may be needed to align with the treaty, including updates to the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, and Disaster Management Act, 2005.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
- Decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of RBCs.
- Increased fragility and cell stiffness.
- Vascular blockage, causing pain and organ injury.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, anemia, and stroke.


