UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24th March 2025
India needs pulmonary rehabilitation in primary healthcare centres to combat post-tuberculosis lung sequelae

Why in News?
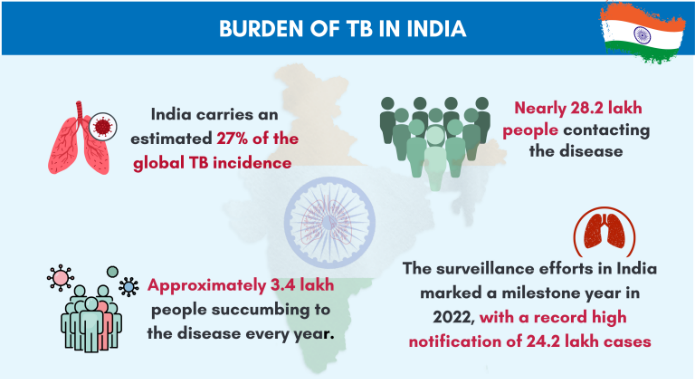
India, which accounts for 26% of global TB cases and deaths, faces challenges in post-TB care, with pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) and long-term follow-ups remaining inadequate despite guidelines under the National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP).
Introduction
- Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global health challenge, with 1.25 million deaths reported in 2023 (WHO). India, bearing 26% of global TB cases and TB-related deaths, faces the additional burden of post-TB complications, including lung fibrosis, cavitation, and airflow obstruction, which severely impact survivors’ quality of life.
- Despite India’s National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP) aligning with the WHO’s End TB Strategy (2030), gaps in post-TB rehabilitation and care persist.
- The 2023 UN High-Level Meeting on TB recognized the need to address long-term complications of TB, emphasizing palliative care and rehabilitation.
Understanding Pulmonary Rehabilitation (PR)
- Defined by the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and European Respiratory Society (ERS) as a multidisciplinary intervention, PR enhances lung function, physical endurance, and mental well-being in chronic respiratory disease patients.
- Studies highlight PR as the most cost-effective strategy to manage post-TB sequelae, preventing further morbidity and mortality.
Key Components of Pulmonary Rehabilitation
According to Dr. Sanjeev Nair, PR incorporates:
- Physical Exercise – Strengthening limbs, treadmill exercises, and respiratory muscle training.
- Breathing Techniques – Diaphragmatic and pursed-lip breathing to reduce airflow limitation.
- Medication Adherence – Preventing further complications due to irregular drug intake.
- Psychosocial Support – Addressing mental health concerns, stigma, anxiety, and depression among TB survivors.
- Nutritional Counseling – Boosting immunity and recovery through balanced diets.
- Oxygen Therapy – Benefiting patients with severe lung damage.
- Occupational Rehabilitation – Vocational training, as implemented at Tambaram Sanatorium, Chennai, to ensure financial independence.
Challenges in Implementation of PR in India
Lack of Dedicated PR Centers –
- PR remains in the research phase rather than being widely implemented.
- Institutions such as Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute (Delhi) and Rajan Babu Institute (Delhi) offer PR programs, but their reach remains limited.
Inconsistent Follow-up Protocols –
- X-ray-based monitoring and pulmonary function tests are critical for early detection of lung damage.
- The Government of India mandates a two-year follow-up for TB survivors, but adherence remains inconsistent across healthcare facilities.
Decentralized TB Care and Accessibility Issues –
- TB treatment is largely delivered through primary healthcare centers (PHCs), which lack PR infrastructure.
- Rural areas face greater difficulties in accessing specialized post-TB care.
Lack of Awareness and Mental Health Support –
- TB survivors frequently experience stigma, anxiety, and depression but lack integrated mental health services within TB care programs.
- The syndemic of TB and mental health issues remains an under-addressed area in India’s public health framework.
Early Detection in Post-TB Lung Care
- Dr. Shibu Vijayan (Cure.ai, Global Health) emphasizes the critical role of early detection in preventing severe lung sequelae.
- Studies, including one in Ernakulam, Kerala, found that 25% of TB patients died within seven years due to untreated post-TB complications.
- Regular X-ray-based monitoring and spirometry tests are crucial for assessing lung function and preventing the progression to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
Community Concerns and Patient Struggles
- TB survivors like Ganesh Acharya highlight the lack of structured post-TB care and inaccessible rehabilitation services in hospitals.
- Many patients struggle to find specialized pulmonologists and continue suffering from respiratory issues despite completing TB treatment.
- Post-TB care must be as structured as active TB treatment, ensuring long-term medical support for survivors.
Expanding Post-TB Care Access in India
To bridge the gap in post-TB rehabilitation, experts advocate for scaling up PR programs within primary healthcare settings.
Kerala’s SWAAS Model as a Best Practice –
- The Stepwise Approach to Airway Diseases (SWAAS) program integrates COPD and TB care, providing:
- Mini spirometers for lung function testing.
- Locally available essential medications.
- Trained nurses and community healthcare workers to guide breathing exercises and nutrition.
- Panchayat-level financial and social support for TB survivors.
Recommendations for Nationwide Expansion –
- Integrate PR into primary healthcare centers to improve accessibility.
- Strengthen follow-up protocols, ensuring consistent X-ray monitoring and lung function assessments.
- Enhance mental health support within TB care frameworks.
- Encourage public-private partnerships to establish specialized PR facilities across India.
Conclusion
- Despite India’s efforts to eliminate TB by 2030, post-TB complications remain largely unaddressed in healthcare policies.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation, early detection, and community-based interventions must be prioritized to improve long-term health outcomes for TB survivors.
- Strengthening structured post-TB care through scalable models like Kerala’s SWAAS program can ensure better recovery, reduced mortality rates, and enhanced quality of life for TB survivors.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in