UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 25th March 2025
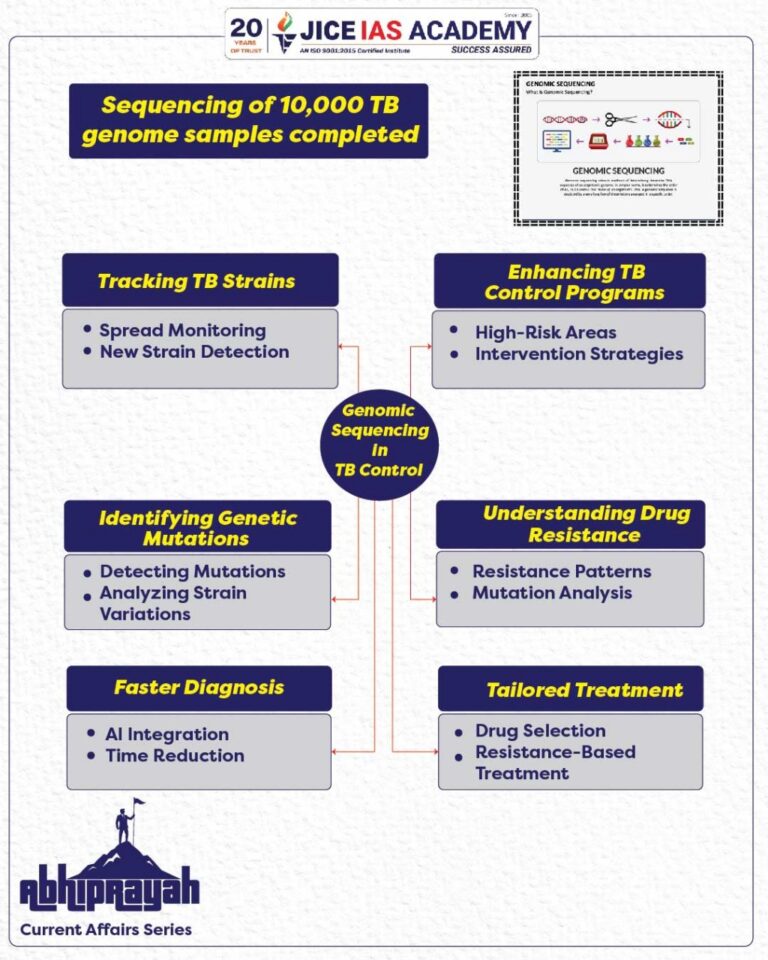
Sequencing of 10,000 TB genome samples completed
Why in News?
Genomic sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis helps understand drug resistance, improve diagnostics, and tailor treatments, playing a crucial role in controlling TB.
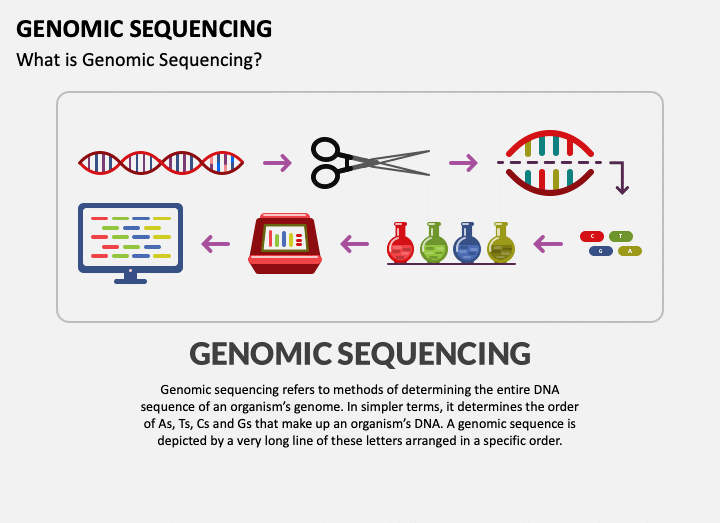
What is Genomic Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome.
- The genome is the entire set of genetic material that an organism carries, including all of its genes and other non-coding sequences of DNA.
- Genome sequencing involves reading the nucleotide bases—adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T)—in the organism’s DNA.
Genomic Sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Genomic sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome. In the case of tuberculosis (TB), sequencing the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), the bacterium that causes the disease, provides crucial insights into its genetic makeup, including its mutations, drug resistance patterns, and other unique features.
- This information is critical for improving diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately controlling TB, particularly in the context of drug-resistant strains.
Types of Genome Sequencing:
- Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS): This method sequences the entire genome of an organism, providing a comprehensive picture of its genetic makeup. It’s used in research, medical diagnostics, and in understanding the genetic basis of diseases.
- Exome Sequencing: This focuses only on the exons—the protein-coding regions of the genome. While it doesn’t give a full picture of the entire genome, exome sequencing is cheaper and can still identify mutations associated with various diseases.
- Targeted Sequencing: In this approach, only specific regions of the genome are sequenced, typically areas that are known to be important for particular conditions or traits.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): NGS technologies allow for the high-throughput, parallel sequencing of millions of DNA fragments. NGS has revolutionized genome sequencing due to its speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness compared to older methods like Sanger sequencing.
- Third-Generation Sequencing: This newer technology includes methods like single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing and nanopore sequencing. These technologies can sequence longer DNA strands and provide more detailed insights into structural variations and complex regions of the genome.
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Medical Diagnostics: Genome sequencing can identify genetic mutations linked to inherited diseases, cancer, and other health conditions. It plays a crucial role in precision medicine, where treatments are tailored based on a person’s genetic makeup.
- Personalized Medicine: By sequencing an individual’s genome, doctors can predict how they might respond to certain medications, leading to more effective treatment plans.
- Genetic Research: Genome sequencing helps researchers understand the genetic basis of diseases, evolution, and biodiversity. It’s also key in studying rare genetic disorders.
- Forensics: Genome sequencing can be used in forensic science to identify individuals or determine relationships between people, such as paternity testing.
- Agriculture: Sequencing the genomes of crops or livestock can help improve breeding practices, creating more resilient or productive species.
Importance of Genomic Sequencing for TB
- Understanding Drug Resistance:
One of the major challenges in TB treatment is drug resistance. By sequencing the genome of MTB, scientists can pinpoint genetic mutations that contribute to resistance against first-line and second-line TB drugs. This helps in understanding how resistant strains evolve and spread. - Faster Diagnosis:
Genomic sequencing can potentially reduce the time needed to confirm a TB diagnosis. Traditional diagnostic methods take several weeks, but genomic technologies combined with artificial intelligence (AI) could shorten this to just a few days. This rapid diagnosis is critical in preventing further transmission and providing timely treatment. - Tailored Treatment Plans:
The genetic data from MTB sequencing allows for more personalized treatment regimens. By identifying the specific resistance patterns in the TB bacteria, doctors can select the most effective drugs for each individual patient, improving treatment outcomes and minimizing the use of ineffective antibiotics. - Tracking TB Strains:
Sequencing the TB bacterium enables scientists to track different strains of MTB circulating in the population. This data is vital for understanding the spread of TB and detecting outbreaks, especially in high-risk areas. It can also be used to monitor the emergence of new resistant strains. - Improving TB Control Programs:
By integrating genomic data into TB control strategies, health organizations can better target interventions. For example, sequencing can help identify high-risk populations or regions where drug-resistant TB is most prevalent, allowing for more focused public health efforts.
The Role of India’s Genomic Sequencing Initiative
- India, which bears a significant portion of the global TB burden, is leveraging genomic sequencing as part of its strategy to eliminate TB by 2025.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), in collaboration with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), has initiated a massive genomic sequencing project under the “Dare2eraD TB” program.
- This program aims to sequence 32,500 Mycobacterium tuberculosis samples from across India. As of March 2025, 10,000 samples have been sequenced, and the results show that 7% of these samples are resistant to at least one TB drug. Such data is critical for understanding the prevalence and spread of drug-resistant TB in India.
- The genomic sequencing project will not only help track resistance patterns but also improve the effectiveness of TB diagnostics and treatment in the country.
- By 2025, this initiative is expected to provide a wealth of genetic data that can be used to refine TB control strategies, improve patient outcomes, and ultimately contribute to the global effort to eliminate TB.
Challenges
- Cost: While sequencing costs have significantly dropped, whole-genome sequencing can still be expensive, particularly in clinical settings.
- Data Complexity: The massive amounts of data generated require sophisticated analysis tools and expertise, and understanding how genetic variations affect traits or diseases is still a challenge.
- Ethical Concerns: The availability of personal genetic information raises concerns about privacy, discrimination, and how genetic data is used.

3rd UN conference on landlocked countries
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / 3rd UN conference on landlocked countries Why in News? At the

Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Issue of soapstone mining in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar Why in News? Unregulated

Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Groundwater Pollution in India – A Silent Public Health Emergency Why

Universal banking- need and impact
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / Universal banking- need and impact Why in News? The Reserve Bank

India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08th August 2025 Home / India’s “Goldilocks” Economy: A Critical Appraisal Why in News? The Finance

U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from Russia
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / U.S.-India Trade Dispute: Trump’s 50% Tariffs and India’s Oil Imports from

Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / Eco-Friendly Solution to Teak Pest Crisis: KFRI’s HpNPV Technology Why in

New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram
UPSC CURRENT AFFAIRS – 07th August 2025 Home / New Species of Non-Venomous Rain Snake Discovered in Mizoram Why in


Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very soon!
Yay google is my queen assisted me to find this great site! .
You are my inspiration , I have few web logs and occasionally run out from to brand : (.
Helpful info. Fortunate me I discovered your web site accidentally, and I’m surprised why this coincidence didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Whats up very nice web site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also?KI am happy to search out so many helpful information here in the publish, we’d like work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Fantastic web site. A lot of helpful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And certainly, thanks to your sweat!
You must participate in a contest for top-of-the-line blogs on the web. I’ll suggest this website!
I precisely desired to appreciate you once again. I do not know what I would have accomplished in the absence of the actual tactics shared by you on that problem. It has been a frustrating difficulty in my circumstances, nevertheless encountering your expert tactic you treated it took me to jump for joy. I’m happier for the information as well as trust you know what a great job you happen to be getting into educating many others via your webblog. I am certain you haven’t got to know all of us.
You made some first rate factors there. I appeared on the internet for the problem and found most individuals will go together with along with your website.
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thank you However I am experiencing challenge with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting similar rss problem? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
I’m not sure exactly why but this blog is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Some truly superb articles on this internet site, thankyou for contribution.
I just like the valuable information you provide to your articles. I will bookmark your blog and check again right here frequently. I am moderately certain I will learn lots of new stuff proper here! Good luck for the next!
I?¦ll right away clutch your rss feed as I can not to find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly let me know in order that I may subscribe. Thanks.
obviously like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very troublesome to inform the reality then again I will surely come again again.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site :).
Hey very cool blog!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also…I am happy to find a lot of useful information here in the post, we need work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Sweet internet site, super design, very clean and utilise friendly.
Some truly excellent info , Glad I detected this.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & help other users like its helped me. Great job.
You made some first rate factors there. I looked on the internet for the problem and found most people will go along with with your website.
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
Hi there, I discovered your web site by way of Google even as looking for a comparable matter, your web site came up, it seems great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
I’ve read several just right stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much attempt you set to make any such magnificent informative site.
It’s the best time to make a few plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I’ve learn this submit and if I may I desire to suggest you few attention-grabbing issues or tips. Perhaps you can write next articles regarding this article. I desire to learn more issues about it!
It’s actually a great and useful piece of info. I am satisfied that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I real lucky to find this website on bing, just what I was searching for : D as well saved to fav.
Useful information. Fortunate me I discovered your website by accident, and I’m stunned why this coincidence did not happened in advance! I bookmarked it.
Some really fantastic info , Gladiolus I noticed this. “No men can be lords of our faith, though they may be helpers of our joy.” by John Owen.
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my problem. You are amazing! Thanks!
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Really enjoyed this update, can I set it up so I receive an update sent in an email every time you write a new update?
I¦ve recently started a blog, the info you provide on this site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clarity to your publish is just great and that i can suppose you are a professional on this subject. Fine along with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to stay up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the gratifying work.
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it grow over time.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I have truly loved surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing in your feed and I’m hoping you write again very soon!
You made some good points there. I looked on the internet for the subject matter and found most individuals will consent with your site.
I was reading some of your posts on this website and I believe this site is real informative! Retain posting.
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include almost all significant infos. I’d like to see more posts like this.
Hi there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
Hello, Neat post. There is a problem with your website in web explorer, may check thisK IE still is the market leader and a good section of people will leave out your fantastic writing because of this problem.
Very well written post. It will be valuable to anyone who usess it, including yours truly :). Keep up the good work – looking forward to more posts.
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awesome site : D.
I love it when people come together and share opinions, great blog, keep it up.
I precisely desired to thank you so much again. I’m not certain what I could possibly have taken care of without these creative concepts contributed by you concerning this question. It had become a real frustrating problem in my view, but finding out your skilled manner you solved that forced me to jump for fulfillment. Now i am happier for your help and trust you find out what a powerful job that you are providing educating many others with the aid of your website. I’m certain you have never encountered all of us.
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
I’m still learning from you, but I’m improving myself. I certainly enjoy reading all that is posted on your website.Keep the posts coming. I liked it!
There is obviously a bunch to know about this. I assume you made some good points in features also.
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I’m quite sure I will learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I am not sure where you are getting your info, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for wonderful information I was looking for this info for my mission.
I love the efforts you have put in this, thanks for all the great articles.
Hi my loved one! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include approximately all vital infos. I¦d like to peer more posts like this .
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
The heart of your writing whilst sounding reasonable initially, did not really sit properly with me personally after some time. Somewhere within the sentences you managed to make me a believer but only for a very short while. I nevertheless have got a problem with your jumps in assumptions and one might do well to fill in those breaks. If you can accomplish that, I would undoubtedly be impressed.
I like the efforts you have put in this, appreciate it for all the great posts.
What i do not realize is in reality how you’re no longer really a lot more neatly-preferred than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You understand thus considerably on the subject of this matter, made me individually believe it from so many various angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated until it’s something to do with Girl gaga! Your individual stuffs great. All the time take care of it up!
Definitely, what a fantastic blog and illuminating posts, I will bookmark your blog.All the Best!
of course like your website but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I’ll definitely come back again.
I think this site has got very superb pent content articles.
I’ve recently started a blog, the information you provide on this website has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I was just seeking this info for some time. After six hours of continuous Googleing, finally I got it in your site. I wonder what is the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this type of informative web sites in top of the list. Usually the top websites are full of garbage.
I have recently started a web site, the information you provide on this site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Thank you for every other informative site. Where else could I am getting that kind of information written in such an ideal method? I’ve a undertaking that I am simply now working on, and I have been at the glance out for such information.
It’s really a nice and useful piece of info. I’m happy that you just shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
At this time it seems like Expression Engine is the best blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to this superb blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will share this blog with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your web site, how could i subscribe for a blog website? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
Please let me know if you’re looking for a author for your site. You have some really good articles and I feel I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d love to write some content for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please send me an e-mail if interested. Regards!
I just could not depart your web site before suggesting that I actually loved the usual info an individual supply to your guests? Is going to be back frequently to inspect new posts.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Have you heard about ThyraFemme Balance? This natural supplement is becoming a sensation among women worldwide because it provides a real, safe, and natural solution for those struggling with hormonal imbalance, slow metabolism, weight gain, fatigue, and lack of energy.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make an excellent article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and under no circumstances appear to get something done.
Flash Burn is a revolutionary natural supplement that has been transforming the lives of thousands of people struggling with excess weight. Developed with a 100 natural and scientifically proven formula
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
naturally like your website but you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand I will certainly come again again.
I always was concerned in this subject and stock still am, appreciate it for posting.
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve remember your stuff previous to and you’re simply too great. I really like what you have got here, certainly like what you are stating and the best way through which you say it. You’re making it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it sensible. I cant wait to read much more from you. This is actually a tremendous website.
I’m impressed, I must say. Actually not often do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you have got hit the nail on the head. Your idea is excellent; the issue is one thing that not sufficient individuals are speaking intelligently about. I am very glad that I stumbled across this in my search for something regarding this.
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.2
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was looking for!
I do not even know the way I finished up here, but I assumed this submit was good. I don’t know who you are however definitely you are going to a famous blogger in case you are not already 😉 Cheers!
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Dead written subject matter, thanks for information .
It’s really a great and helpful piece of info. I am satisfied that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I think you have remarked some very interesting details , regards for the post.
After I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the identical comment. Is there any approach you may take away me from that service? Thanks!
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thank you, I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Magnificent beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
You have brought up a very excellent details, thanks for the post.
Its good as your other articles : D, thanks for putting up.
I think other web site proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and excellent user genial style and design, let alone the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high quality articles or blog posts in this kind of house . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this site. Studying this information So i?¦m satisfied to express that I’ve an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I so much indubitably will make sure to do not fail to remember this website and provides it a glance on a constant basis.
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a speculative conclusion outstanding post! .
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I’m quite certain I’ll learn many new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
whoah this blog is wonderful i like studying your posts. Keep up the great work! You know, lots of individuals are searching around for this information, you could help them greatly.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Great blog here! Additionally your site so much up very fast! What web host are you the use of? Can I am getting your associate link on your host? I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Some really marvelous work on behalf of the owner of this site, dead outstanding content.
I?¦ve recently started a blog, the info you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I carry on listening to the rumor talk about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the most excellent site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i find some?
I think other web-site proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and magnificent user friendly style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Greetings! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having difficulty finding one? Thanks a lot!
I enjoy the efforts you have put in this, thanks for all the great content.
I have read several excellent stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot attempt you place to create one of these excellent informative website.
Your house is valueble for me. Thanks!…
hey there and thank you for your information – I have certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical points using this site, as I experienced to reload the web site lots of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading instances times will often affect your placement in google and can damage your quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for much more of your respective intriguing content. Make sure you update this again very soon..
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
You can definitely see your enthusiasm within the paintings you write. The sector hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to mention how they believe. At all times follow your heart. “In America, through pressure of conformity, there is freedom of choice, but nothing to choose from.” by Peter Ustinov.
I was curious if you ever considered changing the page layout of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or two images. Maybe you could space it out better?
Great blog here! Also your website rather a lot up fast! What host are you the usage of? Can I am getting your affiliate hyperlink to your host? I desire my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Hello there, I found your web site by way of Google even as searching for a similar subject, your web site came up, it appears good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
You got a very fantastic website, Gladiolus I discovered it through yahoo.
Great – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task.
I¦ve recently started a website, the information you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
I really like studying and I believe this website got some really utilitarian stuff on it! .
You have remarked very interesting points! ps decent internet site. “Never take the advice of someone who has not had your kind of trouble.” by Sydney J. Harris.
You really make it seem so easy along with your presentation however I in finding this topic to be actually one thing which I think I’d by no means understand. It kind of feels too complicated and very vast for me. I’m having a look ahead for your subsequent publish, I’ll try to get the dangle of it!
Glad to be one of several visitants on this amazing website : D.
There is obviously a lot to know about this. I believe you made some good points in features also.
I have been surfing online greater than three hours nowadays, yet I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is pretty price enough for me. In my view, if all webmasters and bloggers made just right content material as you probably did, the internet might be a lot more useful than ever before.
The core of your writing whilst appearing reasonable originally, did not really settle very well with me personally after some time. Someplace within the sentences you were able to make me a believer unfortunately only for a short while. I still have a problem with your leaps in assumptions and you might do well to help fill in those gaps. In the event you actually can accomplish that, I would definitely end up being amazed.
I have not checked in here for some time as I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I’ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Aw, this was a really nice post. In idea I would like to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make a very good article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and on no account appear to get one thing done.
There are definitely a lot of details like that to take into consideration. That is a nice level to deliver up. I provide the thoughts above as basic inspiration however clearly there are questions just like the one you bring up the place the most important factor will probably be working in sincere good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged round issues like that, but I’m certain that your job is clearly identified as a good game. Both boys and girls feel the impression of only a second’s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
I’ve been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this kind of house . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this site. Studying this information So i am glad to convey that I have an incredibly good uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I such a lot unquestionably will make certain to do not disregard this web site and give it a glance on a continuing basis.
Some genuinely great info , Gladiolus I observed this.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn something like this before. So good to seek out anyone with some unique ideas on this subject. realy thanks for starting this up. this website is one thing that is wanted on the net, somebody with a bit of originality. useful job for bringing one thing new to the web!
Great V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
You are my aspiration, I possess few blogs and rarely run out from to post : (.
I like your writing style really loving this website .
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other customers like its helped me. Good job.
I used to be very pleased to search out this web-site.I wished to thanks on your time for this excellent learn!! I positively enjoying each little little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
You are a very bright person!
I have recently started a blog, the information you provide on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Sweet web site, super pattern, really clean and use friendly.
Thank you a lot for giving everyone remarkably splendid opportunity to read in detail from this blog. It’s always very useful plus packed with a great time for me personally and my office mates to search your web site at a minimum three times per week to read through the fresh issues you will have. And of course, I’m so always fulfilled with the superb pointers you give. Selected 1 ideas in this posting are undeniably the best I’ve had.
Perfect piece of work you have done, this site is really cool with superb info .
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
I believe this web site has some very great info for everyone : D.
Hi there, You have done an excellent job. I’ll certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Wow, superb blog format! How long have you ever been running a blog for? you make blogging look easy. The entire glance of your site is great, as smartly as the content!
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. But just imagine if you added some great graphics or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and video clips, this site could definitely be one of the most beneficial in its niche. Awesome blog!
I’ll right away grab your rss as I can’t find your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Good website! I truly love how it is easy on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified when a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS which must do the trick! Have a great day!
As I website possessor I conceive the articles here is real fantastic, appreciate it for your efforts.
What’s Taking place i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & aid different customers like its aided me. Great job.
I and my friends came examining the great helpful tips from the website and so the sudden came up with a horrible suspicion I never expressed respect to the website owner for those secrets. All the young boys ended up for this reason joyful to learn them and have in effect really been making the most of those things. We appreciate you truly being indeed thoughtful and for considering this kind of brilliant issues millions of individuals are really desperate to be informed on. My personal honest regret for not expressing appreciation to you earlier.
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
Very nice article and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is actually the best place to ask but do you folks have any ideea where to get some professional writers? Thx 🙂
Yay google is my world beater assisted me to find this great website ! .
I like this web site its a master peace ! Glad I noticed this on google .
Excellent post. I was checking constantly this weblog and I am inspired! Extremely useful information specifically the closing phase 🙂 I maintain such information a lot. I was looking for this particular info for a very lengthy time. Thank you and best of luck.
Hey just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this website. Studying this info So i?¦m happy to express that I’ve a very excellent uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed. I such a lot indisputably will make certain to do not forget this site and give it a look on a continuing basis.
03d09c