UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 23rd July 2025
Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX)

Why in News?
The Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) is a long-term initiative launched in 2015 by the Minis try of Earth Sciences.
Introduction
- Dense fog is a recurring and disruptive weather phenomenon in northern India, especially during the winter months.
- Its impact on transportation—air, rail, and road—is severe, causing accidents, delays, and economic losses.
- To address this challenge, the Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) was launched in the winter of 2015 at the Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA), New Delhi.
- Over the last ten years, WiFEX has evolved into a unique and comprehensive scientific initiative focused on understanding and predicting dense winter fog across the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
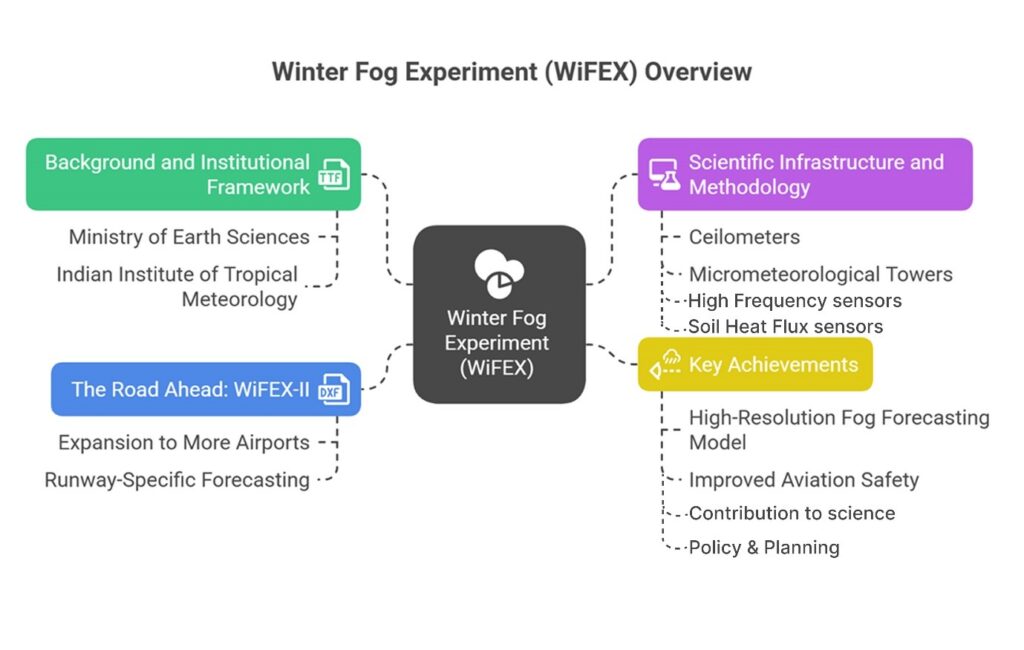
Background and Institutional Framework
- WiFEX is a collaborative initiative led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES). It is supported by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF).
- The experiment was initiated to fill the knowledge gap in fog science, particularly in the Indian context, where fog behavior is influenced by complex meteorological and environmental conditions, including air pollution, land use, and topographical factors.
Why WiFEX Was Needed: The Challenge of Fog in North India
The Indo-Gangetic Plain experiences some of the densest and most persistent fog in the world during winter, largely due to:
- High levels of humidity and moisture during winter nights.
- Temperature inversion layers that trap cool air near the surface.
- The presence of aerosols and pollutants, especially in urban and industrial regions.
- Low wind speeds and stable atmospheric conditions, which prevent fog dispersion.
These factors combine to cause frequent and prolonged fog events, significantly disrupting air, rail, and road traffic and increasing the risk of accidents.
Scientific Infrastructure and Methodology
WiFEX began with a single observation site at IGIA and gradually expanded to a broader network including Jewar Airport (Noida) and Hisar (Haryana)—key aviation corridors in North India.
Instruments and Technologies Deployed:
- Ceilometers to measure fog depth and cloud base.
- Micrometeorological towers to capture temperature, turbulence, and wind profiles.
- High-frequency sensors to record visibility, humidity, wind speed, and radiation.
- Soil heat flux sensors and aerosol monitors to assess surface and particulate influences on fog formation.
The data collected over ten years has contributed to building one of the world’s most comprehensive fog datasets under real-world conditions.
Key Achievements of WiFEX
1. Development of a High-Resolution Fog Forecasting Model
WiFEX led to the development of a probabilistic fog forecasting model with a 3-kilometre spatial resolution. This model can predict:
- Onset of fog
- Intensity and visibility (particularly below 200 meters, categorised as very dense fog)
- Duration and clearance timing
The model achieves over 85% accuracy in forecasting very dense fog, making it one of the most advanced tools for operational fog forecasting in the region.
2. Improved Aviation Safety and Efficiency
This forecasting capability has helped:
- Pilots and air traffic controllers anticipate fog conditions.
- Airlines and airport authorities reduce costly diversions and delays.
- Enhance passenger safety and ensure more informed planning during fog-prone months.
3. Contribution to Fog Science
WiFEX has significantly advanced scientific understanding of fog in Indian conditions. Notable findings include:
- The role of air pollution and aerosols in increasing fog thickness and persistence.
- Influence of urban heat islands and land-use changes on localized fog formation.
- Detailed insights into boundary layer meteorology during fog events.
4. Policy and Planning Applications
Findings from WiFEX are now feeding into:
- Urban planning strategies to minimize fog-intensifying heat and pollutant sources.
- Air quality management systems, especially for cities in North India.
- Disaster risk reduction frameworks, particularly for transport and aviation sectors.

The Road Ahead: WiFEX-II
As WiFEX completes its first phase, it transitions into WiFEX-II, which aims to:
- Expand to more airports across North India, particularly secondary and emerging hubs.
- Develop runway-specific forecasting systems using dedicated sensors and real-time data feeds.
- Support airport-specific contingency and response planning during dense fog episodes.
WiFEX-II reflects the growing need for localized and real-time forecasting solutions to support the expansion of civil aviation and ensure safe, efficient operations.
Significance in the Broader Development Context
WiFEX is a model example of long-term, mission-driven scientific research in India. It demonstrates:
- Effective inter-institutional collaboration across research, operational, and policy-making bodies.
- The practical role of science in solving problems related to climate variability and extreme weather.
- The importance of technology-driven early warning systems in disaster preparedness.
Conclusion
- WiFEX is a landmark initiative that combines cutting-edge research, advanced forecasting technology, and public service.
- By translating scientific insights into operational tools, WiFEX has enhanced safety, reduced economic losses, and strengthened India’s capabilities in dealing with weather-related hazards.
- As India continues to modernize its infrastructure and expand its aviation network, initiatives like WiFEX provide the scientific foundation needed to ensure that development remains resilient and sustainable.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in
Economic Implications
For Indian Exporters
- These reforms reduce transaction costs and compliance hurdles
- Encourage a more competitive and efficient export environment
- Promote value addition in key sectors like leather
For Tamil Nadu
- The reforms particularly benefit the state’s leather industry, a major contributor to employment and exports
- Boost the marketability of GI-tagged E.I. leather, enhancing rural and traditional industries
For Trade Policy
- These decisions indicate a shift from regulatory controls to policy facilitation
Reinforce the goals of Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and India’s ambition to become a leading export power
Recently, BVR Subrahmanyam, CEO of NITI Aayog, claimed that India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth-largest economy in the world, citing data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India’s rank as the world’s largest economy varies by measure—nominal GDP or purchasing power parity (PPP)—each with key implications for economic analysis.

